FY 2002 Performance Report
IV. Performance Management
Relevance, Quality, and Performance
|
RD&T recently received the Quality Breakthrough Award, which recognizes organizations within FHWA that are making significant progress in developing clear plans, building sound processes, and achieving measurable results.
|
The OMB recently adopted relevance, quality, and performance as their investment criteria in Federal research. The criteria were established to conform to the Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA) and to reflect the inherent challenge of measuring research outcomes. R&D investment criteria are designed to help improve R&D program management, funding decisions, and public understanding of the potential benefits of investing in Federal research. The OMB expects agency R&D managers to demonstrate the extent to which their programs meet the following three tests:
Relevance. R&D programs must be able to articulate why this investment is important, relevant, and appropriate. Programs must have well conceived plans that identify program goals and priorities and identify linkages to national and customer needs.
Quality. R&D programs must justify how funds will be allocated to ensure quality R&D. Programs allocating funds through means other than a competitive, merit-based process must justify these exceptions and document how they maintain quality.
Performance. R&D programs must be able to monitor and document how well this investment is performing. Program managers must define appropriate outcome measures and milestones that can be used to track progress toward goals, and assess whether to increase or redirect funding. Descriptions of performance should not, however, be limited only to quantitative measures.
RD&T made considerable progress over the past year in areas directly related to the OMB’s recommendations, most notably by developing a lab assessment process that will incorporate expert peer reviews to improve TFHRC laboratories’ quality and performance. Several retrospective RD&T benefit studies were conducted to identify key performance measures and collect data that will be used to track progress and identify the research contribution to FHWA goals and outcomes. This information will be important as we better define the link between research activities and program outcomes.
Planning and Priority Setting
FHWA’s Office of RD&T coordinates the research and technology program and supports FHWA and U.S. DOT strategic goals for the Nation’s transportation system. The FY 2002/2003 RD&T Performance Plan outlines FHWA research priorities and strategies and shows a clear link between research program goals and FHWA and DOT strategic plans. Research highlighted in the FHWA RD&T plan focuses on providing solutions to complex technical problems by developing economical, environmentally-sensitive designs; efficient, quality-controlled construction practices; and durable materials. The result will be a safer, more reliable highway transportation system.
Stakeholder Advisory Activities and Feedback
The Research and Technology Coordinating Committee (RTCC)
The RTCC reviews, guides, and advises FHWA on research activities and provides policy-level recommendations on the overall direction of the program. The RTCC committee consists of 18 members including top-level administrators, researchers, and practitioners from the States, academia, and private sector. The committee recently examined national highway R&T needs and roles, and in October 2001 released the TRB Special Report 261 urging FHWA to focus on long-term, fundamental research, address gaps and emerging issues, conduct policy research, and engage in technology transfer activities. The report also recommends more substantive stakeholder involvement in making decisions, setting priorities, and allocating resources for FHWA’s research program to ensure that the program addresses the needs of those building, maintaining, and using the Nation’s highways.
The National R&T Partnership Initiative
The national partnership initiative was unprecedented in terms of outreach and participation—with hundreds of individuals and more than 170 organizations. Five working groups were established: Safety, Infrastructure Renewal, Policy Analysis and Systems Monitoring, Operations and Mobility, and Planning and Environment. A report reflecting the views of the working groups was released in April 2002 and is expected to form the basis of a national highway research agenda.
Performance Management Team
The primary purpose of the performance management team is to assist the RD&T leadership developing, coordinating, and implementing organizational performance improvement efforts. Performance management efforts currently underway include:
-
Developing performance goals, measures, strategies, and initiatives to improve organizational performance management in RD&T offices and laboratories;
-
Monitoring results of measures and analyzing performance management information;
-
Conducting the annual RD&T self-assessment process and implementing solutions to issues raised during the process;
-
Developing and conducting RD&T customer satisfaction surveys;
-
Contributing to special projects related to RD&T performance management, such as developing and implementing the expert panel assessment process for RD&T laboratories; and
-
Assisting in conducting and reviewing agency-wide performance improvement initiatives within RD&T.
Lab Assessment
RD&T laboratory assessments will be unbiased, independent expert or peer reviews of the technical and scientific merit of research conducted at TFHRC. The assessment process is designed to:
-
Enhance laboratory performance and quality by providing feedback to laboratory managers;
-
Create a vehicle that will increase the opportunities for customer and stakeholder input to research activities; and
-
Provide a credible, professional, and objective assessment that further improves stakeholder confidence in the value of the work performed and outcomes produced.
Performance Management Framework
One of the conclusions of NCHRP Synthesis 300, Performance Measures for Research, Development, and Technology Programs was that “different types of evaluation methods are appropriate for different types of research projects.” This holds true across organizational functions, as well. The RD&T Performance Management Framework chart identifies existing performance measures and assessment mechanisms used by unit managers. It integrates these measures and mechanisms across management functions using FHWA’s Baldrige-based corporate management strategies. This approach enables RD&T to manage, analyze, and integrate information obtained from a variety of sources. It also helps organize the various dimensions of program results analyses, such as financial performance, customer feedback, and business results. The RD&T Leadership Council uses this framework as a tool to assess unit performance measurement activities and to identify measurement gaps.
| RD&T Performance Management Framework |
| CMS |
Definition |
Related RD&T Performance Measures |
Methodology |
| Leadership |
Leadership focuses on how senior leaders guide the organization. It describes how leaders set direction and high-performance expectations, project a strong customer focus, and communicate clear and visible values to employees. |
• Leadership Effectiveness Inventory (LEI) results
• Action items completed
• Performance plan items fulfilled
• Self-assessment score |
• 360-degree feedback
• Action agenda
• Performance plans
• Quality self-assessments |
| Strategic Planning |
Strategic planning examines how the organization sets strategic goals and develops key action plans. |
• Action items completed
• Self-assessment score
• Progress made on goals established |
• Performance plans and action agenda
• Quality self-assessment
• Lab assessments |
| Customer/ Partner Focus |
Customer and partner focus examines how the organization determines customer and market requirements and expectations. |
• Percent of satisfaction with RD&T products and services
• Number of technology facilitation plans in place
• Self-assessment score
• Lab assessment results (TBD)
• RD&T customer survey results (TBD) |
• American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI)
• Technology Innovation Network (TIN)
• Technology Facilitation Action Plan (TFAP)
• Quality self-assessments
• Lab assessments
• Customer surveys |
| Information and Analysis |
Information and analysis examines the management, effective use, and analysis of data and information to support key organization processes, to include the organization's objectives |
• Performance measurement framework
• Response level and content of feedback mechanisms
• Self-assessment score
• Lab Assessment results (TBD) |
• Performance measurement framework
• ACSI, TIN
• Quality self-assessments
• Lab Assessments |
| Human Resource Development |
Human resource development and management examines how the organization enables its workforce to develop to its full potential and how the workforce is aligned with the organization's objectives |
• Self-assessment score
• Percent of employee satisfaction survey rating
• Percent of payroll spent on training and development
• Number of IDP's in place and in LADs
• Number of “priority 1” training needs met
• Number of vacancies filled
• Number of days positions are vacant
• Number of student interns (Number of Grant for Research Fellowships (GRF), STIPDG, etc.)
• Number of outreach activities |
• Quality self-assessments
• Employee satisfaction survey
• LADS |
| Process Management |
Process Management examines aspects of how key production, delivery, and support processes are designed, managed, and improved. |
• Number of process improvements documented
• Lab Assessment (TBD)
• Number of contracts on time and on budget
• TIN (TBD)
• SBIR (TBD) |
• Quality self-assessments
• Lab assessments
• Project tracking system
• ACSI |
| Business Results |
Business results show the organization's performance and improvement in its key business areas: customer satisfaction, financial and marketplace performance, human resources, supplier and partner performance, and operational performance. The category also examines how the organization performs relative to competitors. |
• Percent of project completion
• Number of success stories
• Research benefit (TBD) |
• Track project and services delivery
• RD&T success stories
• Pilot and case studies |
RD&T Research Benefits Case Studies
RD&T conducted studies to identify quantifiable and articulable research benefits that demonstrate their strategic links to FHWA goals and outcomes. We are conducting these evaluations with the understanding that a combination of evaluation methods within a unified framework is needed. The recent NCHRP Synthesis 300 report supports this conclusion. RD&T benefit assessments are largely retrospective analyses and will require data collection throughout the product development and delivery cycles to produce meaningful conclusions. In the short term, RD&T benefit studies will provide a workable taxonomy for data collection and performance measurements that can be applied to a cross-section of RD&T products—ultimately resulting in customer focus improvements, broader programmatic analyses, and more effective business results reports.
Highway Safety Information System
HSIS is a multistate information system that improves highway safety and design. The HSIS performance assessment goal was to provide value indicators for the system. These indicators will be used to develop a broader framework to assess the benefits of research databases and information tools. Value indicators developed for the study included measurements of HSIS value to internal and external safety research communities, and State and local engineers and planners. Examples of HSIS indicators included bibliometric usage data, expert peer review data, and user survey results.
QuickZone
QuickZone’s evaluation results revealed several useful product benefit measures for State DOT planners. The combination of customer survey data and user cost and benefit modeling proved particularly useful and resulted in immediate improvements to the product’s input modules and analysis options. The metric results from the study have a broader application potential in determining research benefits for similar RD&T products.
Infrastructure R&D
The RD&T Office of Infrastructure R&D is conducting a study that will examine RD&T research benefits in the areas of national design and data standards, new technologies, and new materials developments. The study results will be synthesized and used to develop a more robust measurement methodology for RD&T performance in these areas.
A synthesis report covering lessons learned from the pilot studies will be forthcoming. Highlights will be included in the next RD&T performance report.
RD&T Annual Quality Self Assessment
This year’s self-assessment process contained more approach variations, compared with those done in previous years. Variations in RD&T office size and complexity, plus logistical scheduling issues for employees, facilitators, and customer involvement led to several offices seeking a more flexible, abbreviated format. This did not, however, diminish the process effectiveness. Participants agreed that the experience was still very valuable for providing an opportunity to review and capture the year’s achievements, to refocus on FHWA’s goals, and to supply a forum for employees to discuss organizational concerns.
Comments related to RD&T offices’ relationships with customers and stakeholders were generally positive and reflected a greater awareness of their needs and improved communication, overall. Roughly 90 percent of research projects are on schedule at this point in the year, and customer surveys conducted by several RD&T offices confirmed better timeliness of response and delivery. There also is a recognition that RD&T’s role is expanding. Several offices’ comments support this conclusion and were centered on the need for more joint planning, better customer survey processes, additional face-to-face contact (meetings, visits, etc.), and greater outreach activities.
Although several offices listed the increased need for joint planning as an area for improvement, RD&T accomplished much in this area over the past year. Many RD&T offices introduced initiatives such as the Infrastructure Long Range Vision, the advanced acquisition planning system, the FHWA security product team, the Western Resource Center technology transfer conference, the advanced research program, and efforts aimed at Title V reauthorization—just to name a few. These achievements link directly to the RD&T “Challenges and Commitments” established last year.
“90 percent of research projects are on schedule.”
—Business Results
“Customer surveys confirmed better timeliness of response and delivery.”
—Customer Focus
“These achievements link directly to the RD&T Challenges and Commitments.”
“The Technical Career Track program is a success, and RD&T was well represented this year.”
—Human Resource Development
|
Perceptions of employee development and work-life issues were positive. Offices reported strengths in areas such as flexible work scheduling; work environment; support for training and participation in professional associations; awards and incentives; and relationships with management. The updated technical career track program was an overwhelming success, and RD&T research offices were well-represented in the program this year.
Finally, several key process management improvements were made this year because of input from the previous year’s assessment. These include the updated Leadership Council Action Agenda checkpoint tracking system and improved council meeting format; an advanced acquisition planning system pilot that will be adopted FHWA-wide; the development of a State planning and research (SP&R) handbook for FHWA Field Offices, and the completion of the SP&R (CFR Part 420) rule revision to reflect current practices, conform to plain language standards, and facilitate the overall State planning and research administration processes.
RD&T Organizational Chart
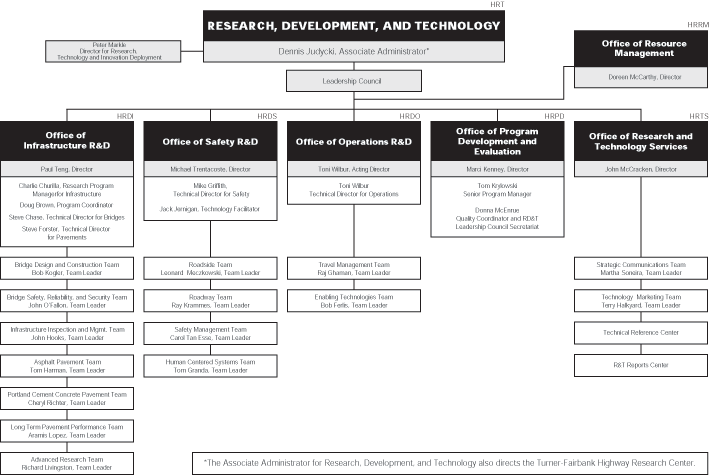
Alternative Text for RD&T Organizational Chart
Previous | Table of Contents | Next
Performance Report Feedback
|
