U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Federal Highway Administration Research and Technology
Coordinating, Developing, and Delivering Highway Transportation Innovations
|
Research & Technology Transporter This newsletter is an archived publication and may contain dated technical, contact, and link information. |
|
| Publication Number: N/A Date: November 1998 |
Publication Date: November 1998
|
In 1994, FHWA sponsored a winter maintenance technology scanning tour to Europe and Japan. The tour participants brought several innovations back to the United States. Based on the findings of that tour and on the need for follow-up research, a second scanning tour, which took place in March 1998 and was jointly sponsored by FHWA and National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP), was conducted to evaluate new technologies, practices, and policies. Twelve Federal, State, local, and academic representatives visited Switzerland, France, Norway, and Sweden to observe the latest in winter road maintenance. The tour concluded at the World Road Association's (PIARC) quadrennial International Winter Maintenance Conference in Lulea, Sweden.

During this second tour, representatives found that the United States has made significant progress in applying winter maintenance techniques that were found in various countries during the first scanning tour. The emphasis by the State departments of transportation (DOTs) and FHWA in the 1990s and the help of the Strategic Highway Research Program has enabled the United States to be among the world leaders in state-of-the-art winter maintenance technology.
The tour also revealed that in Europe, road weather information systems are generally highly integrated into traffic management centers and intelligent transportation systems. This integrated system allows transportation workers to communicate real-time road conditions to the public more quickly and to better coordinate winter service operations.
Two snowplows with new designs and materials were observed by the tour participants. A French innovation allows a snowplow operator to alternate between the conventional steel blade and a new hard plastic blade that is more effective at moving wet snow. A Norwegian design sported a composite blade of tungsten steel in a rubber casing that caused less damage to the road surface and reduced noise in urban areas.
Other innovations were also discovered during the tour. An experimental installation of an in-pavement anti-icing chemical spray system was observed in Switzerland. Also, in France, a new automated avalanche control system that uses pressurized gas to create an explosion was observed.
-Hana Maier, (202) 366-6003, international@fhwa.dot.gov

This past summer, the Oregon DOT (ODOT) concluded an FHWA-sponsored demonstration project on Subsurface Utility Engineering (SUE). SUE is an engineering process used to obtain accurate and comprehensive information about underground utilities. It uses surface geophysical techniques and nondestructive digging equipment to determine horizontal and vertical positions of underground utilities. SUE transfers this information to a computer-aided design and drafting system or onto project plans.
An urban arterial project designed by ODOT was used to demonstrate SUE. The project area was 3.3 km in length and involved reconstruction; partial realignment; and installation of a new storm sewer, signals, and illumination. The demonstration project showed that SUE found approximately 30 percent more utilities than were recorded by utility companies and that SUE provided ODOT designers with comprehensive, reliable utility mapping, thereby reducing project costs and construction delays.
- Paul Scott, (202) 366-4104, paul.scot@fhwa.dot.gov
The Structures Division of FHWA's Office of Engineering R&D has won an R&D 100 Award for its High-Performance Electromagnetic Roadway Mapping and Evaluation System (HERMES). HERMES uses an array of specially designed micro-power impulse radar elements and advanced signal processing techniques to create an image of the internal structure of a reinforced-concrete bridge deck. Data to construct the image can be collected at highway speed.

This award has been presented annually since 1963 by Research and Development Magazine to recognize the 100 most technologically significant inventions worldwide. HERMES is a collaborative project between the Structures Division and the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.
HERMES surpasses conventional radar technology by combining a closely spaced array of 64 compact, low-power impulse radar elements, extremely sensitive receivers, and ultra-precise timing circuits with unique two- and three-dimensional diffusion tomography imaging software to detect and image the features of the reinforced concrete. The entire system has been configured into a towable trailer and can image a 2-m-wide swath of bridge deck with spatial resolution of 3 cm in length and width, and less than 1 mm in depth.
HERMES has been under development since 1992, and the first fully functional prototype system was delivered in October to the Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center (TFHRC). Extensive laboratory and field testing and evaluation of the system are planned for the next 12 months.
- Steven B. Chase, (202) 493-3034, steve.chase@fhwa.dot.gov
On September 22 to 26, Chemically Modified Crumb Rubber Asphalt (CMCRA) was produced on a large scale at the New England Emulsions Corporation in Holliston, CT. Originally invented and developed at TFHRC, CMCRA is a binder produced by the reaction of combining chemically modified crumb rubber with asphalt. It is characterized by its improved homogeneity and rheological properties.
The objectives of this field operation were to determine the possibility of using conventional large-scale production equipment and construction facilities for both spray and hot-mix surface applications and to check that this rubberized asphalt can be used at temperatures lower than those normally used for field application or placement. This field operation was made possible by GreenMan Technologies, Inc., as part of a cooperative research and development agreement with FHWA.
- Brian Chollar, (202) 493-3074, brian.chollar@fhwa.dot.gov
Champions and practitioners in the pavement preservation arena gathered on October 26-28 in Kansas City at the National Pavement Preservation Forum-Forum for the Future. More than 100 participants from academia; industry; and local, State, and Federal agencies attended the conference to identify the obstacles preventing the implementation of pavement preservation and to construct a strategy to address these challenges.

The conference provided an opportunity to discuss the current status of pavement preservation in the Nation and to examine how roadway safety, customer satisfaction, and agency strategies and techniques can be improved. Members of the conference examined goals such as improvement in pavement conditions, reduction of work zone accident rates, and implementation of effective life-cycle cost analyses for maintenance decision processes.
Conference proceedings will be available in hard copy and on TFHRC's web site at www.tfhrc.gov.
- Robert M. Davies, (202) 493-3079, robert.davies@fhwa.dot.gov
The number of people over the age of 65 has increased 11-fold during this century. By the year 2020, these senior citizens are expected to be 16.5 percent of the U.S. population. In response to the needs of this growing group, FHWA's Office of Safety and Traffic Operations R&D has prepared the Older Driver Highway Design Handbook (FHWA-RD-97-135).

The handbook provides information for highway design engineers and traffic operations personnel who must meet the special needs of older drivers in their highway designs. It is a compilation of 4 years of research on the older driver. The handbook will be available online in November.
A workshop to promote the handbook and increase awareness of older drivers' needs in highway design and operations was developed by the Office of Technology Applications and coordinated with the offices of Safety and Traffic Operations R&D, Engineering, and Highway Safety and with the field. Workshops have been held in Harrisburg, PA; San Antonio, TX; Orlando, FL (twice); and Ames, IA. Feedback from the workshops has been positive, and more workshops are planned.
- Leverson Boodlal, (202) 366-8044, leverson.boodlal@fhwa.dot.gov
Through computer simulation, a new guardrail system is being developed to improve roadside safety, reduce liability risks, and diminish the costs associated with crash injuries (medical care and lost work time).
This new guardrail system, called the bullnose system, will be used to protect occupants in incidents in which an out-of-control vehicles nears the drop-off between parallel bridges crossing over a depressed roadway. This drop-off area is commonly termed the "elephant trap." Falling into the "elephant trap" can potentially cause catastrophic harm to motorists if they are not adequately protected. When operational, this bullnose guardrail system will help prevent death and serious injury.
The guardrail system is being developed at the University of Nebraska at one of four centers of excellence in DYNA3D computer analysis establishedby FHWA.
DYNA3D, a finite element code, was used to develop the bullnose guardrail system. The development work associated with this guardrail system is jointly funded by eight Midwestern States in conjunction with FHWA.
When the bullnose system was initially tested with a 2,000-kg pickup truck colliding head-on into the horseshoe shaped system at 100 km/h, the pickup truck broke through the guardrail system. If this test had been an actual accident, the result would have been catastrophic. The pickup truck would have continued into the drop off between the parallel overpass bridges, down the embankment, and onto the roadway below. This would have most likely resulted in seriously injuring, or even killing, the vehicle's occupants. However, by using DYNA3D as an analysis tool, the skilled personnel at the University of Nebraska's DYNA3D center of excellence subsequently redesigned and strengthened this guardrail system.
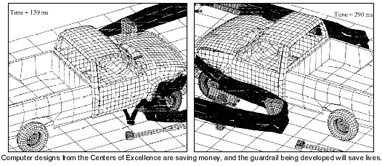
When the improved bullnose guardrail system was retested, the truck's rate of speed during the testing was decreased, and the truck was ultimately contained. Therefore, the threat of serious injury or death to the occupants was eliminated.
- Martin W. Hargrave, (202) 493-3311, martin.hargrave@fhwa.dot.gov
On June 2, a corten steel lighting pole fell across I-894 in West Allis, WI. No one was injured, but a subsequent inspection was performed on the failed pole and other randomly selected poles in the median of I-894 to find out why it fell. Researchers found the pole failed because of section loss at the inside base of the pole near the weld that connected the pole to the base plate. This section loss was caused by moisture, salt spray, and debris buildup. Moisture and salt entered the pole through the hand holes (many of which were loose or missing) and corroded the inside of the pole.

The Wisconsin DOT inspected one out of every five corten poles in the median of I-894 and I-94 to determine the extent of the problem. Researchers measured the thickness of each pole and found serious section loss at the base of the poles. This is a common condition for corten material exposed to salt spray. After examining three locations a total of 294 poles' inspectors recommended that 51 of those poles be replaced within the next 180 days. They inspected an additional 157 poles in adjacent areas and recommended that 103 of those poles be replaced.
To slow severe section loss, high mast poles made from corten steel installed in the median should be painted inside and out to the height of the salt spray zone.
- (202) 493-3364, john.arens@fhwa.dot.gov
Are there that many drivers falling asleep at the wheel and driving off the road? Actually, a significant portion of highway crashes involve drowsy or sleeping drivers. According to the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission, 57 percent of all run-off-the-road crashes are caused by sleepy or inattentive drivers. Similarly, the New York Thruway Authority estimated that 40 percent of all crashes were related to drivers falling asleep. These aren't unique situations most of the authorities and departments that have studied run-off-the-road crashes have reported that between 40 percent and 60 percent of these crashes are related to driver fatigue.
Audible roadway delineators, such as continuous shoulder rumble strips, help to waken drowsy drivers and avoid crashes. The results of such treatments, particularly on highways with long, monotonous tangent sections where drivers tend to drift off to sleep, have been remarkably good. Reviews have shown that up to 80 percent fewer run-off-the-road accidents have been reported after the installation of the delineators.
FHWA's Office of Highway Safety is evaluating information from FHWA field offices and will be working with individual States to enhance their programs and accelerate the application of audible delineation and warning devices on shoulders.
- Henry Sandhusen, (202) 366-2218, henry.sandhusen@fhwa.dot.gov
Moving traffic safely and efficiently through work zones is a major national issue. This past year, Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, and Nebraska decided to create the Mid-America Smart Work-Zone Deployment Initiative. This initiative is guided by the FHWA Midwest Smart Work-Zone Consortium, State highway agencies, and the Mid-America Transportation Center (MATC) located at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln and Iowa State University. Twenty private work-zone technology providers are participating in this effort. Several technologies will be deployed in State work zones throughout the 1999 construction season.
Three workshops were conducted to generate work-zone safety suggestions, build partnerships, and assign technologies to work-zone projects. The first workshop was entitled "Establishing the Requirements." The American Automobile Association, senior citizens, law enforcement, emergency services, highway contractors, and State highway agency construction personnel were included in the target group. In the second workshop, "Defining the Solutions," the audience of private sector technology providers were asked to develop innovative ideas or technologies, to meet the needs identified in the first workshop. The third workshop was titled "Selecting the Technologies." It matched technology providers with individual States and, in many cases, specific projects.
MATC will deliver a consolidated final report. A regional pooled-fund study is being considered to fund the evaluation. Visit the MATC web site at www.unl.edu/matc/workzone.htm to keep up-to-date on this initiative.
- Frank Doland, (402) 437-5967, frank.doland@fhwa.dot.gov
Unfortunately, "traditionally underserved," often means "under-represented" in transportation decisionmaking. One large metropolitan planning organization (MPO) learned that including those typically underrepresented communities is, in fact, worthwhile. A 20-minute-long videotape entitled, Reaching Out to Everyone: Techniques for Inclusive Transportation Planning describes practical lessons learned from an intensive effort designed to include a broader range of citizens in long-range transportation planning.
The video and accompanying report describe the effort of the Transportation Planning Board at the Metropolitan Washington, DC, Council of Government to reach out to four traditionally underserved communities: a predominantly African-American inner-city neighborhood, a suburban Latino neighborhood, a suburban adult education school comprised of recent immigrants learning English, and a community of senior citizens in a rapidly-growing outer suburb. Despite that many residents found it difficult to relate to the long time-frames involved in transportation planning, transportation planners found that working closely with individuals who are not typically a part of the planning process resulted in more thoughtful input from the communities.
For a copy of the report, A System that Serves Everyone: Attracting Non-Traditional Participants into the Regional Transportation Planning Process, call FHWA at (202) 366-2065.
- Florence W. Mills, (202) 366-2062, florence.mills@fhwa.dot.gov
The National Highway Institute (NHI) and the Office of Motor Carriers' National Training Center (NTC) have recently moved to new, improved facilities in Arlington, VA. The two floors occupied by what is now known as the FHWA's Learning Center can accommodate more than 200 training participants simultaneously, and the specially designed training rooms are equipped with modern technology to facilitate new instructional methods, such as videoconferencing and distance learning.

Director of NHI, Dr. Moges Ayele stressed that the Learning Center is open to all FHWA staff. In addition to its main purpose, training, its facilities can also be used for meetings and conferences. Training and conference rooms should be reserved in advance by calling Farrah Benner at (703) 235-1212. For course scheduling, contact NHI's Lynn Cadarr at (703) 235-0528, or visit NHI's web site at www.nhi.fhwa.dot.gov. The Learning Center is also planning an open house for all interested FHWA employees later this year.
The Learning Center is located at 4600 North Fairfax Drive in Arlington. The facilities are just three blocks from the Ballston metro stop and the former NHI/NTC offices, and they can be easily reached by car via I-66, Wilson Boulevard, or Glebe Road.
- Marketta Kopinski, (703) 235-0534, marketta.kopinski@fhwa.dot.gov