Lesson from: 135048 Countermeasure Design for Bridge Scour and Stream Instability
Slide 2
Learning Objectives
- Describe the purpose of a Plan of Action (POA) for a scour critical bridge
- Identify strategies for developing a Plan of Action (POA)
Slide 3
Plan of Action (POA)
- Should be developed for each existing bridge found to be scour critical per FHWA guidance contained in Technical Advisory T 5140.23, "Evaluating Scour at Bridges" dated October 28, 1991
Notes
Technical Advisory provides guidance on:
- Developing and implementing a scour evaluation for designing new bridges
- Evaluating existing bridges for scour vulnerability
- Using scour countermeasures
- Improving the state-of-practice for estimating scour at bridges
Slide 4
Highlights of Changes to Item 113
- Description changed to emphasize that:
- Rating factor of 2 or below requires revising Item 60 and other affected items (load ratings and superstructure rating)
- Plan of Action should be developed for each scour critical bridge
- Coding is based on an engineering evaluation, which includes consideration of NBIS field inspection findings
Notes
NBI Coding Guide Item 113
- Item 113 now refers to HEC-18 and 23 for guidance on scour and countermeasures
Slide 5
Scour Critical Bridge
- A Scour Critical bridge is one with foundation elements that are determined to be unstable for the calculated and/or observed stream stability/ scour conditions
Notes
NBI Coding Guide Item 113
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 3 | Assessed or calculated condition |
| 2 | Comparison of calculated and observed condition |
| 1 | Comparison of calculated and observed; failure is imminent |
| 0 | Bridge failed and is closed |
Slide 6
Code 8
- Expanded guidance for a bridge foundation determined to be stable:
- Assessment - bridge foundations on rock formations determined to resist scour within the service life of the bridge
- Calculations
- Installation of properly designed countermeasures
Notes
NBI Coding Guide Item 113 Use of Countermeasures
- Determination of stability can be based on installation of properly designed countermeasures
| Examples: | Calculated Scour Depth (Left: Spread footing (not founded in rock) Right: Pile footing) |
Action Needed |
|---|---|---|
| A. Above top of footing | 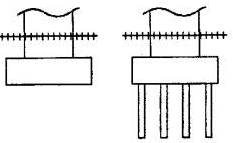 |
None - indicate rating of 8 for this item |
| B. Within limits of footing or piles | 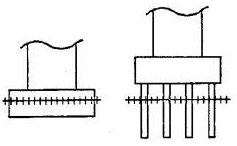 |
Conduct foundation structural analysis |
| C. Below pile tips or spread footing base | 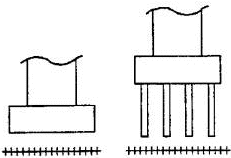 |
Provide for monitoring and scour countermeasures as necessary |
+++++++ = calculated scour depth
Slide 7
Code 7
- Countermeasures installed to mitigate an existing scour problem and to reduce the risk of bridge failure during a flood event
- Instructions in a Plan of Action have been implemented to reduce the risk to users from a bridge failure during or immediately after a flood event
Notes
- Countermeasures can be used to reduce the risk from scour
- Monitoring can be considered a countermeasure when developing a Plan of Action
Slide 8
Code 5
- Foundation determined to be stable for the assessed or calculated scour condition
- Scour within the limits of footings or piles based on an assessment, calculation, or installation of properly designed countermeasures
Notes
- Code 6 - Scour calculation/evaluation has not been made
- Can consider installation of properly designed countermeasures in a Code 5 rating
- Example B
- Code 4 - Foundation stable. Field review indicates action required to protect exposed foundations
Slide 9
Goal of POA
- Provide guidance for Inspectors and engineers that can be implemented before, during, and after flood events to protect the traveling public
Slide 10
Elements of POA
- Management strategies
- Inspection strategies
- Closure instructions
- Countermeasure alternatives and schedule
- Other information
Slide 11
Management Strategies
- Location and identification of bridge
- Type of foundation and foundation material
- Source of scour critical rating
- Importance of roadway to the transportation network
- Programmed for replacement (may suggest a risk-based analysis)
Notes
Evaluating importance of the roadway could include:
- ADT
- Access Route to Emergency Facilities
- Evacuation Route
- Detour
Slide 12
Inspection Strategies
- Type and frequency of inspection
- Need for continuous monitoring
- When to start
- When to stop
- What constitutes a scour critical condition
- Instructions for action when the scour critical condition is reached
Notes
- Normal frequency is 2 years for superstructure and visual or probing underwater where applicable
- 5 years for general underwater inspection
Slide 13
Guidance for Inspectors
- Discharge measurement
- Stage measurement
- High water marks
- Flood watch
Slide 14
Closure Instructions
- Can be load restrictions, lane closure or complete bridge closure
- Criteria for closure should be established by Scour Team
- Identify authority for closing and reopening a bridge
- Communication and coordination
Notes
- Criteria for closure includes:
- Observed scour
- Movement of riprap
- Monitoring bed movement
- Water level
- Discharge
- Rainfall
- Flood forecasting
- Debris buildup
- Communication and coordination instructions for closing and reopening a bridge must be included
Slide 15
Detours
- Availability and description of alternative routes
- Scour vulnerability of bridges along detour route
Slide 16
Countermeasure Alternatives
- Alternatives considered
- More intense monitoring can be one of the alternatives
- Preferred alternative
- Engineering feasibility
- Schedule for timely design and construction
Notes
- The HEC-23 Countermeasures Matrix is designed to assist in selecting countermeasure alternatives
Slide 17
Other Information
- Author and sign-off on POA
- Media alert instructions
- Sources of emergency repair materials
- Detour instructions
Notes
- Communications with the media
- Who is authorized to make statements?
- What information should be provided?
Slide 18
Generic POA
- Bridge Identification:
Location of Bridge:
Year Built:
Replacement Plans (if scheduled):
Foundation Type:
Foundation Soils Types: - ADT:
Service to Emergency Facilities or Evacuation (Y/N): - Sources of scour critical rating (Assessment, Analysis, and/or Observation):
- Comments about rating (e.g., analysis did not account for erosion resistant material; emergency riprap placed after last flood, etc.):
- Inspection and Monitoring:
- Increase inspection frequency:
- Types (Probing, diving, inspection of banklines):
- Special Inspection Criteria (after bankfull events, during major events):
- Monitoring Type (Fixed instrumentation, Portable instrumentation):
- Criteria for monitoring:
- Closure Plans (Limit loads; Lane closure; Full closure):
- Criteria for Closure (Discharge; Floodwater Elevation; Flood Forecast; Scour Soundings):
- Authorization for Closure (Bridge Maintenance engineer; Inspector; Police; Statewide Bridge Closure Procedure):
- Detour Route:
- Criteria for reopening bridge:
- Countermeasures considered:
(1) ___________________________________; Cost: $ ________________________
(2)____________________________________; Cost: $ ________________________
(3)____________________________________; Cost: $ ________________________ - Countermeasure Recommended:
Status: - Author(s) of POA:
Date: - Concurrences on POA: _______________________,
__________________________,
__________________________________
Slide 19
POA Examples
- Oregon DOT
- Florida DOT
Slide 20
Oregon DOT Plan of Action
Click to view Oregon DOT's POA
Slide 21
SR 44 Bridge over St. John's River - POA Example
- Bridge #: 110063
- Location: SR 44 Bridge over St. John's River
- Foundation: Pile
- Scour Mode: Riverline
- Status
- Phase I: Data Collection and Qualitative Analysis => Final
- Phase II: Hydrologic Assessment for Scour Analysis => Final
- Phase III: Geotechnical and Structural Scour Assessment => Final
- Phase IV: Recommended Plan of Action => Final
- Scour Rating 3 => Critical
Slides 22-23


Slide 24
SR 44 Bridge over St. John's River - POA Example
POA Summary
- To mitigate active scour, riprap was recently installed from Bent 5 to the west side of bascule Pier 1
- Riprap in conjunction with a monitoring program will reduce the risk from scour
- If monitoring finds significant degradation below the elevation of the riprap-lined channel, a structural countermeasure may be warranted
Slide 25
SR 44 Bridge over St. John's River - POA Example
Countermeasure Alternatives
| Alternatives | Cost |
|---|---|
| 1. Permanent Monitoring Program / Portable Instrument | $313 per monitoring event |
| 2. Permanent Monitoring Program / Fixed Instrument | $18,500 |
| 3. Install Crutch Bents | Not feasible, riprap in vicinity |
Slide 26
SR 44 Bridge over St. John's River - POA Example
- Plan Developer
- XYZ Engineering, A. Smith, P.E., 01/30/98
- Consultant Recommendation
- Alternative #1
- Action taken by FDOT
- Routine monitoring/riprap already in place
- Work Program
- 238328 (2-98); Project file 8
Slide 27
SR 44 Bridge over St. John's River - POA Example
Closure Plan
- If a scour condition develops, it may be necessary to close the bridge
- If bridge closure necessary, immediately implement District bridge closure plan for state bridges
Slide 28
Learning Objectives
- Describe the purpose of a Plan of Action (POA) for a scour critical bridge
- Identify strategies for developing a Plan of Action (POA)

