March 15, 2018
Innovation of the Month:
Data-Driven Safety Analysis
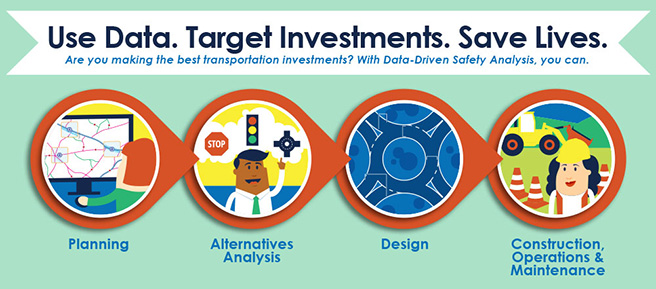
Transportation agencies across the country are deploying data-driven safety analysis (DDSA) to make more informed decisions and target investments more effectively. Their goal is to reduce fatal and serious injury crashes on the Nation’s roadways.
DDSA software tools and methods to analyze crash and roadway data quantify the expected safety impact of each decision in the project development process:
- At the planning stage, DDSA helps identify which roadways aren’t performing as they should, determine the scope and need of potential safety projects, and prioritize the projects.
- DDSA predicts the number and severity of crashes for multiple design options and compares them side by side.
- DDSA helps determine optimal design criteria, considering both safety and cost.
- After construction, DDSA helps monitor the operation of the project and compare observed safety performance to what was predicted.
One agency using DDSA is the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT), which developed a predictive analysis methods manual and tool to help staff perform analyses using regionally calibrated prediction models for Pennsylvania roadways. PennDOT applied Interactive Highway Safety Design Model software to predict the safety performance of interchange alternatives for various freeway projects. PennDOT is also updating its design exception process to require predictive methods.
View a video on DDSA in the project development process.
Michigan Documents Procedure to Collect Utility Location Data
The Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT) developed a draft Geospatial Utility Infrastructure Data Exchange (GUIDE) Procedural Manual to detail processes for collecting and storing 3D geospatial data for underground utility installations in MDOT rights-of-way. State Transportation Innovation Council Incentive funds were used in part for the manual’s development. MDOT is the first State transportation department to document a procedure for collecting location data for permitted underground utility installations. Having accurate utility location information will help MDOT reduce project conflicts, delays, service disruptions, and redesigns, as well as improve worker safety. For information, contact Bradley Wieferich of MDOT.
Learn on Your Schedule
The Center for Accelerating Innovation’s new on-demand webinar library allows you to learn about Every Day Counts innovations at your own pace. Webinars featuring how-to information, case studies, and resources are available for viewing at any time. CAI will continue to add topics to the library, so check back frequently to see what’s new.
Current topics available for on-demand viewing include the following:
- Collaborative Hydraulics: Advancing to the Next Generation of Engineering
- Data-Driven Safety Analysis
- Locally Administered Federal-Aid Projects: Stakeholder Partnering
- Safe Transportation for Every Pedestrian
- Ultra-High Performance Concrete for Prefabricated Bridge Elements
Public Roads Magazine Features Every Day Counts Innovations
In a first for the State, the Oklahoma Department of Transportation (ODOT) used self-propelled modular transporters—computer-controlled vehicles that carry large structures and position them precisely—to install two railroad bridge spans over I-235 in Oklahoma City over a weekend. Using accelerated bridge construction to build the bridge truss structures near the interstate and move them into place greatly reduced the impact on traffic, requiring a road closure from Friday night to Monday morning rather than for several months if traditional construction methods were used. ODOT used DOT and railroad coordination best practices on the project, including working with one point of contact at BNSF Railway, conducting regular meetings on project status, and creating a flow chart for the document submission and approval process to enhance efficiency. The bridge is part of a reconstruction and widening project on I-235. For information, contact Souzan Bahavar of the FHWA Oklahoma Division.