U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Federal Highway Administration Research and Technology
Coordinating, Developing, and Delivering Highway Transportation Innovations
| REPORT |
| This report is an archived publication and may contain dated technical, contact, and link information |
|
| Publication Number: FHWA-HRT-14-067 Date: September 2014 |
Publication Number: FHWA-HRT-14-067 Date: September 2014 |
PHASE 1 AERODYNAMIC DAMPING PLOTS
Note that cables 14A and 13A did not have valid wind data recorded during their testing. In these plots, "Total" refers to wind data recorded over the entire test run, while "Decay Only" refers to wind data that is recorded only between the start and stop values of the time filter.
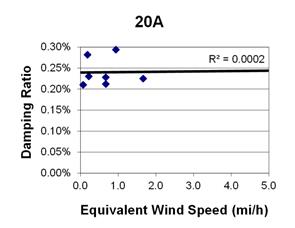
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
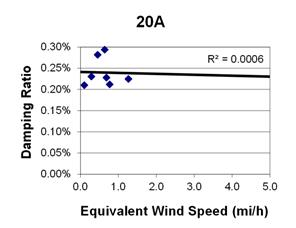
Figure 78. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 20A.
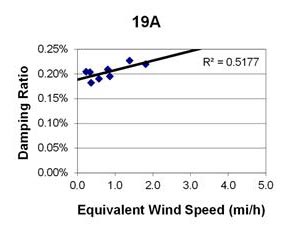
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 79. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 19A.
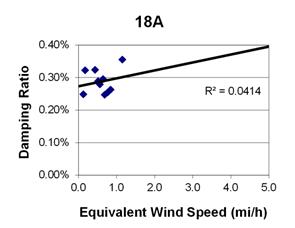
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 80. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 18A.
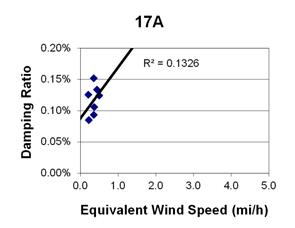
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 81. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 17A.
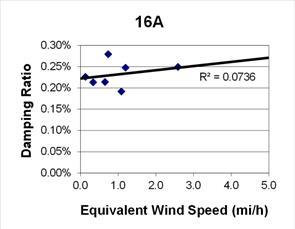
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 82. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 16A.
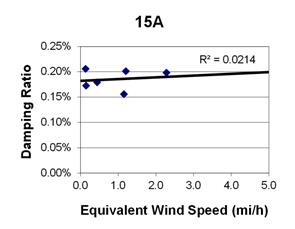
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 83. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 15A.
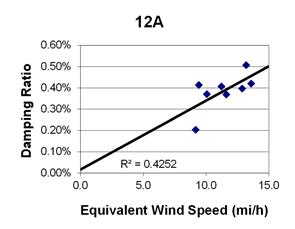
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 84. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 12A.
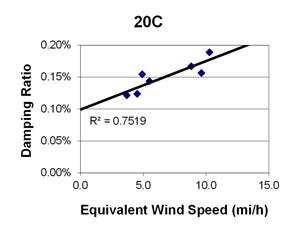
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 85. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 20C.
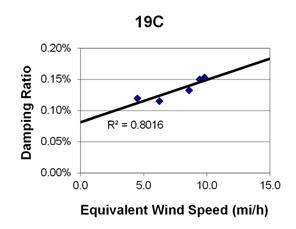
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 86. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 19C.
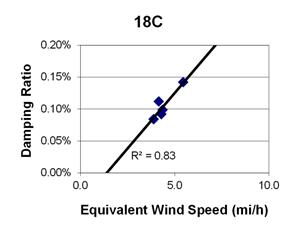
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 87. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 18C.
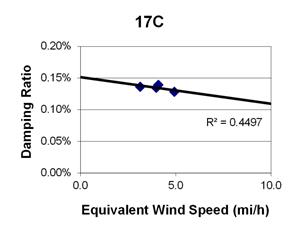
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 88. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 17C.
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 89. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 20A.
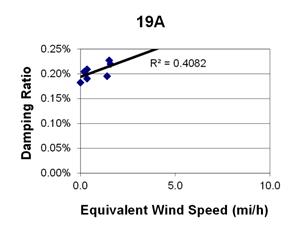
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 90. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 19A.
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
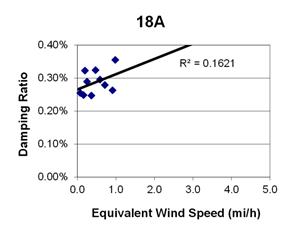
Figure 91. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 18A.
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
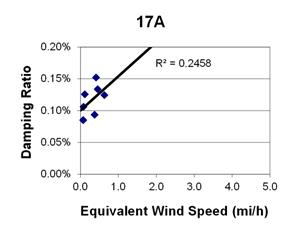
Figure 92. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 17A.
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
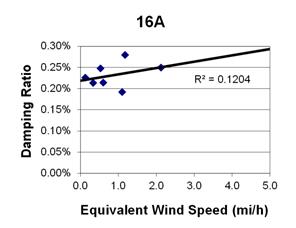
Figure 93. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 16A.
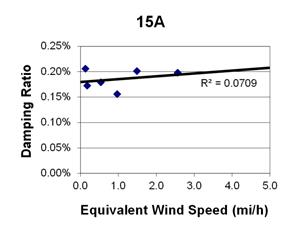
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 94. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 15A.
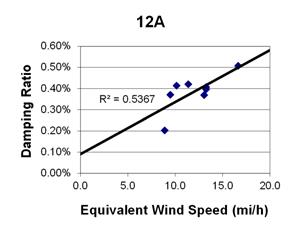
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 95. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 12A.
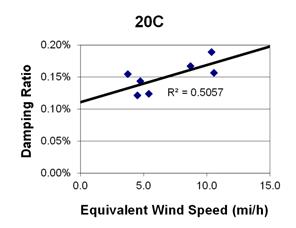
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 96. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 20C.
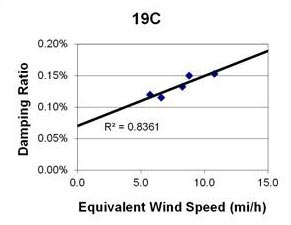
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 97. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 19C.
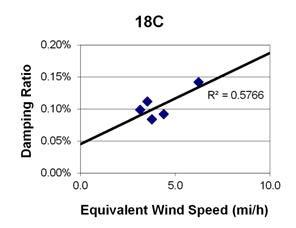
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 98. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 18C.
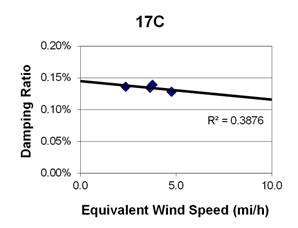
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 99. Graph. Phase 1, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 17C.
PHASE 2 AERODYNAMIC DAMPING PLOTS
Note that cables 20A, 19A, 18A, and 17A did not have significant wind data recorded during their testing. In these plots, "Total" refers to wind data recorded over the entire test run, while "Decay Only" refers to wind data that is recorded only between the start and stop values of the time filter.
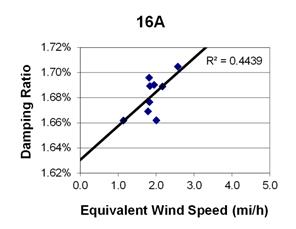
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 100. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 16A.
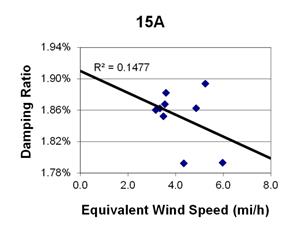
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 101. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 15A.
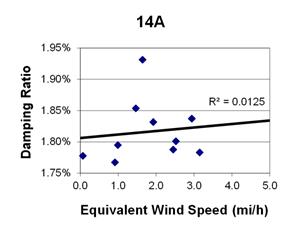
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 102. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 14A.
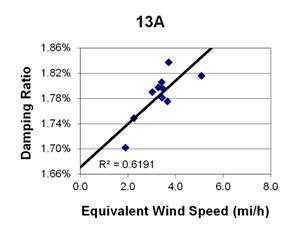
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 103. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 13A.
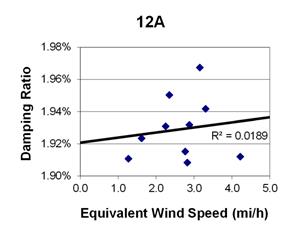
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 104. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 12A.
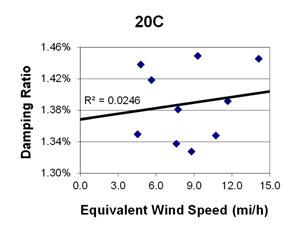
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 105. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 20C.
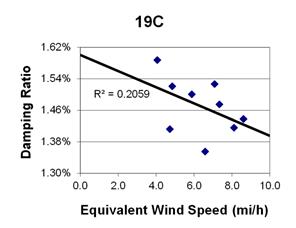
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 106. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 19C.
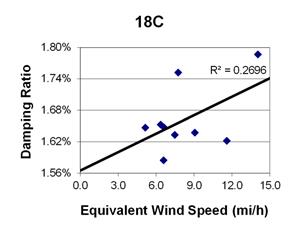
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 107. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 18C.
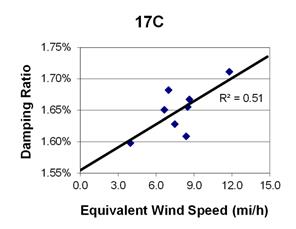
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 108. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 17C.
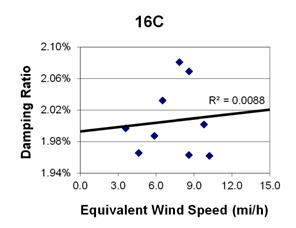
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 109. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 16C.
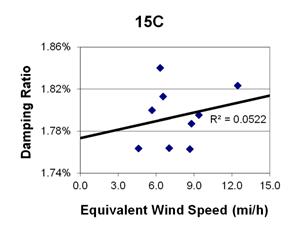
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 110. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 15C.
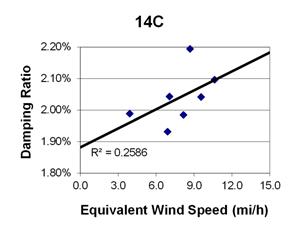
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 111. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 14C.
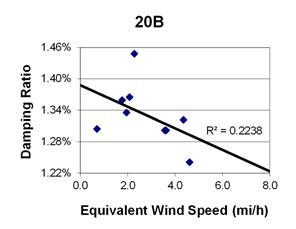
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 112. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 20B.
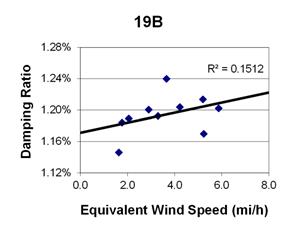
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 113. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 19B.
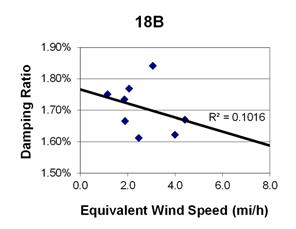
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 114. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 18B.
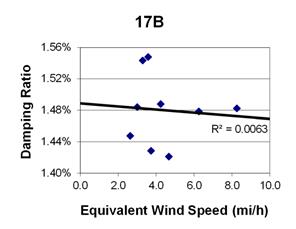
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 115. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 17B.
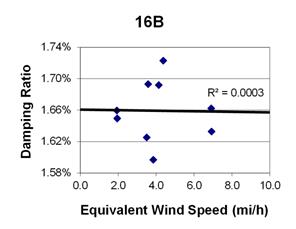
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 116. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 16B.
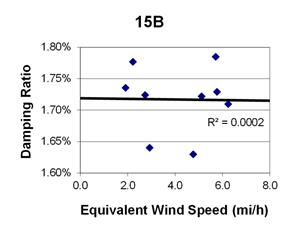
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 117. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 15B.
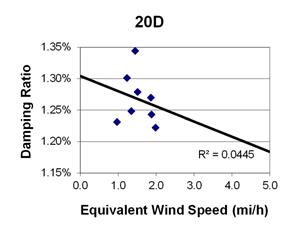
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 118. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 20D.
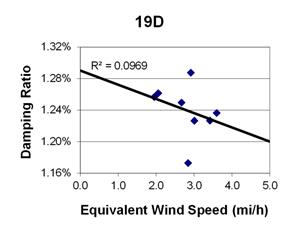
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 119. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 19D.
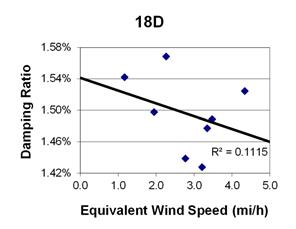
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 120. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 18D.
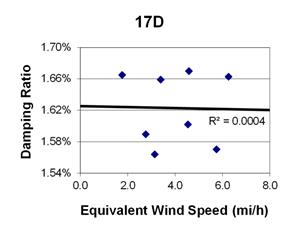
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 121. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 17D.
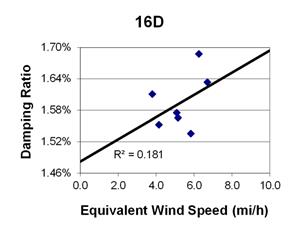
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 122. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 16D.
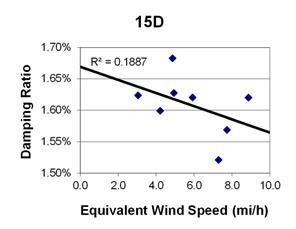
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 123. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 15D.
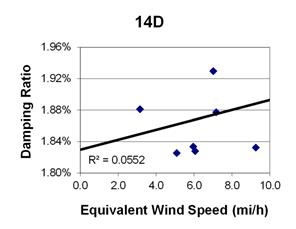
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 124. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 14D.
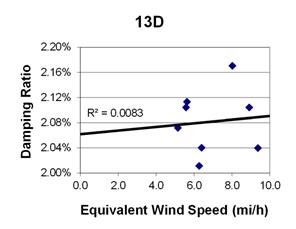
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 125. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus total equivalent wind speed for cable 13D.
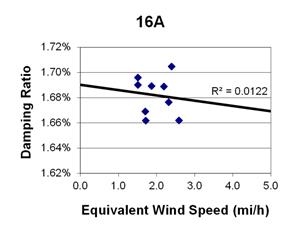
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 126. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 16A.
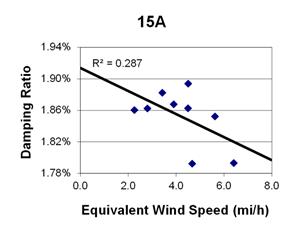
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 127. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 15A.
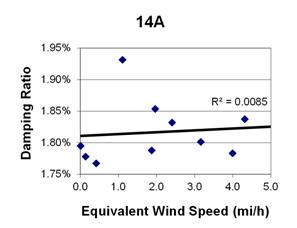
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 128. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 14A.
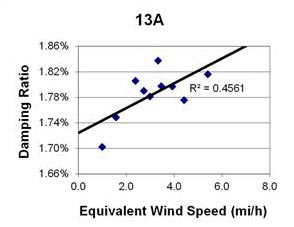
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 129. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 13A.
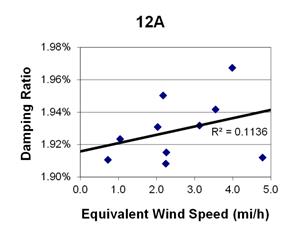
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 130. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 12A.
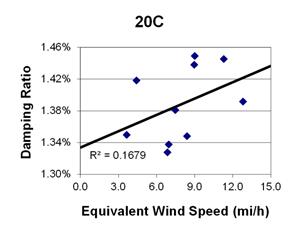
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 131. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 20C.
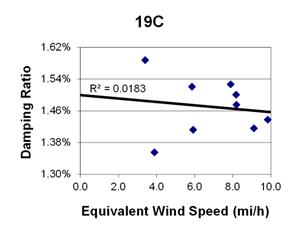
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 132. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 19C.
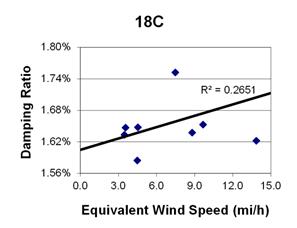
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 133. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 18C.
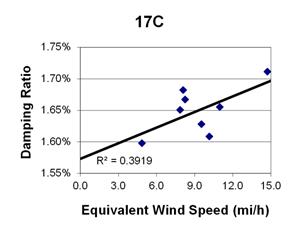
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 134. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 17C.
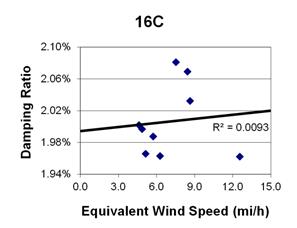
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 135. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 16C.
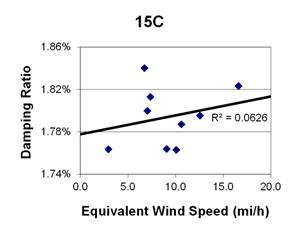
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 136. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 15C.
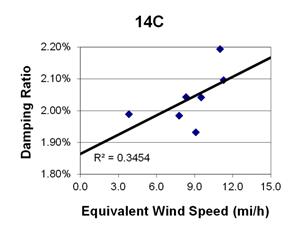
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 137. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 14C.
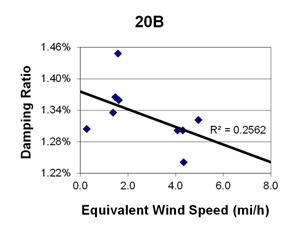
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 138. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 20B.
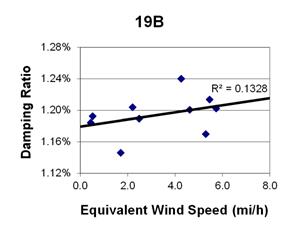
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 139. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 19B.
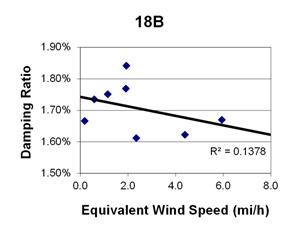
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 140. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 18B.
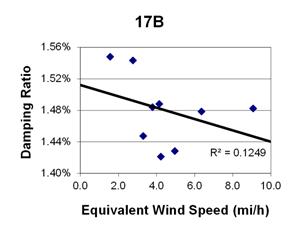
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 141. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 17B.
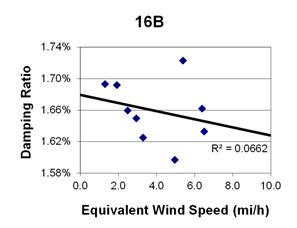
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 142. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 16B.
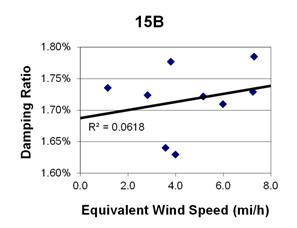
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 143. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 15B.
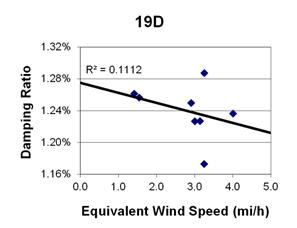
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 144. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 20D.
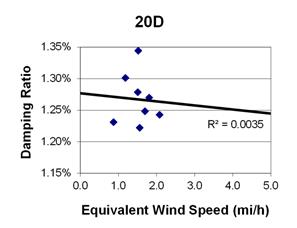
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 145. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 19D.
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
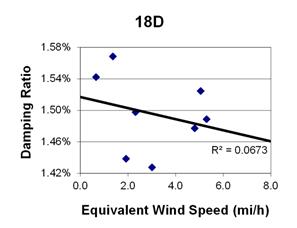
Figure 146. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 18D.
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
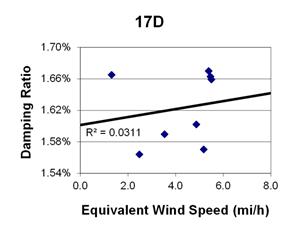
Figure 147. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 17D.
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
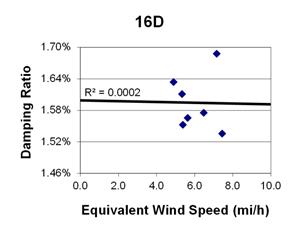
Figure 148. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 16D.
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
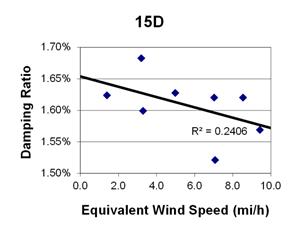
Figure 149. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 15D.
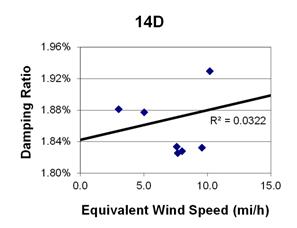
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 150. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 14D.
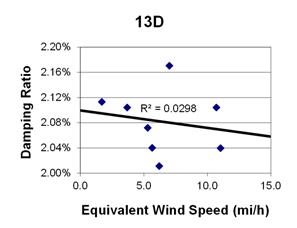
1 mi/h = 1.61 km/h
Figure 151. Graph. Phase 2, damping ratio versus decay-only equivalent wind speed for cable 13D.