Job Plan
The Federal Highway Administration defines Value Engineering as "the systematic application of recognized techniques by a multi-disciplined team which identifies the function of a product or service; establishes a worth for that function; generates alternatives through the use of creative thinking; and provides the needed functions, reliably, at the lowest overall cost."
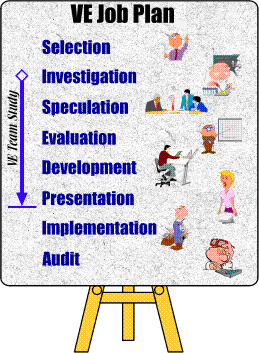
The "systematic application of recognized techniques," referred to in the above definition is embodied in the VE Job Plan. The Job Plan is an organized plan of action for accomplishing VE studies and assuring the implementation of the recommended changes. The Job Plan contains eight phases, five of which are performed by the VE team. The other three phases are carried out in accordance with the policies stated in the agency's VE program.
Each phase of the Job Plan includes several tasks. It is the melding of the various tasks and techniques, coupled with finesse in their application that makes the VE process work.
| Phase | Objective | Key Questions | Techniques | Tasks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection | Select Project |
|
|
|
| Investigation | Investigate Project |
|
|
|
| Analyze Function & Cost |
|
|
|
|
| Speculation | Speculate on Alternatives |
|
|
|
| Evaluation | Evaluate Alternatives |
|
|
|
| Development | Develop Alternatives |
|
|
|
| Presentation | Present Alternatives |
|
|
|
| Implementation | Implement Alternatives |
|
|
|
| Audit | Audit Results |
|
|
|

