Business Logistics 101
Martin Dresner
University of Maryland
Robert H. Smith School of Business
Agenda
- Logistics Defined
- New Logistics Strategies
- Final Remarks
Pipeline View
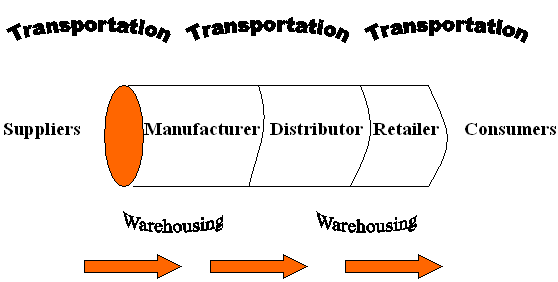
Logistics Activities
- Transportation
- Warehousing
- Inventory Management
- Materials Handling
- Purchasing
- Order Processing
New Paradigm
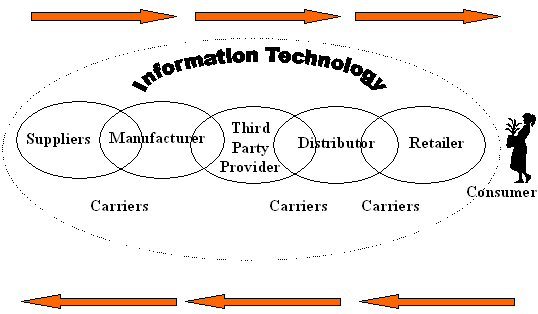
"Alphabet Soup" of Logistics Strategies
- JIT - Just-In-Time
- ER - Efficient Replenishment
- CR - Continuous Replenishment
- ECR - Efficient Consumer Response
- VMI - Vendor Managed Inventory
- SBT - Scan-Based Trading
Just-In-Time Purchasing
- Frequent shipments of small quantities
- Short time windows for deliveries
- Increased traffic on highways and in metropolitan areas
- Partially offset by suppliers locating near customers
Vendor Managed Inventory
- Vendor determines shipment amounts and timing based on customer needs
- Requires tie-in between vendor and customer's inventory system
- Vendor may still deliver on a JIT basis with time windows set by buyer
- Traffic impact remains
Scan-Based Trading
- Suppliers are paid by retailers when consumer purchases are scanned at check-out
- Requires item information (e.g., price paid by retailer) to be included in retailer's cash register information system
- Supplier and retailer need to closely link information systems (e.g., same item codes)
- Big advantage is that retailer no longer needs to check in items when they are delivered by suppliers
- Supplier can set delivery times during off-peak hours
- Supplier can deliver JIT but with a reduced impact on roadways
Final Remarks
- Firms are using information technology to change the way they conduct their logistics operations
- New logistics strategies can have dramatic impacts on transportation infrastructure
- The better these strategies are understood, the better able we will be to make the appropriate infrastructure decisions

