
STICs Deploy Homegrown Innovations
The sixth round of Every Day Counts (EDC-6) kicked off with a Virtual Summit in December 2020 that introduced the seven innovations FHWA is promoting over the next 2 years. The summit also featured a National State Transportation Innovation Council (STIC) Network Showcase that highlighted 245 innovations developed and deployed by agencies throughout the country. The following are just a few examples of the expertise and ingenuity agencies have put into action in areas such as asset management, finance, design, and construction.
Several of the ideas featured used geographic information systems (GIS) to improve asset inventory management. The Vermont Agency of Transportation (VTrans) implemented a GIS-based method for surveying and cataloging cultural resources. VTrans’ Cultural Resources team and its consultant developed new GIS tools to collect, share, and archive data on the State’s historic sites in a paperless and geo-referenced format. An online map is used to track survey progress and share information with project stakeholders. VTrans expects this GIS-based method to greatly expedite project review.
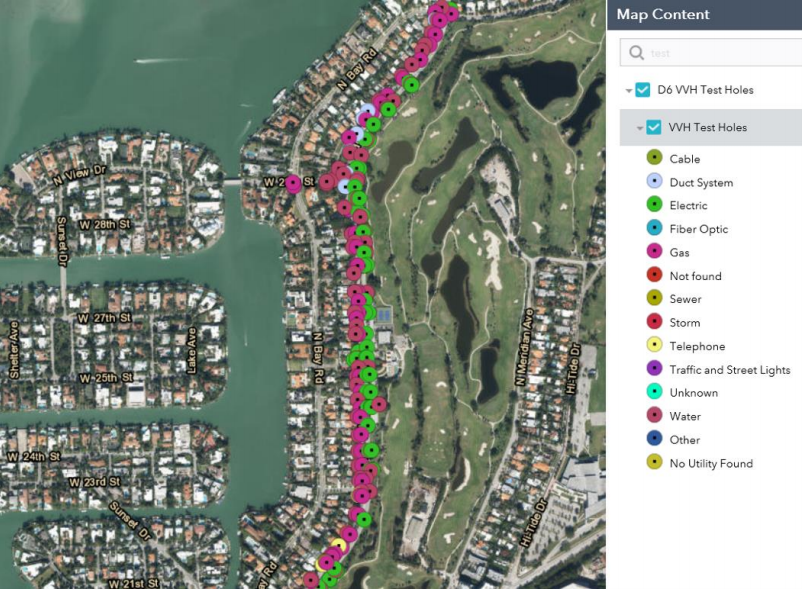
FDOT implemented an enterprise GIS solution for compiling information from test holes.
Credit: Florida Department of TransportationThe Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT) estimates savings close to $223,000 per year by using GIS to compile information on utility test holes, excavations that are commonly 10 to 12 inches wide used to verify the physical location and depth of underground utilities. Projects with extensive reconstruction, drainage, and several improvements with deep foundations usually require a large amount of test holes. In the past, test hole records were not available for all designers to view when working on specific areas. Using its GIS tools, FDOT created a layer with test hole data that designers can access to verify utility locations without having to request additional test holes. In addition to cost savings, reported benefits include streamlined delivery, consistent quality, and enhanced collaboration.
To identify non-compliance of public facilities with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), the Iowa DOT leveraged geospatial data and field data collection technologies to assess thousands of assets within the State’s public transit and pedestrian transportation systems. The agency combined tablet-based data collection, a data visualization dashboard, and automated reporting to develop an in-house process that employs commercial off-the-shelf software to quickly assess assets using a standardized evaluation and reporting method.
In Arizona, three metropolitan planning organizations partnered to determine the economic impacts of transportation projects. Their Sun Corridor Value Impact Analysis resulted in a replicable methodology and toolkit for quantifying the economic value added by large, high-capacity transportation investments. The toolkit helps regional partners understand how transportation connects to the economy of the megaregion and affects different household, employment, and industry groups.

MDOT developed guides to assist local public agencies with a risk-based approach to working with inspection and material testing consultants.
Credit: Mississippi Department of TransportationBecause the State’s local public agencies (LPAs) rely heavily on consultants to develop and deliver projects, the Mississippi DOT (MDOT) adopted a risk-based approach to construction inspection and material testing to help them use administration resources efficiently. MDOT’s Risk Based Inspection and Material Testing Guide sets a baseline for inspection hours and material testing frequencies on LPA projects, and its Critical Inspection Guide focuses inspectors on key components of the work.

IDOT’s digital, shared concrete pour log improves communication during bridge deck construction and deck concrete pours. Watch this video to learn more.
Credit: Illinois Department of TransportationThe Illinois DOT addressed the communication challenges in sharing accurate and timely information that can happen during bridge deck construction and deck concrete pours by developing a cloud-based system using laptops, tablets, and smartphones. The digital, shared concrete pour log allows staff and contractors to access up-to-date information instantly regardless of location, reducing the chances for confusion or incorrect information during a pour.
The Georgia DOT (GDOT) is pursuing faster project delivery from concept to completion by using flash tracking for accelerated project delivery. GDOT identified and prioritized best practices considered crucial for completing time-driven projects successfully, then developed a Flash Track Readiness Assessment Toolkit. The toolkit assesses a team’s preparation to undertake projects on a flash track basis and identifies practices that can remedy a team’s weaknesses.
NCDOT’s instructional video describes how the dynamic left turn intersection works.
Credit: North Carolina Department of TransportationDual left turn lanes are typically operated with protected left turn signals, which means extra delay during non-peak hours compared to permissive operation. To reduce this traffic holdup, the North Carolina DOT (NCDOT), the town of Cary, and the Regional Transportation Alliance teamed up to design, install, and test a new dynamic left turn intersection. This new design allows permissive operation to be used during nonpeak hours using standard traffic control devices. NCDOT expects substantial benefit in terms of delay savings.
—MORE INFORMATION
Register for access to the EDC-6 Virtual Summit on-demand content to learn more about these and other homegrown innovations. After registering, click on the National STIC Network Showcase button.
Recommended Citation: U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration - Washington, DC (2021) Innovator Newsletter, September/October 2021, Volume 15(86). https://doi.org/10.21949/1521364



