a = blocked flow area by abutment
A = unobstructed flow area in approach channel
Af1 = blocked flow area in approach-channel floodplain
b = bridge pier width
Bf = width of floodplain in compound channel
Bm = width of main channel in compound channel
Bm1 = width of approach main channel
Bm2 = width of main channel in contracted section
Cn = units conversion coefficient used in equation 23
C0 = best-fit constant in proposed scour formula
Cr = best-fit coefficient in proposed scour formula
CLB = live-bed scour coefficient
d50 = median diameter of sediment
ds = local scour depth
dsc = theoretical long contraction scour depth
dst = unsteady scour depth at any time t
F0 = approach value of densimetric grain Froude number in Lim scour formula
F1 = approach-flow Froude number
Fab = Froude number adjacent to abutment face
k-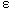 = k-epsilon refers to a numerical modeling technique that uses the ratio of turbulent kinetic energy squared to turbulent energy dissipation rate to define the eddy viscosity term for computations
= k-epsilon refers to a numerical modeling technique that uses the ratio of turbulent kinetic energy squared to turbulent energy dissipation rate to define the eddy viscosity term for computations
kf = spiral-flow adjustment factor in Maryland scour formula
ks = equivalent sand-grain roughness
kv = velocity adjustment factor in Maryland scour formula
K1 = geometric shape factor for abutment in Froehlich scour formula
K2 = embankment skewness factor in Froehlich scour formula
Ks* = abutment shape factor in Melville scour formula
KG = channel geometric factor in Melville scour formula
KI = flow-intensity factor in Melville scour formula
KST = spill-through abutment shape factor for scour formula in present study
K * = abutment alignment factor in Melville scour formula
* = abutment alignment factor in Melville scour formula
La = abutment/embankment length
M = discharge distribution factor in approach section = unblocked Q over total Q
= discharge contraction ratio for a bankline abutment
n = Manning's n
nfp = Manning's n in floodplain of compound channel
nmc = Manning's n in main channel of compound channel
nK = Manning's n calculated from Keulegan's equation
Ns = sediment number (equivalent to densimetric grain Froude number)
Nsc = critical value of sediment number
q1 = flow rate per unit width in approach section in Maryland scour formula
q2 = flow rate per unit width in contracted section in Maryland scour formula
qbv = volumetric sediment discharge per unit width
qf0 = flow rate per unit width in floodplain at normal depth (unconstricted)
qf0c = critical flow rate per unit width in floodplain at normal depth (unconstricted)
qf1 = flow rate per unit width in the approach floodplain (constricted)
qf2 = flow rate per unit width in the contracted floodplain
qm1 = flow rate per unit width in the approach main channel at the beginning of scour
qm2 = flow rate per unit width in the contracted section in the main channel
Q = total discharge in compound channel
Qf1 = discharge in the approach floodplain
Qm0 = discharge in main channel for uniform flow in a compound channel
Qm1 = discharge in the approach main channel
Qm2 = discharge in the contracted main channel
Qobst1 = obstructed discharge in the approach section
R = channel hydraulic radius
SG = specific gravity of sediment
t = time since beginning of scour
te = time to reach equilibrium scour depth
u*1 = approach value of shear velocity = (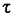 1/
1/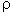 )0.5
)0.5
u*c = critical value of shear velocity = (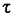 1/
1/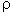 )0.5
)0.5
Vab = maximum resultant velocity near the upstream corner of the abutment face
Vc = critical velocity for initiation of motion
Vf0 = floodplain velocity at normal depth
Vf0c = critical velocity for unconstricted floodplain depth of uniform flow
Vf1 = bridge approach velocity in floodplain of compound channel
Vf2 = floodplain velocity in the contracted floodplain after scour
Vm0c = critical velocity for the unconstricted depth in the main channel
Vm1 = bridge approach velocity in main channel of compound channel
Vm2c = critical velocity in the main channel at the contracted section at equilibrium scour
Vx = mean contraction velocity in GKY scour formula
VR = resultant velocity adjacent to tip of abutment in GKY scour formula
V1 = bridge approach velocity in rectangular channel
y = generic symbol for depth of flow in main channel or floodplain for calculating critical velocity
yab = depth near the upstream corner of the abutment face
yf0 = normal depth in floodplain
yf1 = bridge approach depth in floodplain of compound channel, including backwater
yftw = tailwater depth in floodplain
ym0 = normal depth in main channel
ym1 = bridge approach depth in main channel of compound channel, including backwater
ym2 = depth of flow in main channel in contracted section at equilibrium scour
ysc = total depth of flow after scour, including the contraction scour depth only
(Maryland formula)
y1 = bridge approach depth in rectangular channel
y2 = total flow depth in contracted section after scour (Maryland formula)
y' = vertical coordinate measuring distance above the main-channel bed
y'/ym= ratio of distance above the main-channel bed to depth of the flow in the main
channel
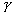 = specific weight of fluid
= specific weight of fluid
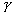 s = specific weight of sediment
s = specific weight of sediment
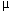 f = general discharge per unit width contraction ratio for the floodplain
f = general discharge per unit width contraction ratio for the floodplain
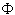 = ratio of boundary shear force to streamwise component of weight
= ratio of boundary shear force to streamwise component of weight
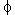 = angle of repose of sediment
= angle of repose of sediment
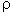 = fluid density
= fluid density
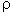 s = sediment density
s = sediment density
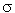 = ratio of Manning's n in the main channel with compound-channel flow to the value for the flow in the main channel alone
= ratio of Manning's n in the main channel with compound-channel flow to the value for the flow in the main channel alone
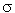 g = geometric standard deviation of sediment grain size distribution
g = geometric standard deviation of sediment grain size distribution
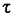 c = critical shear stress for initiation of sediment motion
c = critical shear stress for initiation of sediment motion
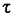 0 = average bed shear stress in uniform flow
0 = average bed shear stress in uniform flow
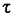 1 = bed shear stress in approach flow
1 = bed shear stress in approach flow
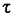 * = Shields' parameter,
* = Shields' parameter, 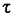 /[(
/[(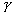 s -
s - 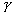 ) d50]
) d50]
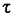 *c = critical value of Shields' parameter,
*c = critical value of Shields' parameter, 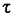 c/[(
c/[(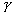 s -
s - 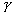 ) d50]
) d50]
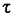 *1 = Shields' parameter in approach flow section
*1 = Shields' parameter in approach flow section
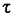 *2 = Shields' parameter in contracted flow section
*2 = Shields' parameter in contracted flow section
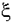 = independent dimensionless ratio in proposed scour formula = qf1/Mqf0c
= independent dimensionless ratio in proposed scour formula = qf1/Mqf0c
Back to Top
Table of Contents | Next
