U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Federal Highway Administration Research and Technology
Coordinating, Developing, and Delivering Highway Transportation Innovations
 |
| This report is an archived publication and may contain dated technical, contact, and link information |
|
Publication Number: FHWA-HRT-05-153
Date: December 2006 |
||||||||
Long-Term Pavement Performance Program Falling Weight Deflectometer Maintenance ManualChapter 2. Falling Weight Deflectometer TrailerThe FWD in this manual is mounted on a towed trailer, which requires some routine maintenance. This section discusses and illustrates the following trailer parts:
TRAILER FRAMEThe trailer frame requires little maintenance. Monthly, a technician should thoroughly check the frame for signs of cracks, corrosion, and missing bolts. Figure 1 shows corrosion on the trailer frame that occurred under the battery box near the battery ground pole. Figure 2 shows a second ground pole, another site of possible corrosion. Figure 3 shows a missing bolt that was drilled out and replaced. The missing bolt was from an optional cover. Damage such as broken bolts can be expected on units with covers, and bolts that attach the covers should be checked monthly. Figure 1. Corrosion caused by battery.  Figure 2. Second battery ground connection.  Figure 3. Missing bolt drilled out, tapped, and replaced. 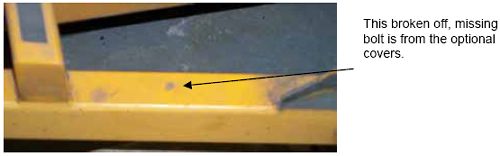 NOTE: The missing bolts that have broken off are from the optional covers. Check the covers monthly and repair or replace missing bolts. This damage is common on units with covers. Figures 4 and 5 show the trailer after it was stripped of all paint and parts to prepare it for the major overhaul. Figure 4. Stripped and sandblasted trailer ready to go to powder coat facility.  Figure 5. Rear view of trailer before powder coat was applied.  Figures 6 and 7 show the newly powder-coated trailer. Figure 6. Front of newly powdered trailer.  Figure 7. Rear of newly powdered trailer  ACCESSORIESAll eight of the Federal LTPP programs’ FWDs have covers (figures 8, 9, and 10). These covers provide some security and help protect sensitive components from outside elements. The covers should be washed and inspected monthly for cracks and dents. Covers should be waxed every 6 months to help prevent scratches caused by dirt and debris. Monthly, all hinges should be lubricated and mounting bolts checked to ensure they are tight. Figure 8. Lower trailer covers.  Figure 9. Top trailer cover("dog house").  Figure 10. Front trailer cover.  TORSION AXLESThe torsion axles must be checked for the correct toe settings and camber. The trailer axles are set at the factory and rarely need to be adjusted; however, it is a good idea to check their alignment every 3 months. To do this, look at the wear on the tires to check them visually or run your hand across the tire surface to feel any abnormal wear such as on the edges or scuffing of the tires. An abnormal amount of wear on the interior or exterior edge of the tire indicates the axles may be out of alignment. Some wear is normal because of the vertical movement in the torsion axle itself. To help reduce unnecessary wear on the tires, rotate them every 8,047 to 16,093 km (5,000 to 10,000 mi). Excessive wear between rotations may indicate the alignment needs to be corrected. To correct this alignment, take the trailer to a reputable trailer repair facility for service; most are equipped to correct alignment. Figure 11 shows the torsion axle and mounting plate configuration. During tire rotation, check the rubber inside the tube housing (figure 12). It should be intact with no pieces missing. In some cases, the rubber may separate from the housing. If this occurs, the axle may need to be replaced. Consult a repair facility to help determine this. Figure 11. Torsion axle and mounting plate.  Figure 12. Torsion tube housing.  Figure 13 shows a bird’s eye view of the torsion axle and shims. Check wheels for loose bearings and check tires for wear and condition (figure 14). Figure 13. Top view of torsion axle and shims.  Figure 14. Trailer tires.  HYDRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEMMake the following precautionary checks before any trip:
Figure 18. Flexible brake lines. 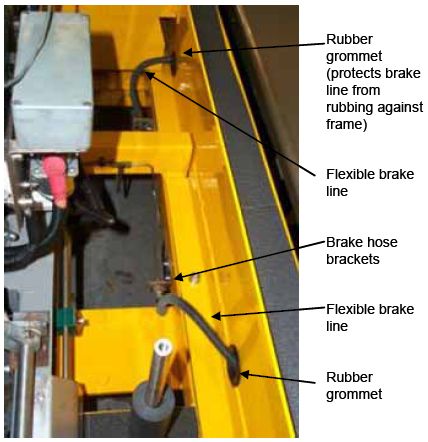 Figure 19. Flexible brake line behind tire.  Figure 20. Rigid brake lines.  TIRES AND WHEELS
Figure 21. Brake drum.  Figure 22. New axle wheel bearings and components. 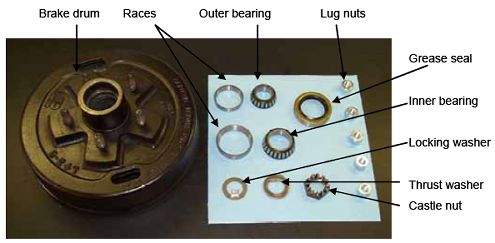 TRAILER LIGHTSCheck trailer lights before traveling. Daily, check brake lights, turn signal, running lights, and strobes to make sure they are working properly (figures 23 and 24). Figure 23. Trailer brake and license plate lights and backup alarm. 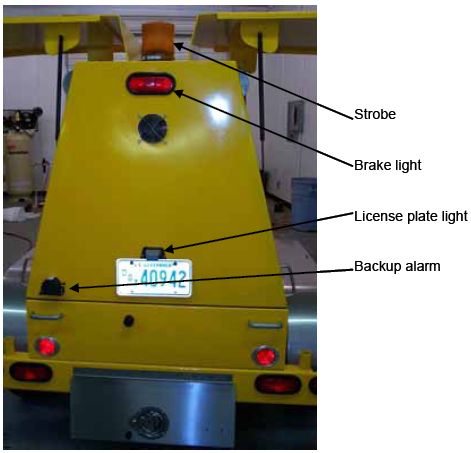 Figure 24. Trailer turn signal and brake lights. 
|