U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Federal Highway Administration Research and Technology
Coordinating, Developing, and Delivering Highway Transportation Innovations
 |
| This report is an archived publication and may contain dated technical, contact, and link information |
|
Publication Number: FHWA-HRT-06-132 Date: December 2006 |
Test plans specify the location of test points at an LTPP section. There are several different test plans. The appropriate test plan for an LTPP section is determined by the experiment designation of the section, and in some cases the surface type or other properties of the section. The test plan applicable to a given LTPP section should be determined according to Table 4.
| Experiment | Surface Type | Test Plan | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS 1 | Flexible | 1 | |
| GPS 2 | Flexible | 1 | |
| GPS 3 | JPCP* | 2 | |
| GPS 4 | JRCP** | 2 | |
| GPS 5 | CRCP*** | 3 | |
| GPS 6 | Flexible | 1 | |
| GPS 7 | Flexible | 1 | |
| GPS 9 | JPCP | 2 | |
| SPS 1 | Flexible | 4 | |
| SPS 2 | JPCP | 5 | |
| JPCP | 7 | 4.3 m lane width sections | |
| SPS 3 | Flexible | 8 | |
| SPS 4 | JPCP | 9 | |
| SPS 5 | Flexible | 4 | |
| SPS 6 | JPCP | 5 | |
| Flexible over JPCP | 10 | Sections 3, 6, 7, 8 | |
| Flexible over JPCP | 11 | Section 4 | |
| SPS 7 | JPCP | 5 | |
| CRCP | 6 | ||
| SPS 8 | Flexible | 4 | |
| SPS 8 | JPCP | 5 | |
| SPS 9 | Flexible | 4 | |
| Flexible over PCC | 10 |
| * | JPCP—jointed plain concrete pavement. |
| ** | JRCP—jointed reinforced concrete pavement. |
| *** | CRCP—continuously reinforced concrete pavement. |
Each test plan consists of one or more test passes. Data from each test pass should be stored in a separate data file. Each test pass should be performed in the direction of the flow of traffic, from the section approach limit (0+000) to the section leave limit (0+152.4 (5+00) for most test sections).
Each test pass consists of testing according to one or more lane specification. It is critical that the operator enter the lane specification appropriate to the test location in the field provided in the data collection software. The longitudinal offset between test locations vary according to the test plan and test pass. Table 5 includes detailed information for each test plan and test pass.
| Test Plan | Pass # | Lane Spec. | Lane Description | Test Type | Test Interval | Number of Testsa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | F1 | ML | Basin | 7.6 m (25 ft) | 21 |
| 3 | F3 | OWP | Basin | 7.6 m (25 ft) | 21 | |
| 2 | 1 | J1 | ML–MP | Basin | 20 slabs | 20 |
| 2 | J2 | PE–CR | Basin | 20 slabs | 20 | |
| J3 | PE–MP | Basin | 20 slabs | 20 | ||
| 3 | J4 | OWP–JA | LT | 20 slabs | 20 | |
| J5 | OWP–JL | LT | 20 slabs | 20 | ||
| 3 | 1 | C1 | ML–MP | Basin | 20 slabs | 20 |
| 2 | C2 | PE–CR | Basin | 20 slabs | 20 | |
| C3 | PE–MP | Basin | 20 slabs | 20 | ||
| 3 | C4 | OWP–JA | LT | 20 slabs | 20 | |
| C5 | OWP–JL | LT | 20 slabs | 20 | ||
| 4 | 1 | F1 | ML | Basin | 15.2 m (50 ft) | 11 |
| 3 | F3 | OWP | Basin | 15.2 m (50 ft) | 11 | |
| 5 | 1 | J1 | ML–MP | Basin | 10 slabs b | 10 c |
| 2 | J2 | PE–CR | Basin | 10 slabs b | 10 c | |
| J3 | PE–MP | Basin | 10 slabs b | 10 c | ||
| 3 | J4 | OWP–JA | LT | 10 slabs b | 10 c | |
| J5 | OWP–JL | LT | 10 slabs b | 10 c | ||
| 6 | 1 | C1 | ML–MP | Basin | 10 slabs | 10 |
| 2 | C2 | PE–CR | Basin | 10 slabs | 10 | |
| C3 | PE–MP | Basin | 10 slabs | 10 | ||
| 3 | C4 | OWP–JA | LT | 10 slabs | 10 | |
| C5 | OWP–JL | LT | 10 slabs | 10 | ||
| 7 | 1 | J1 | ML–MP | Basin | 10 slabs | 10 |
| 2 | J2 | PE–CR | Basin | 10 slabs | 10 | |
| J3 | PE–MP | Basin | 10 slabs | 10 | ||
| 3 | J4 | OWP–JA | LT | 10 slabs | 10 | |
| J5 | OWP–JL | LT | 10 slabs | 10 | ||
| 4 | J7 | WLE–CR | Basin | 10 slabs | 10 | |
| J8 | WLE–MP | Basin | 10 slabs | 10 | ||
| 8 | 1 | F1 | ML | Basin | 30.4 m (100 ft) | 6 |
| 3 | F3 | OWP | Basin | 30.4 m (100 ft) | 6 | |
| 9 | 1 | J4 | OWP–JA | LT | Every third joint/slab starting with first joint/slab | varies |
| J5 | OWP–JL | LT | varies | |||
| J6 | OWP–MP | Basin | varies | |||
| 10 | 1 | F1 | ML | Basin | Same as J1/J3 before overlay | 6 |
| 3 | F3 | OWP | Basin | 6 | ||
| 11 | 1 | F1 | ML | Basin | Same as J1/J3 before overlay | 10 |
| 3 | F3 | OWP | Basin | 10 | ||
| F4 | OWP–JA | LT | Same as J4/J5 before overlay | 10 | ||
| F5 | OWP–JL | LT | 10 |
| a For PCC testing, if fewer effective slabs exist at a section than the number listed in the "Test interval" column, the number of slabs to be tested should equal the number of slabs that exist. |
| b Test 20 slabs for 304.8 m (1,000 ft) test sections. |
| c 20 tests for 304.8 m (1,000 ft) test sections. |
| Abbreviations: ML–midlane; OWP–outer wheel path; PE–pavement edge; WLE–widened lane edge; MP–mid-panel; CR–corner; LT–load transfer; JA–joint approach (load plate on approach slab); JL–joint leave (load plate on leave slab) |
Appendix A contains diagrams of these test plans.
The transverse location of a test pass is given as a relative position in the lane containing the LTPP test section. These relative positions are midlane (ML), outer wheel path (OWP), pavement edge (PE) and widened lane edge (WLE). As shown in table 6, these positions are to be measured from the outside lane edge (OLE) to the center of the FWD load plate.
| Relative Position | Offset from OLE | |
|---|---|---|
| 3.66 m (12 ft) Nominal Lane Width | 4.27 m (14 ft) Nominal Lane Width | |
| ML | 1800 mm ± 150 mm | 1800 mm ± 150 mm |
| OWP | 760 mm ± 75 mm | 760 mm ± 75 mm |
| PE | 150 mma ± 75 mm | 150 mm ± 75 mm |
| WLE | NA | 150 mmb ± 75 mm |
| a If proper seating of the load plate at this offset is impossible due to pavement features, the offset may be increased. |
| b Testing in the widened lane edge is referenced to the outer edge of the pavement slab, not the OLE. |
For a normal paving lane (nominally 3.7 m (12 ft) wide), the OLE is defined as the lane shoulder interface unless the outside edge of the painted shoulder stripe is more than 150 mm (6 inches) inside the lane shoulder interface, in which case the OLE is defined as the outside edge of the painted shoulder stripe. For a wide paving lane (nominally 4.0 m (13 ft) or wider), the OLE is defined as the outside edge of the painted shoulder stripe.
This transverse location must be maintained within the error band listed for all test locations in the test pass.
FWD testing on PCC surfaces is referenced to effective slabs, not absolute longitudinal position. When testing has been performed at a PCC-surfaced section previously, then the operator should test the same slabs again as those tested previously. The operator should use form F10 to identify slabs tested previously. On form F10, slabs are referenced by the station of the joint or crack that defines the approach end of the slab. If a previously tested slab is subdivided by a new transverse crack, then that portion of the slab which is bounded by the original approach joint or crack and the new transverse crack should be tested.
If testing has not been performed previously at a PCC-surfaced section, then the operator should determine the number of slabs to be tested according to the test plan. Then the operator should determine the number of effective slabs that are wholly within the section limits (i.e., only count slabs that begin and end in the test section). Slabs can be bounded by either joints or full-width transverse cracks that are working.
If the number of effective slabs is less than or equal to the number of slabs to be tested, then all effective slabs should be tested. If the number of effective slabs is greater than the number of slabs to be tested, then a subset of the effective slabs equal to the number of slabs to be tested should be selected. The operator should take care to evenly space the slabs to be tested along the test section. Testing in all test passes at the section should be done in reference to the same slabs.
The test plans specify test locations relative to the slab to be tested as mid-panel, joint approach, joint leave, and corner.
Mid-panel testing should be performed with the load plate located as close to the center of the effective slab as possible. The load plate should be within 0.3 m (1 ft) or 10 percent of the effective slab length of the center (as measured along the test pass), whichever is smaller.
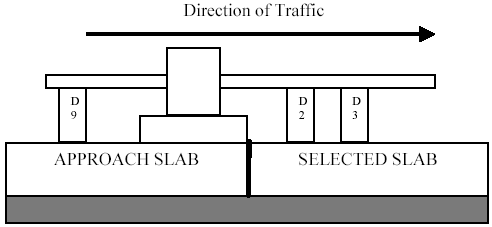
Joint approach testing should be performed with the load plate tangent to the joint or crack defining the approach end of the slab to be tested. The load plate should be located on the slab immediately before the selected slab. The edge of the load plate should be within 50 mm (2 inches) of the joint, but under no circumstances should it bridge the joint. Figure 1 shows a diagram of joint approach testing.
Figure 1. Diagram. Joint approach testing.
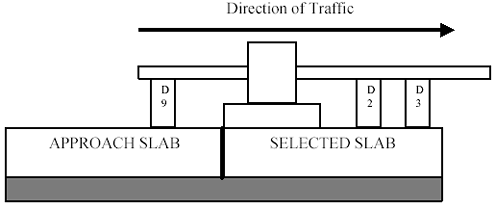
Joint leave testing should be performed with the load plate tangent to the joint or crack defining the approach end of the slab to be tested. The load plate should be located on the selected slab and the edge of the load plate should be within 50 mm (2 inches) of the joint, but under no circumstances should it bridge the joint. A diagram of joint approach leave testing is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Diagram. Joint approach-leave testing.
For JCP pavements (test plans 2, 5, and 7), corner testing should be performed the same as joint leave testing except that the load plate should be tangent to both the joint or crack defining the approach end of the slab and the longitudinal joint defining the outside edge of the slab. The edge of the load plate should be no more than 75 mm (3 inches) from the joint or crack defining the approach end of the slab and no more than 75 mm (3 inches) from the longitudinal joint.
For CRCP pavements (test plans 3 and 6) the corner test should be performed with the load plate centered on the transverse crack defining the approach end of the effective slab and tangent to the longitudinal crack defining the outside edge of the slab. The edge of the load plate should be no more than 75 mm (3 inches) from the longitudinal joint.