FY 2010 Annual Report
Contents
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) Office of Planning, Environment and Realty's (HEP) Surface Transportation Environment and Planning Cooperative Research Program (STEP) ended on September 30, 2012. For current HEP research information, please see HEP's research web site.
Executive Summary
FY 2010 Research Budgets by Category*
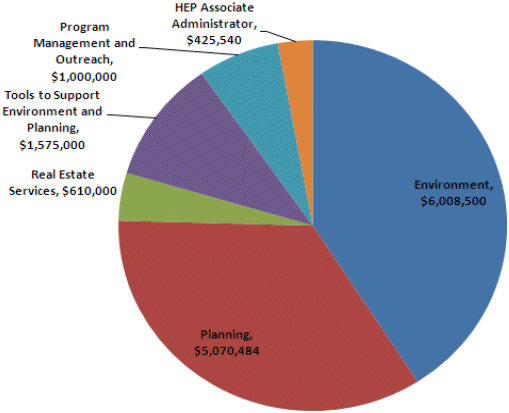
*Includes funds that were provided in supplemental appropriations via technical corrections late in FY2010.
Since 2006, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) has administered the Surface Transportation Environment and Planning Cooperative Research Program (STEP) to encourage new, strategic, and applied research on the relationship between surface transportation planning and the environment. Federal, State, and other stakeholders are involved throughout the STEP process to shape, refine, and implement research agendas.
Funding
Section 5207 of the Safe, Accountable, Flexible Efficient Transportation Equity Act: A Legacy for Users (SAFETEA-LU) established the STEP. SAFETEA-LU and continuing resolutions authorized $16.875 million annually to implement the STEP. After adjusting for obligation limitations, rescissions, and the over-designation of Title V Research in SAFETEA-LU, $14.6 million was available for the FY2010 STEP.
FY2010 STEP Accomplishments
- FHWA improved the state of the practice in planning, environment, and realty through investment in 64 projects identified in the FY2010 STEP Research Plan that fall into four broad research categories: environment, planning, real estate services, and tools to support environment and planning.
- STEP continued to be a model for stakeholder collaboration, outreach, and feedback. Using a Web-based system, stakeholders provided over 200 pieces of feedback on research needs during the FY2010 comment period between September 4 and December 3, 2009.
- FHWA developed tools to improve the quality and efficiency of environmental decision-making.
- FHWA enhanced transportation safety through integration with operations and planning.
- FHWA improved noise and travel modeling capabilities through data collection.
- FHWA promoted interstate and international coordination through facilitating border planning working groups.
Impacts
- The STEP process allowed FHWA to foster interagency collaboration, provide a variety of forums for information sharing, and develop new training courses to improve the effectiveness of the transportation planning and environmental review processes.
- Through the STEP, stakeholders directly participated in prioritizing research needs through meetings and study reviews. Stakeholders also developed and implemented innovative outreach practices; contributed to research through pilot studies, reports, and conference participation; and addressed complex issues in transportation planning through partnerships and workshops.
STEP is the primary source of SAFETEA-LU funding for FHWA research on planning and the environment.
