Safety and Health on Bridge Repair, Renovation and Demolition Projects
APPENDIX G
Table of Contents
EMPLOYEE LEAD IN CONSTRUCTION FACT SHEET
Lead is a toxic substance that may enter the body through breathing or swallowing lead dusts, fumes, or mists. If food, cigarettes, or your hands have lead on them, lead may be swallowed while you are eating, drinking, or smoking. Once in the body, lead enters the bloodstream and may be carried to all parts of the body. The body can eliminate some of this lead, but any remaining stored lead may cause irreversible damage to cells, organs and whole body systems. After exposure stops, it takes months or even years for all lead to be removed from the body.
What Are the Symptoms?
Exposure to lead may affect each person differently. Even before symptoms appear, lead may cause unseen injury to the body. During early stages of lead poisoning, mild symptoms may be overlooked as everyday medical complaints, including:
Loss of appetite
Trouble sleeping
Irritability
Fatigue
Headache |
Joint and muscle aches
Metallic taste
Decreased sex drive
Lack of concentration
Moodiness |
Brief intense exposure or prolonged overexposure may result in severe damage to your blood-forming, nervous, urinary, and reproductive systems. Some noticeable medical problems include:
Stomach pains
Wrist or foot drop
High blood pressure
Nausea |
Tremors
Convulsions or seizures
Anemia
Constipation or diarrhea |
What Protection Do I Have?
The Lead in Construction Standard 29 CFR (1926.62) is designed to protect you if you are exposed to lead on the job. The permissible exposure limit for airborne lead is an 8-hour time weighted average of 50 µg/m³ (micrograms per cubic meter of air). However, the permissible exposure limit is lower if your workday exceeds 8 hours.
Regardless of your exposure, your employer is required to do the following:
-
inform you of the hazards of lead
-
provide handwashing facilities
-
provide clean protective clothing where skin or eye irritation exists
-
provide you with a respirator when you want one
Exposure at or above 30 µg/m³ (the action level) requires the following:
-
periodic air monitoring
-
periodic testing of the level of lead in your blood
-
medical examinations and consultations
-
removal from exposure, with your wages and benefits protected, when your blood lead level exceeds 50 µg/dl
-
more detailed training
Additionally, exposure in excess of the permissible exposure limit requires:
How Do I Know If I’m Overexposed?
Your employer is required to assess your exposure whenever you may be exposed to lead. However, until your employer demonstrates otherwise, it is presumed that you are exposed in excess of the permissible exposure limit if you:
-
spray paint with lead paint
-
use lead-containing mortar
-
engage in lead burning
-
or perform any of the following activities where lead-containing coatings or paint are present:
-
manual demolition of structures
-
manual scraping
-
manual sandingh
-
heat gun applications
-
power tool cleaning
-
river busting
-
welding
-
torch burning
-
abrasive blasting
-
cleanup activities where dry, expendable abrasives are used
-
abrasive blasting enclosure movement and removal
This fact sheet is intended to highlight the major aspects of the Lead in Construction Standard and is not to be interpreted as the complete requirements under the standards.
LEAD IN CONSTRUCTION
COMPLIANCE TABLE
The Federal Lead Exposure in Construction Standard, 29 CFR 1926.62, requires that before beginning any construction work that may result in lead exposure, an employer must determine if any employee may be exposed to lead at or above the action level (30 mg/m³). If any employee may be exposed at or above the action level, the employer must conduct air sampling at the start of the operation that may involve lead exposure. The major requirements of the Lead in Construction Standard are detailed below.
|
Any Airborne Lead
|
At or Above Action Level (30 µmg/m³)
|
Above PEL
(50 µg/m³)
|
|
|
X
X
|
X
X
X
X
|
X
X
X
X
|
CONDUCT EXPOSURE MONITORING
- at start of job
- every 6 months
- every quarter
- when job change may result in new or additional exposure
- if employee complains of symptoms related to lead exposure
Whenever exposure monitoring is performed, employee must be provided with written notice of results. |
|
|
|
X
|
USE FEASIBLE ENGINEERING AND WORK PRACTICE CONTROLS
|
|
|
|
X
|
DEVELOP WRITTEN COMPLIANCE PROGRAM AND REVIEW EVERY 6 MONTHS
|
|
|
|
X
X
X
X
X
|
PROVIDE RESPIRATORY PROTECTION
- as interim measure
- to supplement engineering and work practice controls
- when controls not feasible
- upon employee request
When respirators are provided, a respiratory protection program in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.134(b), (d), (e), and (f) must be established and fit testing must be conducted. A medical examination must be provided if an employee exhibits difficulty breathing during respirator fit test or use. An employer must provide a powdered air purifying respirator at the employee’s request. |
|
|
|
X
X
X
X
X
|
PROVIDE APPROPRIATE PROTECTING CLOTHING AND EQUIPMENT
- clean clothing weekly (daily if exposure above 200 µg/m³)
- ensure protective clothing removed at end of shift
- ensure appropriate laundering or disposal
- clean and repair equipment
Protective clothing and equipment must also be provided when the possibility of skin or eye irritation exists. |
|
|
|
X
X
X
X
|
MAINTAIN ALL SURFACES AS FREE OF LEAD AS POSSIBLE
- prohibit cleaning by compressed air
- use vacuuming or other equally effective cleaning methods
- use wet methods when vacuuming not feasible |
|
|
|
X
X
X
X
|
PROHIBIT EATING, DRINKING, AND SMOKING IN JOB AREA
- provide eating and drinking area
- ensure employees wash prior to eating or drinking
- ensure employees do not enter eating area in lead-contaminated clothing
|
|
X
X
|
X
X
|
X
X
X
X
X
|
PROVIDE CHANGE AREAS AND STORAGE
- ensure employees do not leave job area in contaminated clothes
PROVIDE WASH FACILITIES [29 CFR 1926.51(f)]
- be sure employees wash at end of shift
PROVIDE LAVATORY FACILITIES [29 CFR 1926.51(c)] |
|
|
X
X
X
X
|
X
X
X
X
|
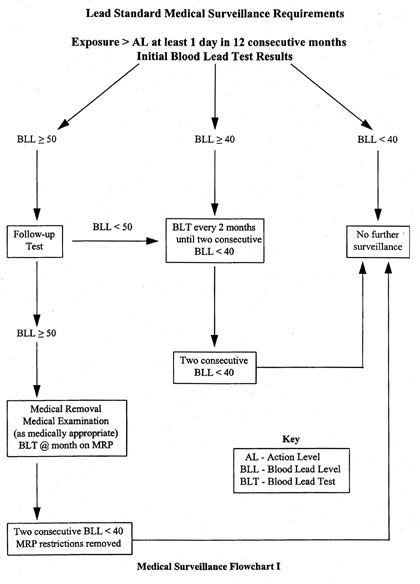
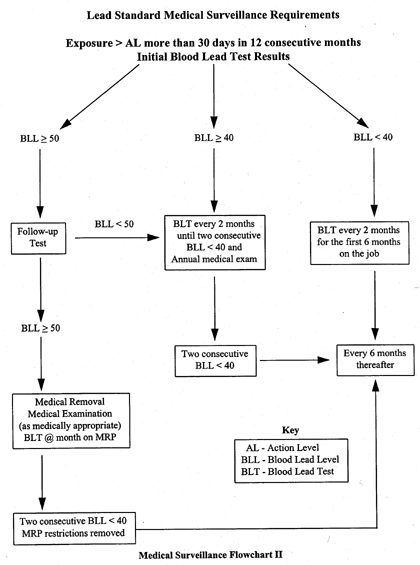
INSTITUTE MEDICAL SURVEILLANCE PROGRAM
Biological monitoring (Blood Lead + ZPP or FEP Levels)
- prior to assignment
- every 2 months for first 6 months of exposure
- written notification of results to employee
Medical examination must be provided when exposure is above action level and employee has developed signs or symptoms associated with lead intoxication, desires advice on effects of exposure on ability to procreate, or employee’s blood lead level is at or above 40 mg/100 g. A medical examination must also be provided when an employee exhibits difficulty breathing during respirator fit test or use. |
|
|
X
X
|
X
X
|
PROVIDE MEDICAL REMOVAL AND PROTECTION
- if blood lead level is at or above 50 mg/100 g
- if indicated by a final medical determination
|
|
X
X
|
X
X
|
X
X
|
INFORM EMPLOYEES OF STANDARD
- make available a copy of standard
|
|
|
X
|
X
|
PROVIDE TRAINING PROGRAM
Training must also be made available if the possibility of skin or eye irritation exists.
|
|
|
|
X
|
POST WARNING SIGNS
|
|
X
X
|
X
X
X
X
|
X
X
X
X
|
MAINTAIN RECORDS OF
- initial determination
- exposure monitoring
- medical surveillance
- medical removal |
This chart is intended to summarize the Federal Lead Exposure in Construction Standard, 29 CFR 1926.62, and is not to be interpreted as the complete requirements under the standard.
APPLICABLE PARAGRAPHS OF 1926.62
RELATED TO SPECIFIC AIR LEAD LEVELS
|
For Specific Air Lead Levels
|
During Assessment of Trigger Tasks
|
|
Regardless of Level
|
> AL
|
|
|
|
1-30 Days
|
> 30 Days
|
> PEL
|
> 4 X PEL
|
|
1926.62(d) - Exposure Assessment and Interim Protection
1926.62(h) - Housekeeping
1926.62(I)(5) - Handwashing Facilities
1926.62(l)(1)(i) - Hazcom Training (and/or 1926.21 - Safety Training and Education)
|
1926.62(d)(4) - Monitoring Representative of Exposure for Each Exposed Employee
1926.62(j)(1)(i) - Initial Medical Surveillance
1926.62(j)(2)(ii) - Follow-up Blood Sampling
1926.62(k) - Temporary Removal Due to Elevated Blood Lead
1926.62(l)(1)(ii) -(iv) - Information and Training
|
1926.62(j)(1)(ii) - Medical Surveillance Program
1926.62(j)(3) - Medical Exams and Consultation (if required)
|
1926.62(e) - Engineering and Work Practice Controls
1926.62(f) - Respiratory Protection
1926.62(g) - Protective Clothing and Equipment
1926.62(I) - Hygiene Facilities and Practices
1926.62(m) - Signs
|
1926.62(g)(2) - Clean Protective Clothing Daily
|
1926.62(f) - Appropriate Respiratory Protection
1926.62(g) - Protective Clothing and Equipment
1926.62(i)(2) - Change Areas
1926.62(I)(5) - Handwashing Facilities
1926.62(j)(1)(i) - Biological Monitoring
1926.62(l)(1)(i) - Hazcom Training
1926.62(l)(2)(iii) - Respirator Training
|
Previous | Main Table of Contents | Back to Appendices | Next
|
