Safety Evaluation of Profiled Thermoplastic Pavement Markings
Chapter 5. Development of SPFs
This chapter presents the SPFs developed for each State. The SPFs were used in the EB methodology to estimate the safety effectiveness of this strategy.(3) Generalized linear modeling was used to estimate model coefficients assuming a negative binomial error distribution, which is consistent with the state of research in developing these models. In specifying a negative binomial error structure, the overdispersion parameter, k, used in the EB calculations, was estimated iteratively from the model and the data. For a given dataset, smaller values of k indicate relatively better models. Estimates of k are provided, along with other model parameters.
SPFs were calibrated separately for Florida and South Carolina using the corresponding reference sites from each State. The SPFs developed are presented by State in the following sections.
Figure 8 presents the form of the SPFs for Florida, which are presented in table 6 for two-lane roads and in table 7 for multilane roads.
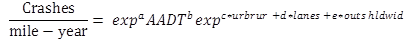
Figure 8. Equation. Form of SPFs for Florida.
Where:
AADT = Annual average daily traffic volume.
urbrur = Urban or rural indicator (1 if rural; 0 if urban).
lanes = Number of lanes indicator (1 if two-lane road; 0 if multilane road).
outshldwid = Total width of outside shoulder in ft.
a, b, c, d, e = Parameters estimated in the SPF calibration process.
Table 6. Parameter estimates and SEs for SPFs for Florida two-lane roads.
Crash Type |
a (SE) |
b (SE) |
c (SE) |
d (SE) |
e (SE) |
k (SE) |
Total |
−6.1605
(0.8484) |
0.7494
(0.0801) |
−0.2376
(0.1281) |
−0.7743
(0.3066) |
— |
0.9997
(0.0961) |
Injury |
−6.6533
(0.8948) |
0.7324
(0.0850) |
−0.2019
(0.1351) |
−0.7081
(0.3151) |
— |
0.8710
(0.1087) |
ROR |
−4.7588
(0.7815) |
0.3733
(0.0875) |
— |
— |
−0.0724
(0.0374) |
1.0195
(0.1496) |
Wet-road |
−7.8781
(0.8857) |
0.6753
(0.0998) |
— |
— |
−0.0983
(0.0478) |
0.7622
(0.1895) |
Nighttime |
−8.9148
(0.7447) |
0.8750
(0.0844) |
— |
— |
−0.0724
(0.0374) |
1.0195
(0.1496) |
Nighttime wet-road |
−9.5244
(1.4369) |
0.6709
(0.1647) |
— |
— |
— |
1.5210
(0.6474) |
For the head-on crash type, the total crash SPFs were used with a multiplier of 2.5 percent.
k is the estimated overdispersion parameter of the SPF.
— Indicates the variable associated with this parameter was not included in the SPF. |
Table 7. Parameter estimates and SEs for SPFs for Florida multilane roads.
Crash Type |
a (SE) |
b (SE) |
c (SE) |
d (SE) |
e (SE) |
k (SE) |
Total |
−10.4061
(0.4791) |
1.1516
(0.0493) |
— |
— |
— |
0.9346
(0.0564) |
Injury |
−10.0352
(0.5059) |
1.0494
(0.0518) |
— |
— |
— |
0.8486
(0.0613) |
ROR |
−6.6828
(0.6114) |
0.5621
(0.0626) |
— |
— |
— |
1.0824
(0.1165) |
Wet-road |
−13.1037
(0.7157) |
1.2323
(0.0724) |
— |
— |
— |
1.0926
(0.1116) |
Nighttime |
−10.1507
(0.5544) |
0.9945
(0.0566) |
— |
— |
— |
0.7552
(0.0677) |
Nighttime wet-road |
−12.8712
(0.9752) |
1.0912
(0.0982) |
— |
— |
— |
1.1884
(0.2054) |
For the head-on crash type, the total crash SPF was used with a multiplier of 1.5 percent.
k is the estimated overdispersion parameter of the SPF.
— Indicates the variable associated with this parameter was not included in the SPF. |
The form of the SPFs for South Carolina, which are presented in table 8 and table 9, is shown in figure 9.
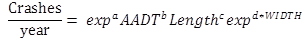
Figure 9. Equation. Form of SPFs for South Carolina.
Where:
Length = segment length in mi.
WIDTH = total lane width in ft.
Table 8. Parameter estimates and SEs for SPFs for South Carolina two-lane roads.
Crash Type |
a (SE) |
b (SE) |
c (SE) |
d (SE) |
k (SE) |
Total |
−4.6715
(1.0491) |
0.8865
(0.1326) |
0.6618
(0.0754) |
−0.0902
(0.0310) |
0.5065
(0.1121) |
Injury |
−4.1584
(1.1961) |
0.7081
(0.1483) |
0.7489
(0.0870) |
−0.0968
(0.0418) |
0.4419
(0.1385) |
ROR |
−2.4670
(1.1849) |
0.5305
(0.1474) |
0.8336
(0.0904) |
−0.1153
(0.0463) |
0.3736
(0.1187) |
Head-on + sideswipe-opposite-direction |
−8.5087
(1.7023) |
0.7328
(0.2087) |
0.9831
(0.1650) |
— |
0.3830
(0.3248) |
Sideswipe-same-direction |
−10.6206
(2.3048) |
0.9467
(0.2800) |
0.5159
(0.1520) |
— |
0.5231
(0.4623) |
Wet-road |
−5.7593
(1.1402) |
0.8714
(0.1348) |
0.7403
(0.0892) |
−0.1146
(0.0453) |
0.1601
(0.0917) |
Nighttime |
−4.3691
(1.0210) |
0.6535
(0.1248) |
0.7327
(0.0764) |
−0.0660
(0.0335) |
0.2625
(0.0916) |
For the nighttime wet-road crash type, the total crash SPF was used with a multiplier of 8 percent.
k is the estimated overdispersion parameter of the SPF.
— Indicates the variable associated with this parameter was not included in the SPF. |
Table 9. Parameter estimates and SEs for SPFs for South Carolina multilane roads.
Crash Type |
a (SE) |
b (SE) |
c (SE) |
d (SE) |
k (SE) |
Total |
−18.2646
(1.4823) |
2.0712
(0.1578) |
0.7742
(0.0717) |
— |
0.2524
(0.0884) |
Injury |
−15.7429
(1.5549) |
1.6966
(0.1635) |
0.7458
(0.0758) |
— |
0.5953
(0.2394) |
ROR |
−6.0470
(3.0778) |
0.5845
(0.3276) |
1.0229
(0.1434) |
— |
0.5953
(0.2394) |
Head-on + sideswipe-same-direction |
−20.5081
(3.3853) |
1.9528
(0.3442) |
0.8685
(0.1508) |
— |
0.1024
(0.1716) |
Sideswipe-same-direction |
−17.9590
(2.0064) |
1.8196
(0.2068) |
0.8101
(0.0943) |
— |
0.1228
(0.1131) |
Wet-road |
−18.8293
(2.1940) |
1.9640
(0.2296) |
0.7955
(0.1072) |
— |
0.3254
(0.1529) |
Nighttime |
−17.4415
(1.6741) |
1.8433
(0.1750) |
0.8167
(0.0824) |
— |
0.1581
(0.0786) |
For the nighttime wet-road crash type, the total crash SPF was used with a multiplier of 8 percent.
k is the estimated overdispersion parameter of the SPF.
— Indicates the variable associated with this parameter was not included in the SPF. |