Lesson 8: Pedestrian Characteristics

Lesson Outline
- Pedestrian age groups.
- Pedestrians with special needs.
- Walking speeds.
- Spatial needs.
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) design issues.
Pedestrian Age Groups
- Infants and toddlers (ages 0 to 4).
- Young children (ages 5 to 12).
- Preteens (ages 13 to 14).
- High school aged (ages 15 to 18).
- Adults (ages 19 to 40).
- Middle–aged adults (ages 41 to 65).
- Senior adults (age 65+).
Infants and Toddlers
- Just learning to walk.
- Developing peripheral vision and depth perception.
- Acting impulsively and unpredictably.
|  |
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Young Children
- Are impulsive and unpredictable.
- Have limited peripheral vision.
- Lack experience/training.
- Are short and hard for drivers to see.
- Are susceptible to darting or dashing into intersections.
|  |
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Preteens
- Lack experience.
- Walk and bicycle more.
- Ride more frequently under risky conditions.
- Get involved in more intersection dash collisions.
- Have a sense of invulnerability.
|  |
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
High School Aged
- Are very active.
- Feel invincible.
- Are capable of traveling at higher speeds.
- Attempt to use bicycles, skates, etc., based on practices carried over from youth.
|  |
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Adults
- Are active and fully aware of the traffic environment.
- Comprise only 1–4 percent of bicycling population in most communities.
- Tend to be very vocal and interested in improving conditions.
- Are interested in serving as instructors or task force leaders.
|  |
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Middle–Aged Adults
- Are still active.
- May experience a slowing of reflexes, range of motion, and observational skills.
|  |
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Senior Adults
- Walk more for exercise/independence.
- Experience a reduction in vision, agility, balance, speed, concentration, and strength.
- Have difficulty hearing vehicles approaching from behind.
- Have reduced abilities under low light/night conditions.
|  |
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Pedestrians with Different Needs
- Children.
- Seniors.
- Mobility–impaired.
| 
|
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Walking Speeds
| Pedestrian Type | Mean Walking Speed, ft/s |
|---|
| Average adult | 4.00 |
| Wheelchair user | 3.55 |
| Pedestrian with immobilized knee | 3.50 |
| Older/senior adult | 2.80 |
| Cane or crutch user | 2.62 |
| Below–knee amputee | 2.46 |
| Pedestrian with knee arthritis | 2.46 |
| Pedestrian with hip arthritis | 2.24 to 3.66 |
| Pedestrian with walker | 2.07 |
| Above–knee amputee | 1.97 |
| 4.0 feet per second (ft/s) = 1.2 meters per second (m/s)
|
Spatial Needs
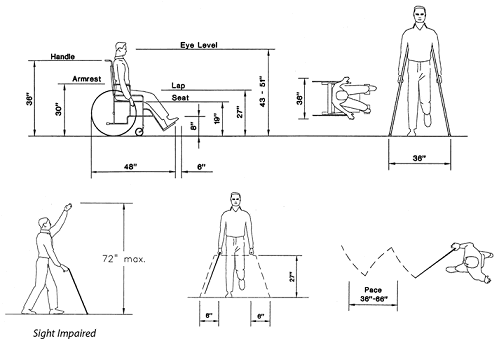
| 1 inch = 2.54 centimeter | |
Source: Pedestrian Facilities Guidebook |
| Source: ADAAG, http://www.access–board.gov/adaag/html/adaag.htm |
Accessible Design Issues
- Sidewalks.
- Ramps.
- Street furniture.
- Pushbuttons.
- Curb cuts/wheelchair ramps.
Sidewalks
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Ramps
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Street Furniture
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Pushbuttons
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
Curb Cuts/Wheelchair Ramps
| Source: PBIC, www.pedbikeimages.org |
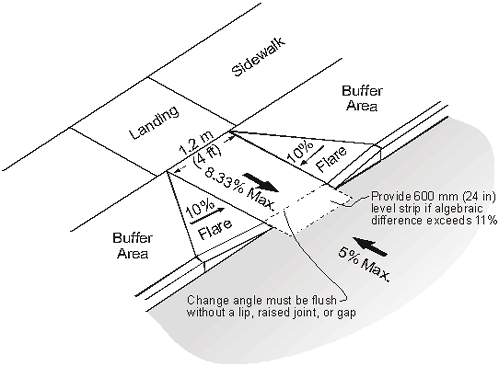
Curb Ramp Slopes
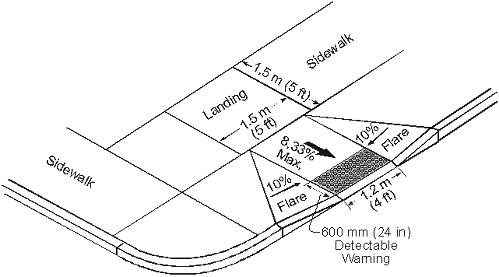
Slope and Counter Slope
Lesson Summary
- Pedestrians can have many different needs and abilities.
- Accessible design will allow ALL pedestrians to more easily and safely navigate the system.
FHWA-HRT-05-100
|
