Lab & Field Testing of AUT Systems for Steel Highway Bridges
6. RESULTS
Laboratory evaluation and field testing of the P-scan system in parallel with both RT and
manual UT was performed on 10 laboratory specimens and 46 field specimens. The
results produced from this testing illustrate the potential benefits of
implementing AUT.
LABORATORY RESULTS TC "LABORATORY RESULTS"
The results of
the laboratory evaluation are summarized in table 6. The first column of table
6 indicates the specimen identification code. The second, third, and fourth
columns indicate the inspection method performed on each specimen. "Rejected" or "Accepted" indicates that the specimen was either rejected or accepted,
respectively, by the employed inspection method. "Ind." stands for indication, and the angle (q)
indicates the transducer's refracted angle. The indication characteristics in
the fourth column (i.e., indication rating (d), length (L), depth (Z), x-position,
and y-position) are obtained from P-scan images. These characteristics are
compared with the UT acceptance-rejection criteria in tables 6.3 and 6.4 from
the AASHTO/AWS D1.5M/D1.5: 2002 Bridge Welding Code(1) to determine whether
the indication should be accepted or rejected.
The category 1
laboratory specimens were rejected by all three inspection methods (table 6). Figure 10 shows the radiographic image of laboratory specimen S033. Figure 12 shows
the P-scan images of the toe and root cracks in specimen S033. The radiographic
image provides the spatial dimensions of the defects (i.e., length and
position), while the P-scan images provide three-dimensional information
(including length, depth, and global position). Specimen S034 (figure 33)
contained two manufactured cracks. This 12.7-mm- (0.5-inch-) thick plate
contains a longitudinal crack in the weld (figure 34) and a transverse crack in
the weld (figure 35). Both cracks were detected by RT and manual UT. Figure 36
shows the radiographic image of specimen S034. The two cracks can be seen
clearly. The transverse crack in specimen S034 was detected by manual UT when
the weld was inspected in the transverse direction. The P-scan system detected
only the longitudinal/centerline crack in specimen S034 (figures 37 and 38).
The photographs, radiographic images, and P-scan images of the remaining
laboratory specimens that contained rejectable defects are shown in figures 39
through 71.
The results
provided in table 6 showed that the indication rating (d) given by the P-scan system
varied from the conventional UT rating in some cases. This variance may be
caused by one of the following parameters:
-
High sensitivity of P-scan system.
-
Manual versus computer determination of spatial
characteristics of defects (including sound path and time of flight).
-
Attenuation.
-
Slightly varying scanning patterns.
-
Table 6. Inspection results of laboratory specimens.
|
Specimen ID |
RT |
Manual UT |
AUT |
S033 |
Rejected
Ind. 1: Toe Crack
Ind. 2: Root Crack |
Rejected
Ind. 1: Toe Crack
Ind. 2: Root Crack
|
Rejected
Ind.1: Toe Crack
d = -3 dB
L = 2.45", Z = 0"
X = +0.13", Y = 0.57"
Ind. 2: Root Crack
d = -4 dB
L = 1.03", Z = 0.44"
X = -0.19", Y = 8.39"
|
S034 |
Rejected
Ind. 1: Centerline Crack
Ind. 2: Transverse Crack |
Rejected
Ind. 1: Centerline Crack
Ind. 2: Transverse Crack |
Rejected*
Ind. 1: Centerline Crack
d = 0 dB
L = 1.37", Z = 0.02"
X = +0.07", Y = 3.94" |
*AUT is not configured to
detect transverse cracks.
1
inch = 25.4 mm
Table 6. Inspection results of laboratory specimens (continued).
Specimen ID |
RT |
Manual UT |
AUT |
S125 |
Rejected |
Rejected
Ind. 1:  = 70° = 70°
d = -1 dB
L = 0.38", Z = 0.63"
X = -0.38", Y = 2.25"
Ind. 2:  = 70° = 70°
d = +6 dB
L = 0.50", Z = 0.50"
X = 0", Y = 7.50"
Ind. 3:  = 70° = 70°
d = +7 dB
L = 0.25", Z = 0.33"
X = 0", Y = 13.38" |
Rejected
Ind. 1:  = 70° = 70°
d = +3 dB
L = 0.55", Z = 0.65"
X = -0.34", Y = 2.29"
Ind. 2:  = 70° = 70°
d = +6 dB
L = 0.47", Z = 0.35"
X = +0.053", Y = 7.81"
Ind. 3:  = 70° = 70°
d = +8 dB
L = 0.23", Z = 0.39"
X = +0.09", Y = 13.32" |
S126 |
Rejected |
Rejected
Ind. 1:  = 70° = 70°
d = -2 dB
L = 1.25", Z = 0.82"
X = -0.25", Y = 2.5"
Ind. 2:  = 70° = 70°
d = +5 dB
L = 0.63", Z = 0.69"
X = +0.25", Y = 6.88"
Ind. 3:  = 70° = 70°
d = +11 dB
L = 0.50", Z = 0.25"
X = -0.38", Y = 8.63"
Ind. 4:  = 70° = 70°
d = -2 dB
L = 0.50", Z = 0.88"
X = -0.13", Y = 11.25" |
Rejected
Ind. 1:  = 70° = 70°
d = -6 dB
L = 1.51", Z = 0.67"
X = -0.25", Y = 2.46"
Ind. 2:  = 70° = 70°
d = +7 dB
L = 0.87", Z = 0.47"
X = +0.09", Y = 6.85"
Ind. 3:  = 70° = 70°
d = +4 dB
L = 0.55", Z = 0.33"
X = -0.15", Y = 8.84"
Ind. 4:  = 70° = 70°
d = -5 dB
L = 1.17", Z = 0.91"
X = +0.04", Y = 11.23" |
S131 |
Accepted |
Accepted |
Accepted |
S132 |
Rejected |
Rejected
Ind. 1:  = 70° = 70°
d = +9 dB
L = 12", Z = 1.00"
X = +0.56", Y = 0" |
Rejected*
Ind. 1A: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +8 dB
L = 0.60", Z = 1.0"
X = +0.52", Y = 0"
Ind. 1B: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +9 dB
L = 1.2", Z = 0.72"
X = +0.53", Y = 2.6"
Ind. 1C: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +7 dB
L = 0.48", Z = 0.72"
X = +0.48", Y = 4.52"
Ind. 1D: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +5 dB
L = 0.56", Z = 0.86"
X = +0.50", Y = 5.88"
Ind. 1E:  = 70° = 70°
d = +9 dB
L = 1.1", Z = 1.49"
X = +0.25", Y = 9.10"
Ind. 1F: TSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +5 dB
L = 7", Z = 0.133"
X = +0.44", Y = 0"
Ind. 1G: TSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +4 dB
L = 0.80", Z = 0"
X = +0.42", Y = 7.0"
Ind. 1H: TSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +4 dB
L = 0.95", Z = 0.36"
X = +0.42", Y = 8.93" |
S133 |
Rejected |
Rejected
Ind. 1:  = 70° = 70°
d = +8 dB
L = 5.75", Z = 0.94"
X = -0.56", Y = 0" |
Rejected*
Ind. 1A:  = 70° = 70°
d = 0 dB
L = 0.28", Z = 0.21"
X = +0.39", Y = 0"
Ind. 1B:  = 70° = 70°
d = +6 dB
L = 1.28", Z = 0.29"
X = +0.32", Y = 2.77"
Ind. 1C:  = 70° = 70°
d = +6 dB
L = 0.88", Z = 0.21"
X = +0.32", Y = 4.28" |
S134 |
Accepted |
Accepted |
Accepted |
S135 |
Rejected |
Rejected
Ind. 1:  = 70° = 70°
d = -2 dB
L = 2.25", Z = 0.38"
X = +0.13", Y = 3.50"
Ind. 2:  = 70° = 70°
d = +9 dB
L = 2.38", Z = 0.19"
X = +0.25", Y = 8.13"
Ind. 3:  = 70° = 70°
d = +1 dB
L = 1.25", Z = 0.56"
X = +0.25", Y = 11.75" |
Rejected*
Ind. 1A: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +6 dB
L = 1.76", Z = 0.47"
X = +0.09", Y = 3.72"
Ind. 1B: TSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = -11 dB
L = 0.72", Z = 0.39"
X = +0.09", Y = 4.44"
Ind. 2A: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +1 dB
L = 0.79", Z = 0.35"
X = -0.35", Y = 9.57"
Ind. 2B: TSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +2 dB
L = 1.07", Z = 0.30"
X = -0.05", Y = 9.95"
Ind. 3A: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = 0 dB
L = 1.13", Z = 0.65"
X = +0.30", Y = 12.20"
Ind. 3B: TSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = -4 dB
L = 0.89", Z = 0.50"
X = +0.42", Y = 12.27" |
S136 |
Rejected |
Rejected
Ind. 1:  = 70° = 70°
d = +2 dB
L = 2.0", Z = 0.38"
X = +0.13", Y = 2.0"
Ind. 2:  = 70° = 70°
d = +6 dB
L = 2.38", Z = 0.25"
X = 0", Y = 9.5" |
Rejected*
Ind. 1A: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = -7 dB
L = 0.96", Z = 0.30"
X = +0.96", Y = 2.21"
Ind. 1B: TSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = -4 dB
L = 1.12", Z = 0.35"
X = -0.45", Y = 2.61"
Ind. 2A: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = -2 dB
L = 0.641", Z = 0.73"
X = -0.65", Y = 9.16" Ind. 2B: BSC,  = 70° = 70°
d = +3 dB
L = 1.23", Z = 0.13"
X = -0.65", Y = 10.53" |
*Under the provisions of table
6.3 in the AASHTO/AWS D1.5: 2002 Bridge Welding Code (i.e., class B and class C
flaws shall be separated by at least 2L), Ind. 1A, Ind. 1B, ... are considered as
a single defect, Ind. 2A, Ind. 2B, ... are considered as a single
defect, etc.
1 inch = 25.4 mm
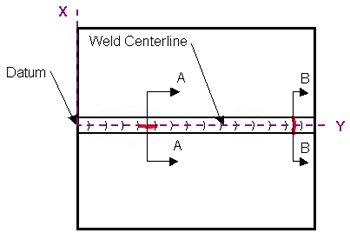
Figure
33. Laboratory specimen S034: Schematic
diagram showing two implanted cracks.
|
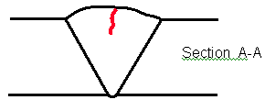
Figure
34. Laboratory specimen S034:
Schematic diagram of longitudinal/centerline crack.
|
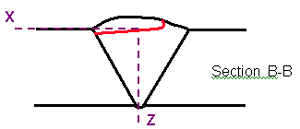
Figure 35. Laboratory specimen S034: Schematic diagram of transverse crack.
|
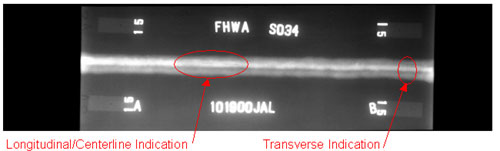
Figure 36. Laboratory specimen S034: Radiographic image showing the two implanted cracks.
|

Figure 37. Laboratory specimen S034: Top view of
joint.
|
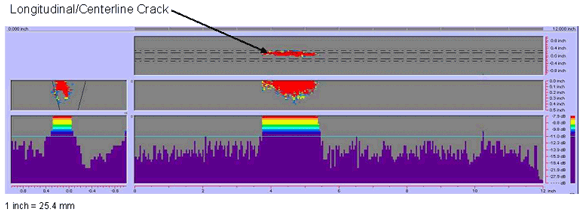
Figure 38. P-scan images of laboratory specimen S034: Images of longitudinal/centerline indication in the weld.
|
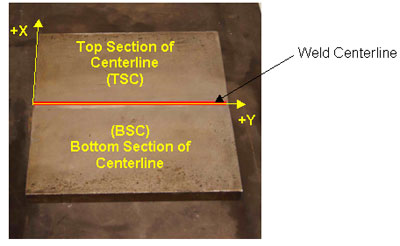
Figure 39. Laboratory specimen S125: Top view of joint.
|
|
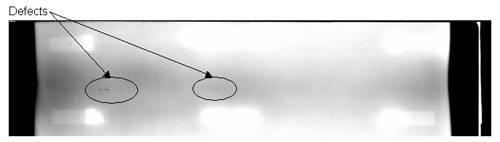
Figure 40. Laboratory specimen S125: Radiographic image showing discontinuities in the weld.
|
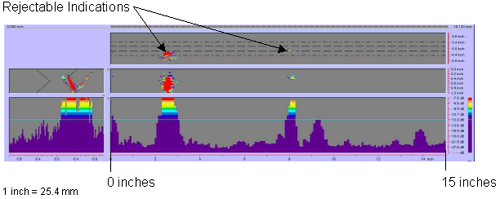 |
| Figure 41. P-scan images of laboratory specimen S125: From TSC side of centerline. |
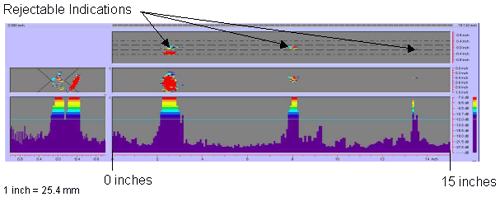
Figure 42. P-scan images of laboratory specimen S125: From BSC side of centerline.
|
|

Figure 43. Laboratory specimen S126: Top view of joint.
|
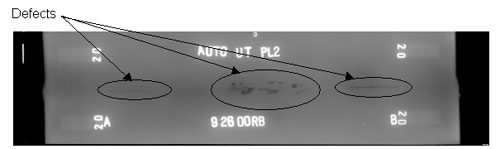
Figure 44. Laboratory specimen S126: Radiographic image showing discontinuities in the weld.
|
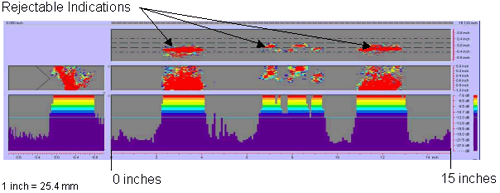
Figure 45. P-scan images of laboratory specimen S126: From TSC side of centerline.
|
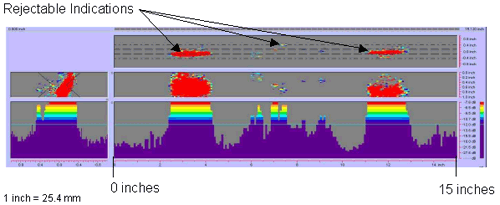
Figure 46. P-scan images of laboratory specimen S126: From BSC side of centerline. |

Figure 47. Laboratory specimen S132: View of joint.
|

Figure 48. Laboratory specimen S132: Radiographic image showing discontinuities in the weld.
|
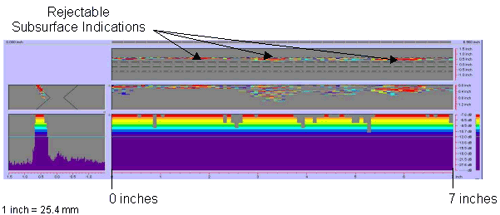
Figure 49. P-scan images of laboratory
specimen S132: From TSC side of centerline
between 0 and 177.8 mm (0 and 7 inches).
|
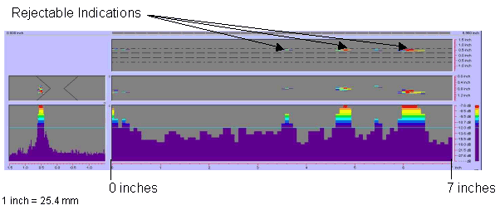
Figure
50. P-scan images of laboratory
specimen S132: From BSC side of centerline between 0 and 177.8 mm (0 and 7
inches).
|
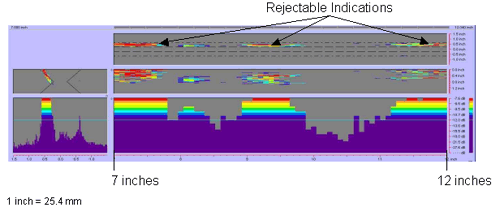
Figure
51. P-scan images of laboratory
specimen S132: From TSC side of centerline between 177.8 and 304.8 mm (7
and 12 inches).
|
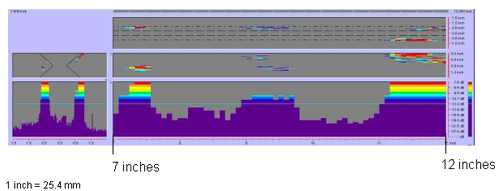
Figure 52. P-scan images of laboratory specimen S132: From BSC side of centerline between 177.8 and 304.8 mm (7 and 12 inches).
|

Figure 53. Laboratory specimen S133: Top view of joint.
|
 Figure 54. Laboratory specimen S133: Radiographic image showing discontinuities in the weld. Figure 54. Laboratory specimen S133: Radiographic image showing discontinuities in the weld. |
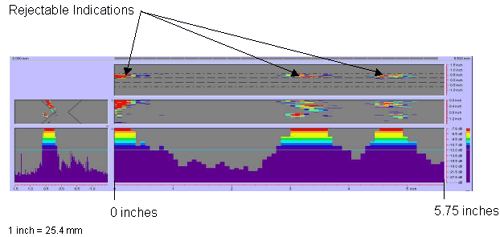
Figure 55. P-scan images of laboratory specimen S133. |

Figure 56. Laboratory specimen S135: Side view of joint.
|

Figure 57. Laboratory specimen S135: Top view of joint. |
|
