U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Federal Highway Administration Research and Technology
Coordinating, Developing, and Delivering Highway Transportation Innovations
| FACT SHEET |
| This fact sheet is an archived publication and may contain dated technical, contact, and link information |
| Publication Number: FHWA-HRT-18-014 Date: December 2017 |
Publication Number: FHWA-HRT-18-014 Date: December 2017 |
PDF Version (236 KB)
PDF files can be viewed with the Acrobat® Reader®
This fact sheet describes the open source software platform—FHWA Driver Model Platform v0.6—developed for modeling and analyzing specialized driver behaviors in microsimulation software packages.
The FHWA Driver Model Platform v0.6 was created to interface with commercially available microsimulation software packages, so that planners and engineers could more accurately predict and assess the operational impacts of specialized events and technologies—such as work zones, road weather, or connected and automated vehicle applications. Version 0.6 is a beta release, and is available through the Open Source Application Development Portal (OSADP).1 It includes the FHWA Work Zone Driver Model (version 1.1).2
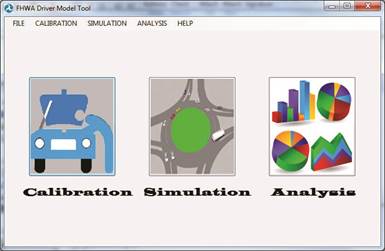
Figure 1. Home Screen – FHWA Driver Model Platform v0.6 (source: FHWA).
Certain scenarios, events, and technologies elicit unique driver behaviors with significant operational impacts. These events alter driver behavior on a per-vehicle level, therefore microsimulation is well-suited to predict their impacts.
Unfortunately, current microsimulation packages do not feature specialized algorithms to accurately reflect the unique driver behavior observable for each scenario. This limits the ability of planners and engineers to predict their impacts. Specialized algorithms in the Driver Model Platform consider the effects of the following:
Even with accurate microscopic models, planners and engineers need streamlined and useful methods for analyzing microscopic model output. FWHA provided recommendations on analytical methods in the Traffic Analysis Toolbox.4 It would be beneficial, however, to automate these methods and incorporate them into a single, user-friendly platform for microsimulation.
The FHWA Driver Model Platform was created as a single, consolidated repository for specialized microscopic models. It also includes tools that assist users in model calibration, in-simulation diagnostics (coming soon), and post-simulation analytics.
Version 0.6 will be available through the OSADP in January 2018.1 New releases are expected annually through 2021; user feedback is welcomed to guide and improve future releases.
Version 0.6 interfaces with PTV’s VISSIM (v7.0 and newer), and future versions will be interfaced with other microsimulation packages (such as AIMSUN, TrafficModeler, or SUMO). The FHWA Driver Model Platform is published open-source under the Apache License, v2.0 to enable third party developers to integrate the software into additional microscopic modeling platforms.
The Calibration section of the FHWA Driver Model Platform houses specialized driver models developed by FHWA and third party developers. It includes information about each model (algorithm description document) and interfaces for model recalibration. Future releases will include data processing tools that assist with calibration and models for CAV applications. This release (v0.6) features the FHWA Work Zone Model v1.1.2
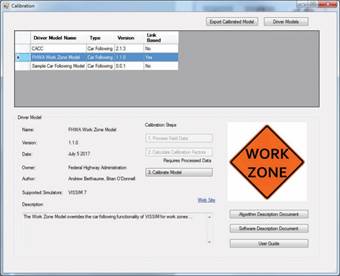
Figure 2. The Calibration section of the FHWA Driver Model Platform v0.6. (source: FHWA).
Future releases of the FHWA Driver Model Platform will also contain tools that analyze microsimulation model output using standardized methods. These tools produce data and graphs that practitioners can use to validate network performance and assess operations on a network level, link/lane level, and even trajectory level.
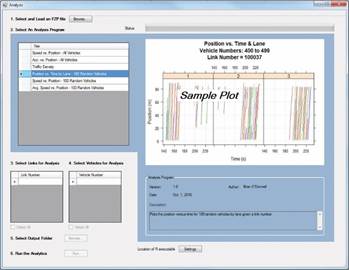
Figure 3. The Analysis section of the FHWA Driver Model Platform v0.6 (source: FHWA).
For more information, please contact:
Andrew.Berthaume@dot.gov.
FHWA-HRT-18-014
HRDO-20/12-2017(200)E