Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Bridges and Structures
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a set of technologies and processes used to create a 3-dimentional virtual model of a project. This 3-D virtual model contains all project information that may be from more than one source. The information from that 3-D virtual model can be shared, used, reused, and exchanged among stakeholders of the project.
The application of BIM in infrastructure projects is growing both nationally and internationally, based on information from a pooled fund initiative. As BIM matures with voluntary and non-binding Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) data schema and exchange file format being established, the bridge design and construction industry is recognizing the benefits of digital bridge project delivery. Bridge owners are interested in those benefits as well including reduction in both initial cost of construction and the whole life cycle cost of bridges; reduction in the overall time from planning and preliminary design to completion for new construction followed by inspection and maintenance of bridges; and increase of return on investment of BIM in infrastructure.
FHWA Resources
FHWA Efforts in Advancing BIM for Bridges and Structures
- AASHTO BIM Roadmap for Bridges and Structures shows FHWA efforts
- Bridge Data File Protocols for Interoperability and Life Cycle Management: Volume I, Volume II, and Volume III, FHWA-HIF-16-003, 2013
- Bridge Information Modeling (BrIM) Using Open Parametric Objects, FHWA-HIF-16-010, 2015
- Bridge Information Modeling Standardization: Introduction, Volume 1, Volume 2, and Volume 3, FHWA-HIF-16-011, 2016
- IFC Bridge Design to Construction Exchange (U.S.) was developed under contract to FHWA by National Institute of Building Sciences, 2016
- The FHWA is one of the sponsor organizations of the Transportation Pooled Fund (TPF) Program – BIM for Bridges and Structures TPF-5(372)
- Demonstration of Bridge Project Delivery Using BIM, FHWA-HIF-21-031, 2021
FHWA Ongoing Research
- BIM for Bridges and Roadways – Project Delivery Workflow and National Library
- Objectives:
- Study the opportunities and obstacles in transition to BIM-based workflows for delivery of highway bridges and roadway projects
- Develop suggestions to support ongoing BIM initiatives of FHWA and AASHTO
- Develop a framework and process for creating and maintaining a possible National BIM Transportation Library (NBTL)
- Objectives:
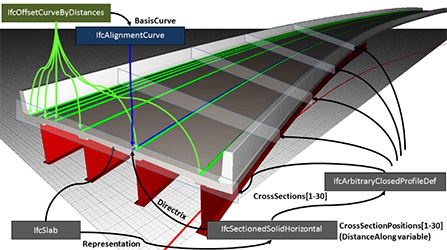
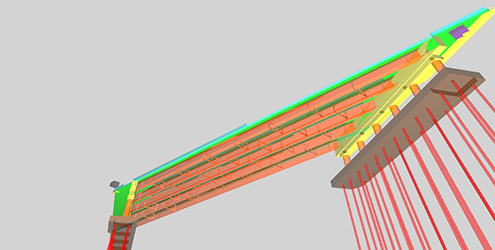
External Resources
- Transportation Pooled Fund Program
- National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP)
- NCHRP Report 576 – TransXML: XML Schemas for Exchange of Transportation Data, 2007
- NCHRP 20-07/Task 377 Updates 2013 Roadmap – Standardized Format for Bridge and Structure Information Models, 2016
- Other Resources

