This assessment and evaluation sought to take a wide-angle view of the TMIP Peer Review Program. A great deal can be learned about the peer review program by simply looking back at what the program has achieved so far. This section of the report provides a historical glimpse of the program by categorizing the peer reviews conducted since the program's inauguration based on the following:
Since 2003, twenty-eight peer reviews have been conducted.
Table 1 below identifies the peer reviews conducted from 2003 to 2011. The table notes which reviews have been included in a previous synthesis and/or evaluated in past FHWA sponsored reports.
Table 1 also illustrates that twelve new peer reviews have been convened between 2008 and 2011 that have not yet been included in a synthesis report. This assessment and evaluation will not summarize these new peer reviews in the same manner as previous synthesis report efforts. The reader is encouraged to review the final reports from each of those agency peer reviews for specific details regarding those individual meetings. In contrast, this assessment will examine all twenty-eight peer reviews, the results of the program in totality, to identify common trends, themes, and challenges.
| City | State | Agency | Year | Synthesis & Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Louisville | Kentucky | OKI | 2003 | 2004_Volpe |
| Anchorage | Alaska | AMATS | 2004 | 2004_Volpe |
| Atlanta | Georgia | ARC | 2004 | 2004_Volpe |
| Iowa | IaDOT | 2004 | 2004_Volpe | |
| North Carolina | NCDOT | 2004 | 2004_Volpe | |
| Denver | Colorado | DRCOG | 2003, 2004 | 2004_Volpe, 2009_Volpe |
| Los Angeles | California | SCAG | 2003, 2004, 2006 | 2004_Volpe, 2009_Volpe |
| San Francisco | California | MTC | 2004 | 2005_TTI |
| Colorado Springs | Colorado | PPACG | 2005 | 2005_TTI |
| Memphis | Tennessee | MATA | 2004, 2006 | 2005_TTI |
| Detroit | Michigan | SEMCOG | 2004 | 2005_TTI, 2009_Volpe |
| Baltimore | Maryland | BMC | 2004, 2005 | 2005_TTI, 2009_Volpe |
| Newark | New Jersey | NJTPA | 2005 | 2009_Volpe |
| San Diego | California | SANDAG | 2005 | 2009_Volpe |
| St. Louis | Missouri | EWGCG | 2006 | 2009_Volpe |
| Boise | Idaho | COMPASS | 2007 | 2009_Volpe |
| Logan | Utah | CMPO | 2008 | not synthesized |
| Davenport | Iowa | BRC | 2008 | not synthesized |
| St. George | Utah | DMPO | 2008 | not synthesized |
| Dubuque | Iowa | ECIA | 2008 | not synthesized |
| Sacramento | California | SACOG | 2008 | not synthesized |
| Austin | Texas | CAMPO | 2009 | not synthesized |
| Philadelphia | Pennsylvania | DVRPC | 2009 | not synthesized |
| Omaha | Nebraska | MAPA | 2010 | not synthesized |
| Burlington | Vermont | CCMPO | 2011 | not synthesized |
| Chattanooga | Tennessee | CHCNGA-TPO | 2011 | not synthesized |
| Monterey | California | AMBAG | 2011 | not synthesized |
| New York | New York | NYMTC | 2011 | not synthesized |
The number of peer reviews conducted each year has varied considerably. In 2004 for example, ten peer reviews were conducted, while only one peer review was conducted in 2007 and 2010 respectively. The variability by year is a function of host agency interest in the program, timing of application submittals, and scheduling, as opposed to program resource constraints. Since the program began there have been approximately three to four peer reviews per year on average. Figure 1 presents the number of peer reviews conducted during each calendar year.
Figure 1 TMIP Peer Reviews by Calendar Year
TMIP peer reviews have thus far been performed in nineteen states across the country, for two State Departments of Transportation (NCDOT, IaDOT) and twenty-six different Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPOs). There are approximately 385 MPOs in the United States, so there are certainly opportunities to hold many more additional reviews. Some notable regions where peer reviews have not yet been requested include the Pacific Northwest (Portland, Seattle), parts of Texas (Dallas, Houston), the Gulf Coast and Florida, the northern Midwest, as well as portions of the Southwest (Arizona, New Mexico, Nevada). Where reviews have been conducted is of course a function of host agency interest and not determined by TMIP staff. Figure 2 illustrates the agencies that have participated in TMIP peer reviews since 2003.
Figure 2 TMIP Peer Reviews by Geography
The twenty-eight peer reviews conducted since 2003 utilized eighty-seven different panelists from a variety of backgrounds. The eighty-seven panel members included representatives from MPOs, State DOTs, private consulting firms, educational institutions (colleges/universities), federal government officials (FHWA, FTA), and other groups including environmental advocacy groups. Overall, the program has experienced very good participation and representation on the peer review panels among practitioners from different industry sectors (federal, state, local, private, and academic). Figure 3 illustrates the breakdown of panel representatives by affiliation type.
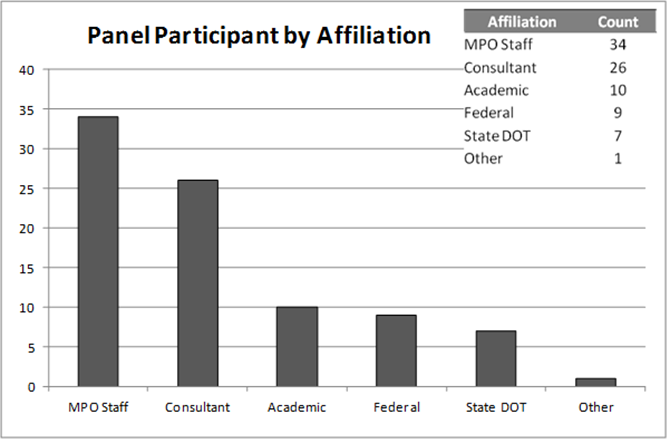
Figure 3 TMIP Peer Reviews by Panel Participant Affiliation
Because peer review panels are often comprised of nationally recognized practitioners and researchers in the industry, a number of individuals have participated in multiple peer reviews. Eighty-seven different individuals have participated in the twenty-eight peer reviews to date. Figure 4 illustrates panel participation among individuals who have participated in two or more peer reviews. Fifty-one individuals have only participated in a single peer review (not shown in Figure 4). Seventeen individuals have participated in two peer reviews, and nineteen individuals have participated in three or more peer reviews.
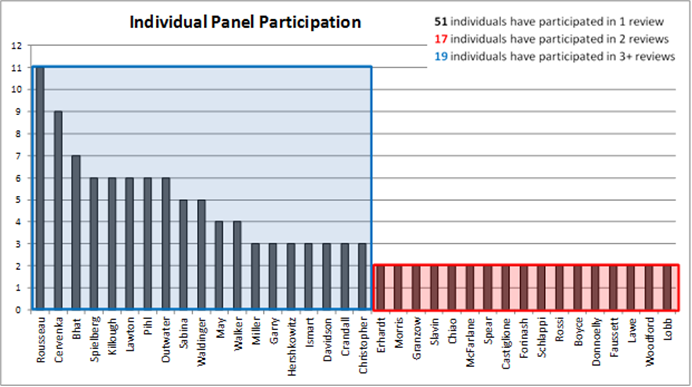
Figure 4 TMIP Peer Reviews by Panel Participant Affiliation
TMIP peer reviews have been convened in some of the largest metropolitan areas in the country (e.g. New York City, Los Angeles), as well as some relatively small planning areas such as Dubuque, Iowa and Logan, Utah. Over the eight-year period during which TMIP peer reviews have been conducted there's been an almost equal distribution of reviews across agencies of differing sizes (large, medium, small).
For this assessment and evaluation, the population ranges used to classify the size of the agency is somewhat subjective. The population ranges do however produce logical breakpoints when all the reviews are considered together. Table 2 below illustrates the population ranges used to determine agency size and the number of reviews performed. Figure 5 plots the host agency population and illustrates the large-size, medium-size, and small-size agency breakpoints. These same large, medium, and small agency size classifications are utilized throughout the remainder of this report. Figure 6 presents a zoomed-in look at the host agency population within each agency size category.
| Agency Size | Population Range | #of Reviews |
|---|---|---|
| Large | >3 million | 10 |
| Medium | 750,000-3 million | 9 |
| Small | <750,000 | 9 |
Figure 5 TMIP Peer Reviews by Agency Size
Figure 6 TMIP Peer Reviews by Agency Size Category (Large, Medium, Small)
Each TMIP peer review is unique in that the host agency has the freedom and flexibility to frame the meeting in many different ways. The goal is to develop a peer review meeting agenda and schedule that supports a discussion of the issues, challenges, and questions faced by the host agency and their own particular travel modeling needs. Nonetheless, there are some common stated reasons for why agencies express interest in and subsequently participate in the TMIP peer review program.
In general, there are four primary motivating factors for agencies when requesting a peer review:
Figure 7 presents the four primary motivating factors by agency size. The desire to have an independent model assessment and obtain a list of specific and prioritized model improvements are the two most frequently expressed motivating factors. Agencies regardless of size tend to identify the same motivating factors.
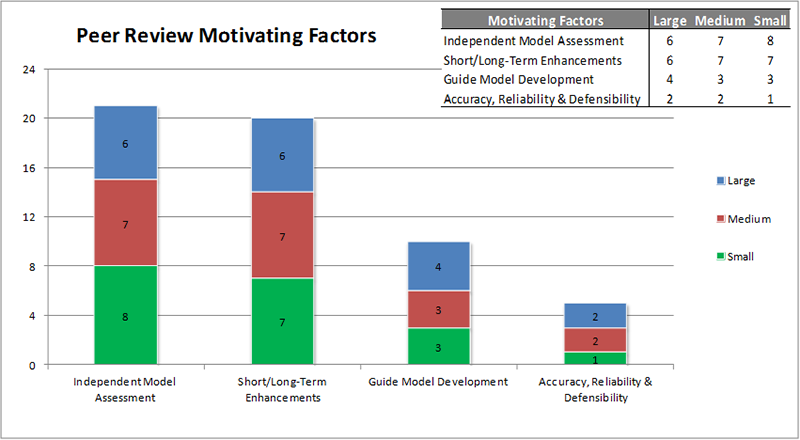
Figure 7 TMIP Peer Review Motivating Factors by Agency Size
[2] http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/planning/tmip/resources/peer_review_program/peer_review_program_synthesis_report.cfm
[3] http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/planning/tmip/resources/peer_review_program/peer_review_program_synthesis_report_2.cfm
[4] http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/planning/tmip/resources/peer_review_program/peer_review_program_evaluation.cfm
[5] During this analysis, peer reviews were convened in Detroit (SEMCOG) and Arizona (AZDOT).