U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Office of Highway Policy Information
Federal Highway Administration
May 4, 2017
| Vehicle Class | Compound Annual Growth Rates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Economic Growth Outlook* |
Baseline Economic Growth Outlook* |
High Economic Growth Outlook* |
||||
| 2015 - 2035 (20 Year) |
2015 - 2045 (30 Year) |
2015 - 2035 (20 Year) |
2015 - 2045 (30 Year) |
2015 - 2035 (20 Year) |
2015 - 2045 (30 Year) |
|
| Light-Duty Vehicles | 0.89% | 0.61% | 1.01% | 0.71% | 1.12% | 0.78% |
| Single-Unit Trucks | 1.43% | 1.24% | 1.72% | 1.50% | 1.98% | 1.77% |
| Combination Trucks | 1.04% | 1.05% | 1.46% | 1.45% | 1.74% | 1.79% |
| Total | 0.92% | 0.66% | 1.07% | 0.78% | 1.19% | 0.89% |
*See the following sections for detailed descriptions of the Baseline and alternative economic outlooks.
The Federal Highway Administration’s spring 2017 long-term forecasts of nationwide VMT are based on long-term economic and demographic forecasts produced by the economic forecasting firm IHS.1 FHWA’s national VMT forecasts are produced using statistical models that incorporate factors affecting historical variation in motor vehicle use through 2015; these models are then used to develop forecasts that begin in 2016 and extend through 2045. The following sections highlight the IHS Baseline forecasts of the key economic and demographic factors that are expected to influence future growth in passenger and freight travel, and discuss their influence on the resulting VMT forecasts. Following this is a brief discussion of the alternative forecasts of U.S. economic performance provided by IHS and their implications for future VMT growth.
Table 2 summarizes the IHS spring 2017 long-term Baseline forecast of key measures of U.S. economic activity that are used to develop FHWA’s VMT forecasts. As it shows, the U.S. population is projected to grow 0.63% annually over the 30-year forecast period, a rate well below its 1.01% annual growth over the previous 30 years. Aggregate economic output, measured by real GDP (2009$) is anticipated to increase 2.06% annually through 2045, which is lower than the yearly growth rate the U.S economy has experienced in recent decades.
| Demographic and Economic Indicators | Historical Growth Rate2 |
Forecast Growth Rate: 2015-45 |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. Population3 | 1.01% | 0.63% |
| GDP (Real 2009$) |
2.80% | 2.06% |
| Real Goods Component of GDP (Real 2009$) |
3.21% | 2.89% |
| Disposable Personal Income per Capita (Real 2009$) |
1.97% | 1.67% |
| Gasoline Price per Gallon (Real 2009$) |
0.65% | 0.63% |
The IHS baseline forecast projects that growth in disposable personal income per Capita will average 1.67% annually over the 30-year forecast period, slightly lower than its growth over the past few decades, which averaged close to 2% annually. Growth in the goods producing sector of the economy is expected to outpace overall economic growth, as Table 2 also shows. Fuel prices are expected to slowly return to a long run average of around $2.70 per gallon (2009$), after reaching a peak in the mid-2020s. Figure 1 presents the long run forecasts from 2015 to 2045 of the real price per gallon of gasoline and diesel.
Figure 1. Price per Gallon of Diesel and Gasoline (2015-2045 2009$)
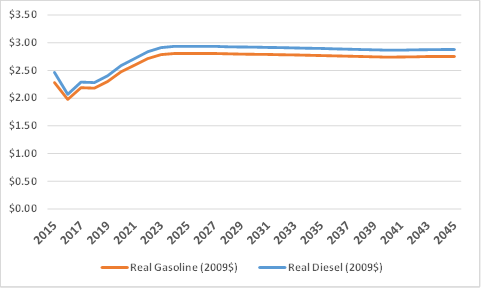
Under the IHS Baseline economic outlook, steady growth in employment, business investment, and productivity are expected to lead to continuing gradual increases in real economic output (Gross Domestic Product) and personal income, while after increasing during the coming decade energy prices remain relatively stable. These trends combine with moderating population growth to generate sustained increases in both passenger vehicle and truck travel, although at significantly slower rates than those experienced in recent decades.
In 2015, travel by light-duty vehicles – including automobiles and light-duty trucks used primarily for passenger travel – amounted to 2.78 trillion miles, an increase of 2.55% from 2014. Use of light-duty vehicles now accounts for about 90% of total U.S. motor vehicle travel. As Table 3 reports, growth in light-duty VMT is projected to average 1.01% per year from 2015-2035. Over the following decade, however, growth in light-duty vehicle travel is expected to moderate, so that through the entire 30-year forecast period, its growth is projected to average only 0.71% per year.
| Vehicle Class | Compound Annual Growth Rates | |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 – 2035 (20 Year) |
2015 – 2045 (30 Year) |
|
| Light-Duty Vehicles | 1.01% | 0.71% |
| Single-Unit Trucks | 1.72% | 1.50% |
| Combination Trucks | 1.46% | 1.45% |
| Total | 1.07% | 0.78% |
Truck travel in the U.S reached 280 billion miles in 2015, increasing by 0.26% from 2014 and accounting for almost all of the remaining 10% of U.S. motor vehicle use.4 Table 3 shows that truck travel is projected to grow more rapidly than light-duty vehicle travel under the Baseline economic outlook, but is also expected to slow during the last decade of the forecast period.
Growth in VMT by single-unit trucks is projected to average 1.72% per year from 2015-35, and 1.50% annually for the entire 30-year period from 2015-45. VMT by combination trucks is expected to grow steadily during this period, reflecting the outlook for sustained growth in transportation related sectors of the economy: U.S. goods manufacturing and international trade. Combination truck VMT is projected to increase by 1.46% annually for the 20 years from 2015-35, and by 1.45% per year over the complete 30-year forecast period.
Finally, Table 3 reports that aggregate VMT by all vehicle classes is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 1.07% over the 20 years from 2015-35. Reflecting the projected slowing of growth in use of both passenger vehicles and trucks during the last decade of the forecast period, growth in total VMT is expected to average 0.78% annually for the entire 30-year forecast period.
Changes in vehicle use over the past two decades, particularly during the 2008-09 recession and prolonged recovery, have highlighted the uncertainty that surrounds forecasts of future growth in motor vehicle travel. Important sources of such uncertainty include concerns about prospects for future economic growth, alternative interpretations of the causes of recent declines in vehicle ownership and use (particularly among younger Americans), and the potential effects on vehicle use of dramatic innovations in technology such as the advent of autonomous vehicles. To acknowledge this uncertainty, FHWA provides a range of alternative forecasts for future VMT growth that reflects uncertainty about the outlook for future economic growth, travel behavior, and vehicle technology, while also incorporating statistical uncertainty in its VMT forecasting models.5
To develop these alternative forecasts, FHWA used projections of population growth, U.S. economic output and its composition, growth in personal income, and energy prices from the Optimistic and Pessimistic scenarios reported as part of IHS' spring 2017 30-year economic outlook. FHWA’s alternative forecast of higher total VMT growth relies on IHS' Optimistic economic outlook, which projects stronger growth in productivity, labor force participation, employment, and business investment levels than under the Baseline outlook.
These factors combine with a more robust hou s ing sector and lower energy prices to produce st ronger growth in real GDP, goods production, and disposable income than in the Baseline outlook. In turn, these developments produce significantly faster growth in freight shipments and truck VMT under the Optimistic economic outlook. Under this more optimistic economic growth scenario, however, passenger vehicle VMT is predicted to grow only slightly faster when compared to the baseline outlook. The modest effect of more rapid economic growth on travel is primarily a result of the specification of FHWA’s passenger travel model, which accounts for the effect of increasing income on the cost of traveling and the dampening influence this is ultimately expected to have on travel demand as personal disposable income continues to increase.6 The forecasting model attempts to capture the dual effects of income growth on household and business travel using light-duty vehicles: on one hand, rising income increases the demand to participate in economic, social, and recreational activities outside the home, which gives rise to increased demand for travel, while on the other, rising incomes also increase the effective cost of time spent driving and thus dampen travel demand.
In contrast, FHWA’s alternative forecast of lower growth in vehicle use reflects the Pessimistic economic outlook from IHS’ spring 2017 forecast. This alternative outlook predicts weaker growth in productivity, labor force participation, and business investment, together with higher interest rates and more rapid price inflation. These factors combine with less robust activity in the housing sector and higher energy prices to dampen projected future growth in real GDP and personal income compared to the Baseline economic outlook. Under this scenario, slower economic growth leads to lower demand for personal travel, and passenger vehicle use increases primarily as a result of U.S. population growth. At the same time, slower growth in goods manufacturing, freight shipments, and construction activity dampen growth in truck use significantly from the levels projected in the Baseline forecast.
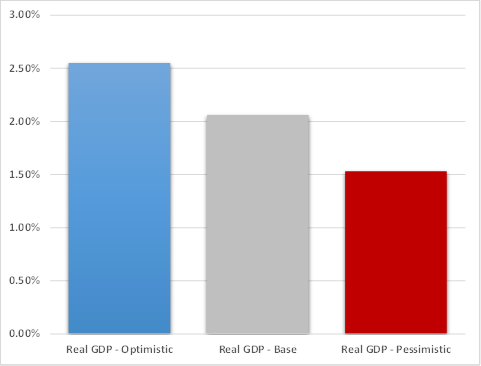
To illustrate the important differences in future economic trends affecting vehicle use among the alternative economic outlooks, Figures 2-4 below compare forecast growth in real GDP, personal disposable income, and gasoline prices in the Pessimistic and Optimistic scenarios to the Baseline outlook. As Figure 2 shows, real GDP is anticipated to grow about 2.55% per year over the 30-year forecast period under the Optimistic outlook, compared to 2.06% annual growth projected for the Baseline scenario, but is projected to average only about 1.53% annually in the Pessimistic scenario.
Figure 2. Real GDP Growth under Alternative Economic Outlooks
(30-Year Average Annual Growth)
Similarly, Figure 3 shows that growth in real personal disposable income per person is forecast to average about 1.91% per year in the Optimistic scenario, only slightly above its projected annual growth of 1.67% in the Baseline outlook, but well above the 1.46% annual rate projected under the Pessimistic economic outlook. Finally, Figure 4 illustrates that inflation-adjusted retail gasoline prices are expected to increase at about 0.22% annually under the Optimistic scenario, whereas the Baseline and Pessimistic economic outlooks predict average yearly growth in gasoline prices of 0.63% and 1.02% respectively.
Figure 3: Growth in Real Personal Disposable Income per Capita under Alternative Economic Outlooks
(30-Year Average Annual Growth)
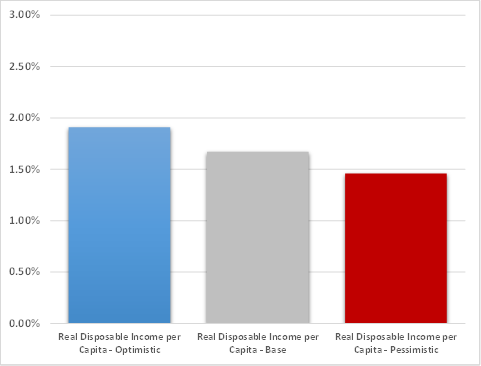
Figure 4: Changes in Real Gasoline Prices under Alternative Economic Outlooks
(30-Year Average Annual Change)
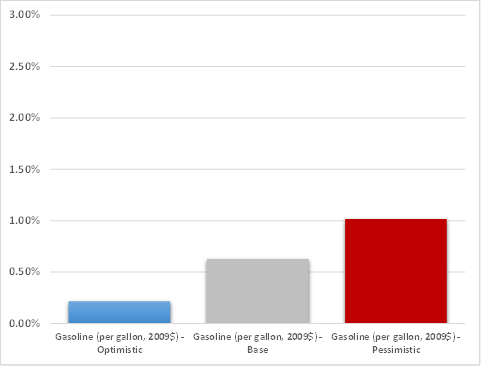
Table 4 reports alternative forecasts of future growth in VMT under the Optimistic and Pessimistic economic outlooks; the range between them reflects the effect of uncertainty about future economic growth. These alternative outlooks have a relatively minor effect on the forecast of future growth in light-duty vehicle use, primarily because the forecasts of growth in disposable personal income and gasoline prices do not deviate significantly from the baseline, and the countervailing effects of income growth incorporated in the model tend to maintain the forecasts within a certain range. In contrast, the difference between the forecasts of long-term growth in truck travel between the Optimistic and Pessimistic economic outlooks is much larger, since they reflect differing outlooks for the investment and manufacturing sectors of the U.S. economy. Because light-duty vehicles account for the largest share of total VMT, however, the long-term forecast of total VMT varies only within a comparatively narrow range between the Optimistic and Pessimistic economic outlooks.
| Vehicle Class | Compound Annual Growth Rates | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pessimistic Economic Outlook |
Optimistic Economic Outlook |
|||
| 2015-2035 (20 Year) |
2015-2045 (30 Year) |
2015-2035 (20 Year) |
2015-2045 (30 Year) |
|
| Light-Duty Vehicles | 0.89% | 0.61% | 1.12% | 0.78% |
| Single-Unit Trucks | 1.43% | 1.24% | 1.98% | 1.77% |
| Combination Trucks | 1.04% | 1.05% | 1.74% | 1.79% |
| Total | 0.92% | 0.66% | 1.19% | 0.89% |
Volpe, The National Transportation Systems Center, U.S. Department of Transportation has performed the modeling underlying these forecasts and provided technical assistance to the Federal Highway Administration.
1 http://www.ihs.com/index.aspx
2 Historical data:1966 through 2015
3 The IHS population forecast is based on the Census Bureau’s long-term population projections.
4 Motorcycles and buses, which are excluded from the forecasts reported in Table 3, together accounted for only about 1% of all U.S. motor vehicle travel during 2015.
5 Uncertainty about future VMT growth arising from the potential for fundamental changes in travel behavior or vehicle technology is likely to be resolved only with the passage of time, the availability of more detailed information about personal travel, and experience with real-world deployment of advanced vehicle technologies. Thus FHWA’s forecasts of future VMT growth do not attempt to incorporate these sources of uncertainty.
6 For more information on the VMT models, please refer to the technical document at: http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/policyinformation/tables/vmt/vmt_model_dev.cfm