U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Conditions and Performance
Status
of the Nation's Highways, Bridges, and Transit:
2002 Conditions and Performance Report
|
Exhibit 11-25:
Year of Construction and
Cumulative ADT - Deficient Concrete Superstructure Bridges (excluding prestressed
concrete superstructures)
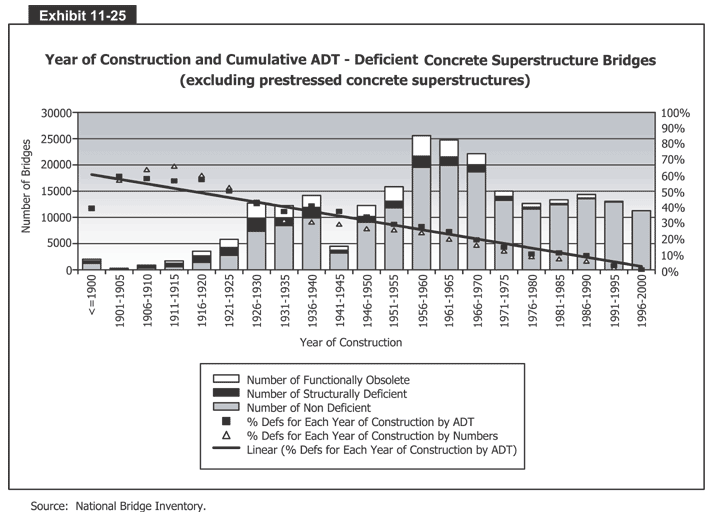 Exhibit 11-25 is a bar graph that shows year of construction and cumulative ADT for deficient concrete superstructure bridges (excluding prestressed concrete). The vertical axis measures number of bridges from 0 to 30,000 in increments of 5,000 bridges. The horizontal axis has 21 bars, one for each 5-year period between 1900 and 2000. Each bar has three parts, measuring the distribution of functionally obsolete, structurally deficient, and non-deficient concrete superstructure bridges. In the first 20 years of the 20th century, about half the Nation's new concrete superstructure bridges were structurally deficient, with the rest being non-deficient or obsolete in varying amounts. From 1920 to 1930, about half of the Nation's new concrete superstructure bridges were non-deficient, one-fourth were structurally deficient, and one-fourth were obsolete. From 1931 to 1955, two-thirds were non-deficient, with the rest split about evenly between obsolete and structurally deficient. From 1956 to 1970, about four-fifths were non-deficient, with the balance split between obsolete and structurally deficient roughly 2 to 1. And from 1971 to 2000, the number of deficient concrete superstructure bridges dwindles from one-tenth to almost zero. There are three other items and a second vertical axis (measuring percentages from 0 to 100 in increments of 10 percent) in this chart. A line, representing the "linear" percent of deficient concrete superstructure bridges for each year of construction by ADT, starts in 1900 at about 60 percent and drops in a straight line to 50 percent by 1920, 25 by 1955, 10 by 1990, and just over 0 by 2000. A series of small squares, representing the percent of deficient concrete superstructures for each year of construction by ADT, starts at about 40 percent in 1900, climbs to a peak of 65 percent by 1910, then drops steadily to 50 percent by 1925, 30 by 1955, 20 by 1970, and 0 by 2000. And a series of small triangles, representing the percent of deficient concrete superstructures for each year of construction by numbers, starts at about 60 percent in 1905, climbs to a peak of 65 percent by 1915, then drops steadily to 30 percent by 1940, 20 by 1970, and 0 by 2000.
Exhibit 11-25 is a bar graph that shows year of construction and cumulative ADT for deficient concrete superstructure bridges (excluding prestressed concrete). The vertical axis measures number of bridges from 0 to 30,000 in increments of 5,000 bridges. The horizontal axis has 21 bars, one for each 5-year period between 1900 and 2000. Each bar has three parts, measuring the distribution of functionally obsolete, structurally deficient, and non-deficient concrete superstructure bridges. In the first 20 years of the 20th century, about half the Nation's new concrete superstructure bridges were structurally deficient, with the rest being non-deficient or obsolete in varying amounts. From 1920 to 1930, about half of the Nation's new concrete superstructure bridges were non-deficient, one-fourth were structurally deficient, and one-fourth were obsolete. From 1931 to 1955, two-thirds were non-deficient, with the rest split about evenly between obsolete and structurally deficient. From 1956 to 1970, about four-fifths were non-deficient, with the balance split between obsolete and structurally deficient roughly 2 to 1. And from 1971 to 2000, the number of deficient concrete superstructure bridges dwindles from one-tenth to almost zero. There are three other items and a second vertical axis (measuring percentages from 0 to 100 in increments of 10 percent) in this chart. A line, representing the "linear" percent of deficient concrete superstructure bridges for each year of construction by ADT, starts in 1900 at about 60 percent and drops in a straight line to 50 percent by 1920, 25 by 1955, 10 by 1990, and just over 0 by 2000. A series of small squares, representing the percent of deficient concrete superstructures for each year of construction by ADT, starts at about 40 percent in 1900, climbs to a peak of 65 percent by 1910, then drops steadily to 50 percent by 1925, 30 by 1955, 20 by 1970, and 0 by 2000. And a series of small triangles, representing the percent of deficient concrete superstructures for each year of construction by numbers, starts at about 60 percent in 1905, climbs to a peak of 65 percent by 1915, then drops steadily to 30 percent by 1940, 20 by 1970, and 0 by 2000.
Source: National Bridge Inventory.
Back
to Chapter 11
Return to top
Page last modified on November 7, 2014
