U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Federal Highway Administration Research and Technology
Coordinating, Developing, and Delivering Highway Transportation Innovations
|
R&T NOW This newsletter is an archived publication and may contain dated technical, contact, and link information. |
|
| Publication Number: Date: January/February 2019 |
Publication Date: January/February 2019
|

PDF files can be viewed with the Acrobat® Reader®
In this issue…
The Office of Infrastructure Research and Development at the Federal Highway Administration's Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center published Foundation Reuse for Highway Bridges, a report that examines the reuse of bridge foundations for bridge reconstruction projects.(1) The report addresses critical issues encountered during the decisionmaking process, including the assessment of existing bridge foundations for structural/geotechnical integrity, durability, and load carrying capacity, as well as the strengthening and design of bridge foundations for future reuse. The report includes numerous case examples on the reuse of bridge foundations to highlight significant benefits of foundation reuse from social, environmental, and economic perspectives.
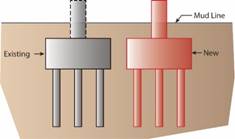
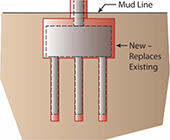
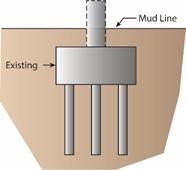
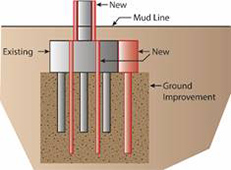
The reuse of existing bridge foundations during reconstruction or major rehabilitation can result in significant savings in costs and accelerated project delivery, as was the case with the Milton Madison Bridge project. The reuse and rehabilitation of the bridge, which connects Milton, KY, and Madison, IN, saved an estimated $50 million.(2) The bridge is a preassembled steel truss superstructure (placed on temporary piers) that was moved laterally 55 feet on refurbished piers. Four different options are available when replacing an existing bridge foundation. Option 1 involves the construction of a new foundation on a new alignment while avoiding the existing foundation. Construction of the new elements does not interfere with the existing foundation or impact user mobility (although there may be mobility impacts while switching to the new alignment). Option 2 maintains the existing alignment on new substructure elements. Option 3 reuses the existing foundation as is, with or without minor repairs. Option 4 reuses foundations with some form of retrofitting or strengthening. Options 3 and 4 both illustrate the case of foundation reuse.
Source: FHWA
Option 1: Install new foundation on new alignment.
Source: FHWA
Option 2: Install new foundation on the existing alignment.
Source: FHWA
Option 3: Reevaluation and reuse of existing foundation.
Source: FHWA
Option 4: Reuse existing foundation by strengthening it.
For more information, contact Frank Jalinoos, 202-493-3082, frank.jalinoos@dot.gov.
The Long-Term Bridge Performance (LTBP) Program is deploying newly acquired commercial versions of the RABIT™ (Robotic Assisted Bridge Inspection Tool). This system was developed to collect high-quality data using multiple nondestructive evaluation (NDE) technologies mounted on a single platform to assess the condition of bridge decks.

Source: FHWA
RABIT™ being deployed from the systems operations center. The center is used to store and transport the equipment.
The RABIT™ includes several NDE technologies for assessing untreated (bare) concrete decks. These technologies include ground penetrating radar (used to assess the condition of underlying concrete and to map the location and cover of the top-most reinforcement embedded in the concrete deck); impact echo (acoustic wave method used to detect the presence and extent of subsurface deck delaminations); ultrasonic surface waves (acoustic wave technology used to assess the quality of concrete through determination of the in situ concrete modulus); and electrical resistivity of the concrete deck (used to assess the potential corrosive environment). The RABIT™ also has two high-resolution cameras mounted on the chassis to capture images of the deck. The images are stitched together into one large composite image of the deck to provide documentation of the deck's surface condition.
With the implementation of this new tool, the LTBP Program is gearing up for another round of data collection in the Gulf and Northwest States.
The initial round of data collection on 24 bridges in the Gulf States and 24 bridges in the Northwest States was performed in 2015, which included extensive visual inspections and deck material sampling (cores were removed and tested for chloride penetration and compressive strength). These bridges will be assessed with the RABIT™ during the 2018-2019 timeframe to collect high-quality data using the NDE technologies described in the previous paragraph to quantify the condition of the reinforced concrete bridge decks.
For more information, contact Robert Zobel, 202-493-3024, robert.zobel@dot.gov.
Shana Baker, Director of the Office of Corporate Research, Technology, and Innovation Management (HRTM), and Mary Huie, HRTM Program Coordinator, attended the Fed Tech Startup Studio Pitch Day on November 27, 2018. The Fed Tech Program helps Federal laboratories identify inventions and pairs the laboratories with entrepreneurs, graduate students, and industry experts to examine potential opportunities to further the development of the invention.
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) sponsored Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center's (TFHRC) J. Sterling Jones Hydraulics Research Laboratory's In Situ Scour Testing Device (ISTD) as one of the inventions. The ISTD is a field testing device used to determine the scour-depth potential of soils that support structural foundations built in flowing water. The device measures the scour potential in situ using a columnar containment vessel driven into the soil.
Entrepreneurs associated with the Fed Tech program have interviewed potential users of the ISTD and believe that it has the capacity to be used broadly within the transportation industry and its data would be valuable to many stakeholders.
Pitch Day is an event for early-stage venture teams to demonstrate and present ideas built around the innovations from Federal labs. Twenty teams of entrepreneurs and inventors representing emerging technologies from the country's premier labs attended the event, including the Air Force Research Laboratory, Army Research Laboratory, TFHRC's J. Sterling Jones Hydraulics Laboratory, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Princeton University, and the Space and Naval Warfare Systems Command.
For more information, contact Mary Huie, 202-493-3460, mary.huie@dot.gov.
A full-scale crash test was conducted at Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center's Federal Outdoor Impact Laboratory (FOIL) at the Office of Safety Research and Development on December 13, 2018. During the test, a small passenger vehicle weighing 1,100 kg (2,425 lbs) traveled at 100 km/h (62 mph) crashed into a series of experimental polymer concrete segments at a 25-degree impact angle. Each segment of the experimental barrier weighs 454 kg (1,000 lbs). The barriers are lighter and stronger than concrete and easier to transport on the back of a flatbed truck. They are also faster to produce. A polymer barrier can cure in 2 hours; a concrete barrier needs at least 28 days to cure.

Source: FHWA
A closeup view of one of the experimental polymer concrete segments.
The test will be used to evaluate the benefits of using materials other than cement, such as polymer concrete, to construct roadside barriers.
Models suggested that the barrier would move approximately 1.5 feet during the collision. The experiment, however, showed that the barrier moved 2.5 feet due to some unexpected cracks, which the research team will analyze and improve upon over the next month. The difference of a foot has safety implications for the placement of barriers on highways that serve to protect other vehicles, drivers and passengers, and road workers.

Source: FHWA
A man walks in front of a portion of the barrier that was moved by the test vehicle during the crash test at the FOIL.
Once the new analysis is complete, the team plans on conducting at least two more full-scale crash tests, another with a similar small car, and one with a large pick-up truck.

Source: FHWA
The test vehicle after the crash test.
For more information, contact Eduardo Arispe, 202-493-3291, eduardo.arispe@dot.gov.
The Federal Laboratory Consortium for Technology Transfer (FLC) publishes a yearly planner that features many of the Federal research laboratories throughout the Nation. January 2019 kicked off the year by featuring Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center's Federal Outdoor Impact Laboratory (FOIL).
The FOIL is an ISO 17025-accredited crash test facility used to support the Federal Highway Administration's Safety Research and Development programs and other Federal security initiatives with research related to roadside hardware and roadway departure issues. Researchers use this facility to extend their understanding of crash events and dynamic loading that occur during impacts. This is accomplished by staging controlled, high-speed motor vehicle and pendulum collisions into roadside hardware and components. Other activities at the FOIL include the application of advanced digital simulation tools, such as Finite Element Analysis, to the design and testing of roadside safety systems.
The FLC is the formally chartered, nationwide network of over 300 Federal laboratories, agencies, and research centers. The FLC fosters commercialization of best practice strategies and opportunities for accelerating Federal technologies out of the laboratory and into the marketplace.
For more information, contact Mary Huie, 202-493-3460, mary.huie@dot.gov.
FHWA's Office of Safety seeks submissions for its spring 2019 issue of Safety Compass. This newsletter is an ideal way to highlight your road safety-related activities and programs.
New FHWA safety-focused products, resources, and publications; guidance, policy, and rulemaking notices; and innovative safety-focused products from our partners and stakeholders are all great things to communicate in Safety Compass.
Submit articles and related graphics to Tara McLoughlin by March 15, 2019.
Congratulations to Mohammed Yousuf, Program Manager for the Accessible Transportation Technology Research Initiative (ATTRI) and Transportation Specialist at Federal Highway Administration's Turner-Fairbank Highway Research Center (TFHRC), who was recognized by The Viscardi Center as one of ten recipients of the 2018 Henry Viscardi Achievement Awards. The awards honor leaders in the global disability community who are reshaping societal perceptions and making significant changes in the quality of life of people with disabilities.
The ceremony was held in New York City on December 4, 2018. The Viscardi Center recognized 10 global leaders with disabilities.
Mohammed has dedicated his work to bringing emerging accessible transportation technologies to widespread use. He has focused his research on developing technologies that include accessible transportation systems, automated vehicles, and robotics, among others.
ATTRI is a joint initiative with the United States Department of Transportation, co-led by the Federal Highway Administration, Federal Transit Administration, and Intelligent Transportation Systems Joint Program Office, with support from the National Institute on Disability, Independent Living, and Rehabilitation Research, and other Federal partners. The ATTRI Program is leading efforts to develop and implement transformative applications to improve mobility options for all travelers, particularly those with disabilities. ATTRI research focuses on removing barriers to transportation for people with visual, hearing, cognitive, and mobility disabilities.

© The Viscardi Center. Used with permission.
Mohammed Yousuf, center, receives his award from John D. Kemp, left, President and CEO of The Viscardi Center, and Russ Cusick, right, Chair of The Viscardi Center's Board of Directors.
For more information, contact Mohammed Yousuf, 202-493-3199, mohammed.yousuf@dot.gov.
The issue includes the following articles: Ready for Round Five; Weather-Responsive Management Strategies; Modernizing Signal Management; Mobile Solution for Assessment and Reporting; States Innovate!; Explore Innovation at Transportation Research Board Annual Meeting
The issue is available online.
1 Agrawal, A.K., Jalinoos, F., Davis, N., Hoomaan, E., and Sanayei, M. (2018). Foundation Reuse for Highway Bridges, Report No. FHWA-HIF-18-055, FHWA, McLean, VA.
2 Jalinoos, F. (2015) "Reusing Bridge Foundations," Public Roads, 79 (3), FHWA, McLean, VA.
Please forward this newsletter to others you think might find it interesting and/or useful.
Suggestions may be submitted to: FHWA_Now@fhwa.dot.gov.