JUST RELEASED! Value Capture Implementation Manual/Guidebook »

Airport MAX Red Line - Portland, Oregon
The Airport MAX is a 5.5-mile light rail extension to Portland's existing Red Line, connecting Downtown Portland to the Portland International Airport (PDX). As part of a public-private partnership, Bechtel Enterprises funded $28.2 million (23 percent) of the extension's $125.8 million project costs, delivered the extension under a design-build contract, and received an 85-year, rent-free lease to develop the 120-acre mixed-use commercial site near the airport. In addition, the City of Portland funded its portion of project costs (19 percent) by using a form of Tax Increment Financing (TIF).
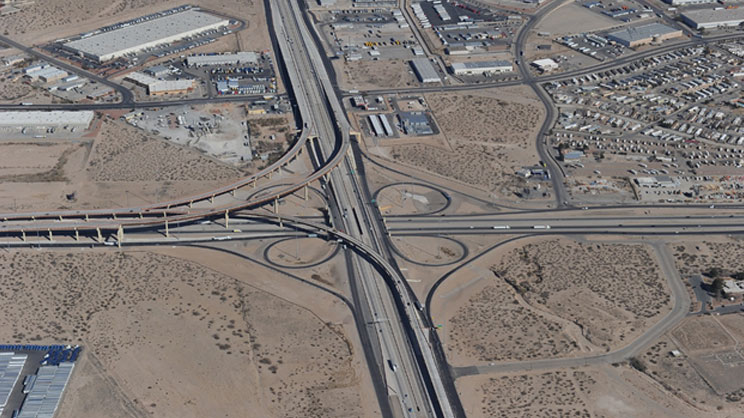

Americas Interchange Project - El Paso, Texas
The Americas Interchange is a four-level, fully directional interchange between I-10 and Loop 375 15 miles east of downtown El Paso, Texas. The project was constructed in three phases, the first of which relied on $30 million from a City Transportation Reinvestment Zone that acts as a form of Tax Increment Financing.

Atlanta BeltLine - Atlanta, Georgia
The Atlanta BeltLine is a transportation and economic development program will transform abandoned rail corridors into a 33-mile trail network and 22-mile light rail transit extension. It is projected to generate $20 billion in economic development in Atlanta, part of which will support ongoing project costs through a Tax Allocation District (TAD), Georgia's terminology for tax increment financing.
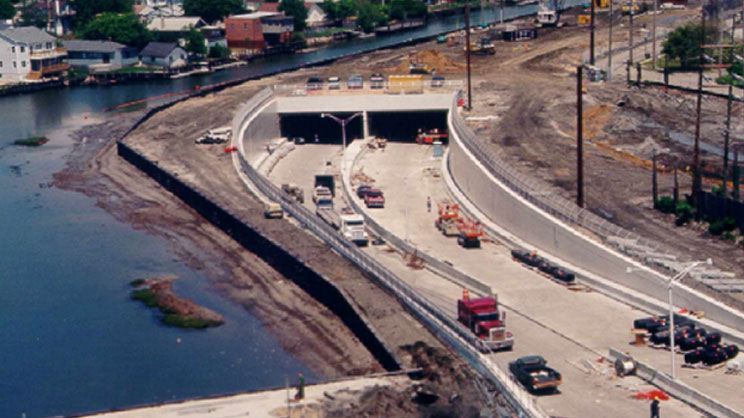

Atlantic City-Brigantine Connector - Atlantic City, New Jersey
The 2.4-mile Atlantic City-Brigantine Connector is a roadway, tunnel, and related ramps that link the Atlantic City Expressway to a former landfill site, now home to the Borgata Hotel Casino & Spa, in Atlantic City, New Jersey. This $330 million design-build project, completed in 2001, involved a funding partnership among several public agencies and Mirage Resorts, Inc. that included private cash and advance alternative cash credits from incremental property, sales, and business tax proceeds resulting from the newly constructed hotel and casino.

Atlantic Station 17th Street Bridge - Atlanta, Georgia
The Atlantic Station 17th Street Bridge is a critical component of a major redevelopment known as Atlantic Station, located on a former brownfield site in the northwest part of downtown Atlanta. The bridge links the redevelopment site with Midtown Atlanta. Funding for the bridge included bonds backed by incremental property and sales tax revenue from the development's tenants, together with a contribution from the private developer.

Baldock Solar Station - Clackamas County, Oregon
The Baldock Solar Station is a 1.75 megawatt solar array at the French Prairie Safety Rest Area south of Portland, Oregon. It was developed by Oregon DOT in partnership with Portland General Electric through a third-party ownership development model. PGE financed, built, owns, operates, and maintains the site, which helps the utility meet its legislatively mandated requirement to acquire 25 percent of new electrical generation from renewable energy resources by 2025. In return for use of the land, ODOT receives a small annual site license fee and a percentage of the renewable energy certificates.
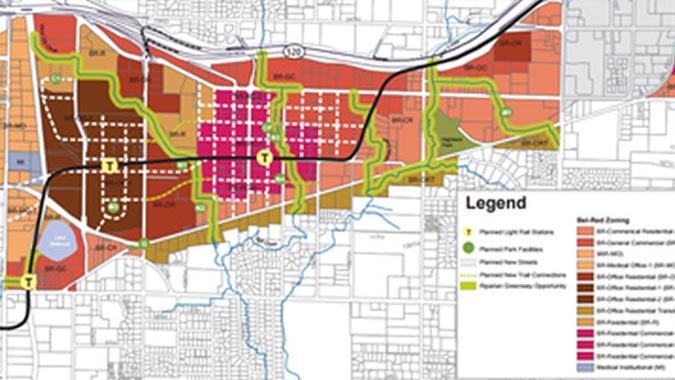
Belred Street Network - Bellevue, Washington
The BelRed Street Network is part of BelRed Transformation, a plan for redevelopment and economic growth within a 900-acre area between downtown Bellevue and Overlake/Microsoft, 10 miles east of Seattle, Washington. The project is a combination of 12 multimodal roadways to support development of the new BelRed neighborhood. In tandem with the East Link light rail, the project will provide multimodal mobility enhancements that are expected to improve access to transit, reduce travel times, and improve access to employment. The street improvements are financed with a TIFIA loan and mix of local revenue tied to new development.

Big Cottonwood Canyon Fiber Optic Deployment - Salt Lake City, Utah
In the summer of 2013, the Utah Department of Transportation partnered with the wireless infrastructure provider Crown Castle International to install nearly 13 miles of fiber-optic cables, poles, and other facilities in Big Cottonwood Canyon. This agreement permitted UDOT to use the fiber backbone to supply connectivity to new ITS devices for active traffic management, improving traffic operations in the region.

Butler County Veterans Highway (State Route 129) - Butler County, Ohio
The Butler County Veterans Highway (State Route 129) is a 10.7-mile, four-lane, east-west state highway connecting the City of Hamilton, Ohio with I-75, about 25 miles north of Cincinnati. The $158.5 million project opened in December 1999 and was financed by revenue bonds backed by payments from the Ohio Department of Transportation. The Butler County Transportation Improvement District, a regional governmental organization, sponsored the project.

Capitol Crossing / Third Street Tunnel - Washtingon, D.C.
The Capitol Crossing project is constructing five buildings providing 2.2 million square feet of retail, commercial and residential space above a recessed segment of I-395 near its terminus several blocks north of the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C. In addition to purchasing the air rights from the District of Columbia, the developer is paying for associated transportation improvements to access and egress between I-395 and local streets, together with the restoration of the street grid above.

CATS LYNX Blue Line Extension - Charlotte, North Carolina
The LYNX Blue Line Extension is a $1.16 billion extension of the existing 9.6-mile LYNX Blue Line light rail that opened in the South Corridor of Charlotte, North Carolina, in 2007. The 9.3-mile extension includes 11 new stations and associated parking facilities and will provide service north to the campus of UNC Charlotte. Funding comes from a federal capital investment grant, a TIFIA loan, the state and city, the Charlotte Area Transit System, and donated right-of-way.

CenterPoint Intermodal Center - Joliet - Joliet, Illinois (Metropolitan Chicago region)
CenterPoint Intermodal Center - Joliet is a 3,600-acre facility housing industrial facilities, Class I rail intermodal centers, and yards for container management. CIC - Joliet is located 40 miles southwest of Chicago. Since opening in 2010, it has combined with its neighbor two miles to the south, CenterPoint Intermodal Center - Elwood, home to BNSF Logistics Park. The combined 6,400-acre intermodal facility is the nation's largest inland port. CIC - Joliet is currently home to a Union-Pacific Terminal (shown in the photo), a Class I intermodal facility, and has the capacity to accommodate additional facilities. It is partially financed with a private activity bond allocation.

Central 70 - Denver, Colorado
The Central 70 project will redesign 10 miles of I-70 in Denver, Colorado from I-25 on the west to Chambers Road on the east. The project will reconstruct and expand the corridor by providing one new express toll lane in each direction, removing a 50-plus-year-old, 2-mile-long viaduct while lowering this section below grade, and placing a 4-acre park over a 1,000-foot portion of the lowered section, uniting two separated neighborhoods. The project is being delivered under a 34-year design-build-finance-operate-maintain availability-payment concession. The concessionaire's financing includes a TIFIA loan and private activity bond proceeds.

Central Texas Turnpike System - Austin, Texas
The Central Texas Turnpike System, now simply referred to as Austin Area Toll Roads, consists of three contiguous toll highways serving the Austin metropolitan region and the Austin-San Antonio corridor: SH 45 North, Loop 1, and SH 130 (Segments 1-4). State and local funding sources were combined with a Federal TIFIA loan to finance the project. SH 130 (Segments 1-4) was delivered via a design-build contract procured through Texas' first application of legislation permitting expanded private sector involvement.

Century Garden Community Development District (Expansion Area Project) - Miami-Dade County, Florida
The Century Gardens Community Development District is using Special Assessment Bonds to cover a portion of the cost for roadway improvements and a stormwater management system in a 9.8-acre Expansion Area of the Century Gardens development that will contain 86 townhomes in Miami-Dade County, Florida.

Chicago Region Environmental and Transportation Efficiency Program (CREATE) - Chicago, Illinois
The CREATE project is an innovative collaboration between freight railroads, the State of Illinois DOT, the City of Chicago DOT, Metra, and Amtrak. CREATE is maximizing the use of four train transportation corridors, including three primarily handling freight traffic and one primarily handling passenger traffic. The project involves 70 improvements, including rail, auto, and pedestrian grade separations using new overpasses and underpasses, as well as viaduct improvements, grade crossing safety enhancements, and extensive upgrades of tracks, switches and signal systems.

Chicago Skyway - Chicago, Illinois
The Chicago Skyway is a 7.8-mile elevated toll road connecting I-94 (Dan Ryan Expressway) in Chicago to I-90 (Indiana Toll Road) at the Indiana border. It was leased to a consortium of Cintra and Macquarie in 2005 for an upfront payment of $1.83 billion, which the City used to pay down Skyway and city debt and establish reserve funds. The Skyway was sold to a Canadian pension fund consortium in 2015 for $2.8 billion.

Chicago Transit Authority 95th Street Terminal Improvement Project - Chicago, Illinois
Chicago Transit Authority 95th Street Terminal Improvement Project at the terminus of Chicago Transit Authority's Red Line consists of a redesign of the existing North Terminal building, surrounding sidewalks, and rail platforms. This project also includes the construction of a new South Terminal building. The existing 95th/Dan Ryan Terminal is a critical intermodal hub connecting downtown commuters to the Far South Side communities and suburbs through bus connections. The project is being delivered under a design-build contract, funded by TIFIA, federal, state, and local funds.

Chicago Transit Authority Blue Line Project - Chicago, Illinois
The Chicago Transit Authority Blue Line Project (Your New Blue improvement program) is a series of modernization projects along a 19-mile section of Chicago Transit Authority's Blue Line O'Hare Branch. It includes track improvements, traction power and signal upgrades, and station renovations to improve service, reliability, and accessibility. The nearly half-billion dollar, four-year program is being funded by a combination of federal, state, and local sources.

Chicago Transit Authority Rail Fleet Replacement Project - Chicago, Illinois
The Chicago Transit Authority is investing over $772.5 million for the purchase of new rail cars to replace aging rolling stock. The new rail cars will increase the size of the fleet to meet growing ridership demands, provide a smoother ridership experience, and improve passenger security with the inclusion of more up-to-date technology. Agency revenue bonds, a TIFIA loan, and federal formula funds will pay for the new rail cars.

City of Las Vegas Special Improvement District No. 610 (Skye Canyon Phase 3) - Las Vegas, Nevada
The City of Las Vegas will issue Special Improvement District Bonds to finance local street improvement projects, a storm sewer project, a sanitary sewer project, drainage projects, and a water project in Special Improvement District No. 610, which is a 267-acre site that will form Phase 3 of the Skye Canyon master-planned community in Northwest Las Vegas.

Conroy Road Bridge - Orlando, Florida
The Conroy Road Bridge and approach ramps are located just west of the City of Orlando where it crosses I-4. The bridge and ramps provide accessibility to a 400+ acre parcel situated on the east side of I-4 that contains the Mall at Millenia and other commercial development, including retail space and an office park. A partnership among the City of Orlando, Orange County, Florida DOT, and the Millenia project development group in the late 1990s relied on Tax Increment Financing to back revenue bonds and a Florida DOT loan to finance the bridge and link repayment to resulting economic development.

Copley Place - Boston, Massachusetts
Copley Place is a $400 million mixed-use development project built on a 9.5-acre land-air parcel above the Massachusetts Turnpike in Boston, Massachusetts through a right-of-way use agreement. Completed in 1984, it includes two hotels, a convention center, a shopping complex, 800,000 square feet of office space, 100 mixed-income housing units, and 1,432 parking spaces.

Crenshaw/LAX Transit Corridor Project - Los Angeles, California
The Crenshaw/LAX Transit Corridor Project is a new 8.5-mile light rail transit line extending from the existing Metro Expo Line south to Aviation/LAX Station along the Metro Green Line, including eight transit stations (with off-street parking), the procurement of up to 28 light rail vehicles, and the construction of a full service maintenance facility. The project is supported by a TIFIA loan backed by local sales tax revenue, as well as other state funds, including those from general obligation bonds, and additional local sales tax revenue.

Dallas Area Rapid Transit Project Orange Line Extension (Irving-3) - Dallas, Texas
The DART Orange Line is a light rail transit line connecting downtown Dallas with the City of Irving and Dallas/Fort Worth (DFW) International Airport northwest of Dallas. The 14.5-mile, $1.3 billion project opened in three sections. A TIFIA loan helped finance construction on the project's $397 million third phase (Irving-3).

Denver Union Station - Denver, Colorado
The Denver Union Station project is a public-private development venture located on approximately 50 acres in lower downtown Denver. Redevelopment of the site as an intermodal transit district surrounded by transit-oriented development includes light and commuter rail stations, a regional bus facility, new transit service, and pedestrian improvements. The project is sponsored by a public benefit corporation formed by the City of Denver and its elements have been transferred to the Regional Transportation District as they were completed. The project achieved substantial completion in February 2014. Financing included TIFIA and RRIF loans, federal grants and stimulus funding, and state, regional, and local contributions.

Dulles Corridor Metrorail Project - Northern Virginia
The Dulles Corridor Metrorail Project (Silver Line) is a 23-mile extension of the existing Metrorail system from the Orange Line's East Falls Church Station in Arlington to Route 772 in Loudoun County, including 11 new stations. The extension serves Tysons Corner, Virginia's largest employment center, and the Reston/Herndon area, the region's second largest employment concentration. It also will provide a one-seat ride from Washington Dulles International Airport to downtown Washington, DC. The project is being financed with an FTA New Starts grant, three TIFIA loans as well as other state, county, and airport revenues.

E-470 Tollway - Denver, Colorado
The E-470 is a 47-mile orbital toll road running along the eastern perimeter of the Denver metropolitan region. The tollway was financed entirely by private enterprise and the E-470 Public Highway Authority using an innovative mix of revenue sources including: tolls, vehicle registration fees, a highway expansion impact fee, and private sector contributions ranging from office space, to right-of-way, property assessments, and monetary donations.

East Fifth Street Rehabilitation Project - Newberg, Oregon
The rehabilitation of East Fifth Street from River Street to Wynooski Street (four blocks) in Newberg, Oregon is one of the first pavement maintenance projects funded by a transportation utility fee (TUF) adopted by the City Council in May 2017 to close a significant annual funding gap in its pavement maintenance budget. Sixty-five percent of the roughly $1 million project was paid for with the TUF. Construction took place between March and November 2018.

Eagle Project - Denver Metro Area, Colorado
The Eagle Project is part of RTD's FasTracks initiative, a voter-approved program to expand rail and bus transit throughout the Denver metropolitan region. The Eagle Project has been procured through a concession agreement between RTD and Denver Transit Partners to design, build, finance, operate, and maintain the project's components - three new commuter rail lines and a maintenance facility - for 34 years.

East Link Extension - Seattle, Washington Metropolitan Area
The $4.031 billion East Link Extension and included I-90 Two-Way Transit and HOV Operations project will provide a new 14.5-mile Light Rail Transit (LRT) line across Lake Washington linking the Eastside communities of Redman and Bellevue with Mercer Island and Downtown Seattle and eight miles of High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes across the I-90 Floating Bridge. This multimodal program will be paid for with an innovative financial plan backed by federal, state, local and private stakeholders.

Eleventh Street Bridge Project - Washington, DC
The Eleventh Street Bridge Project replaced the existing twin bridges that carry I-295 over the Anacostia River in the southeast quadrant of the District of Columbia. Three new bridges were constructed and improvements were made to the interchanges at both ends, including adding missing movements to and from the north onto the Anacostia Freeway (I-295/DC 295). Project funding comprised a mixture of federal, local, and private funds including GARVEE bonds used in combination with tapered match.

Foothill/Eastern and San Joaquin Hills Toll Roads - Orange County, California
The Foothill/Eastern and San Joaquin Hills Toll Roads comprise 51 total miles across four public toll roads providing congestion relief and connectivity within Orange County, California. Development impact fees levied on developers of residential and commercial properties are used to supplement toll revenues for debt service payments.

Green Light Plan - Baton Rouge, Louisiana
Improvements to Lobdell Blvd. in Baton Rouge, Louisiana is one of 42 projects included in the Green Light Plan. This program responded to the increased congestion and demand for transportation in the region following Hurricane Katrina. An existing half-cent sales tax devoted to roads was extended by voters in 2006 and used to back bonds expediting project completion. As of 2018, the program is more than 70 percent complete.

Hackberry Hidden Cove Public Improvement District No. 2 Project - City of Hackberry, Texas
The City of Hackberry, Texas created the Hackberry Hidden Cove Public Improvement District to issue Combination Special Assessment and Contract Revenue Road Bonds to reimburse the developer for half of the cost of implementing roadway and utility improvements in a new 208-acre residential community in an unincorporated area of Denton County, north of Dallas.

Heartland Corridor - Virginia, West Virginia, Kentucky, Ohio
Due to the Norfolk Southern's rail network, the Port of Virginia (Newport News) has always had good rail access to the Midwest markets. The Heartland Corridor project makes the most direct rail route to the major markets of Columbus and Chicago accessible to double-stack container trains and shortens trip-times. Extending through Virginia, West Virginia, Kentucky and Ohio, the Heartland Corridor consists of a series of five separate intermodal projects designed to improve mobility and increase freight capacity.

Hiawatha Light Rail Transit (METRO Blue Line) - Minneapolis/St. Paul, Minnesota
The 12-mile, 17-station METRO Hiawatha Line (now known as the Blue Line) links downtown Minneapolis and the Target Field Station with Minneapolis-St. Paul International Airport and the Mall of America. The project utilized two separate design-build contracts: one for light rail vehicles and one to place rail and signal and communication equipment along the alignment. Due to high risk levels, tunnels and stations bored below the airport were procured using the traditional design-bid-build model.

I-5 Fern Valley Interchange - Phoenix, Oregon
Located 24 miles north of the California border at the northern edge of the city of Phoenix, the Fern Valley Interchange project replaced the previous I-5 interchange with Fern Valley Road with a diverging diamond interchange, the first of its kind in the state. Funding sources for the $72 million project included a commitment of $6.8 million from the City of Phoenix through an interchange development charge, a form of value capture (development impact fee).

I-5 Woodburn Interchange and Transit Facility Project - Woodburn, Oregon
The $75 million Woodburn Interchange and Transit Facility Project improves traffic flow, congestion and safety conditions at the intersection of I-5 with OR 214 and OR 219 in Woodburn, Oregon, 30 miles south of Portland. The City of Woodburn contributed $8 million generated from value capture development impact fees related to the project.

I-10 Corridor Express Lanes (Contract 1) - San Bernardino County, California
The San Bernardino County Transportation Authority (SBCTA) plans to implement 33 miles of dual express lanes in each direction along the I-10 corridor from the Los Angeles County line west to Redlands. The first 10 miles (Contract 1) between Los Angeles County and I-15 is being delivered under a design-build contract supported by federal, state, and local resources, including a $225 million TIFIA loan and nearly $135 million in Measure I local option sales tax revenue. The total project cost is $929 million, and substantial completion is expected in 2023.

I-15 Express Lanes Project - Riverside County, California
The I-15 Express Lanes project will provide two new tolled express lanes and other improvements along 14.6 miles of I-15 in Riverside County, California. The project will address projected increases in congestion and improve travel time reliability. The design-build project is funded with a TIFIA loan, Measure A sales tax bond proceeds and revenue, CMAQ funds, and interest income.

I-40 and Radio Road Interchange Project - El Reno, Oklahoma
The I-40 and Radio Road Interchange project is a new interstate interchange in the City of El Reno, 24 miles west of downtown Oklahoma City. Initially advanced and partially funded by Seventy Seven Energy Corp. to improve access to its offices along Radio Road, this $17 million partnership with the private sector was a first for the Oklahoma Department of Transportation.

I-285/SR 400 Interchange Reconstruction - Fulton and DeKalb Counties, Georgia
The I-285/SR 400 Interchange Reconstruction project will rebuild the I-285/SR 400 Interchange and make improvements along 10 miles of I-285 and SR 400 roughly 13 miles north of Atlanta. The improvements will be made to an interchange that handles over 400,000 vehicles daily while maintaining all travel lanes and movements in the peak period. The state will provide a design-build-finance partner with funds to cover roughly one-quarter of the project cost upfront. The private partner will finance the remaining project cost and will be repaid by the state following project completion.

I-405 Improvement Project - Orange County, California
The I-405 Improvement Project will add one new general purpose lane, one new express lane, and convert the existing HOV lane to express lane operation in each direction along 16 miles of I-405 in Orange County, CA between SR-73 and I-605. The design-build project is funded by a TIFIA Loan, Measure M2 sales tax bond proceeds and revenue, and state and federal grants.

Indiana Toll Road - Indiana
In operation since 1956, the Indiana Toll Road stretches 157 miles across the northernmost part of Indiana from its border with Ohio to the Illinois state line, where it provides the primary connection to the Chicago Skyway and downtown Chicago. The Indiana Toll Road was leased to a consortium of Cintra and Macquarie in 2006 for an upfront payment of $3.8 billion, which was primarily being reinvested in statewide roadway and bridge improvement projects. The lease was rewarded to a consortium of Australian and American pension funds for $5.7 billion in 2015 following the original consortium's bankruptcy.
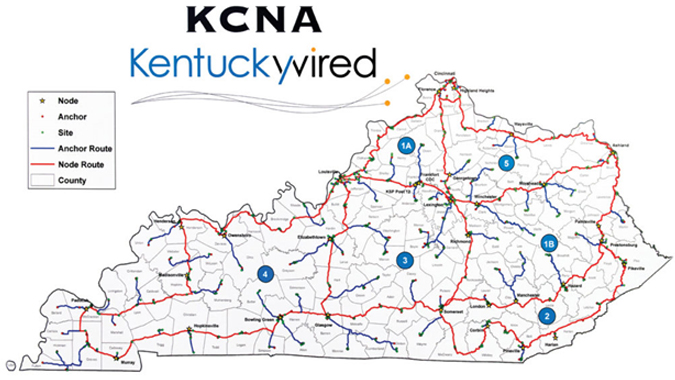
KentuckyWired - Kentucky (statewide)
KentuckyWired is a 3,200-mile statewide network of major fiber optic cable to provide broadband internet connectivity. The network will be open access, allowing local public or private Internet service providers (ISPs), cities, partnerships, or other groups to connect to the network and extend services to local communities. The project is being delivered through a 30-year design, build, finance, operate, and maintain availability payment concession between the state and a private concessionaire.

King Coal Highway - West Virginia
The King Coal Highway is a planned four-lane highway approximately 95 miles long running through McDowell, Mercer, Mingo, Wyoming, and Wayne Counties, West Virginia along or near currently existing US Route 52. To date, one of eleven sections has been constructed, the 12-mile "Red Jacket" section in Mongo County. It used an innovative partnership among public agencies, the local redevelopment authority, and private coal mining enterprise. A negotiated special agreement that resulted in significant cost savings to the state and an accelerated construction timetable permitted coal mining along the highway corridor in exchange for the private construction of the highway foundation and grading.
Lake Shannon Road Improvement Project - Tyrone Township, Michigan
Local residents within the Lake Shannon Association in Tyrone Township, Michigan petitioned the Township to repave local roadways in exchange for a 10-year tax assessment. The town issued Special Assessment Bonds to cover the cost and Livingston County Road Commission completed the improvements.

Las Vegas Monorail - Las Vegas, Nevada
The Las Vegas Monorail was originally a joint venture between MGM Grand and Bally's Hotel, creating a one-mile system linking the hotels in 1993. Plans for expansion further along the Strip led to the State of Nevada in 1997 passing legislation that enabled a private company to own, operate, and charge a fare as a public monorail system. It expanded the system to 3.9 miles in 2004.

Loop 202 South Mountain Freeway - Phoenix, Arizona
The Loop 202 freeway, also known as the South Mountain Freeway, is a 22-mile, 8-lane freeway that will complete the Loop 202 and Loop 101 freeway system in the southwestern quadrant of the Phoenix metropolitan area. The $1.8 billion project has been procured as a P3 where the selected design-build team will also maintain the roadway under a 30-year agreement once it opens in late 2019 or early 2020.

Lyman County Shuttle Train Access Road - Presho, South Dakota
The new construction of Dakota Mill and Grain's state of the art grain loading facility in Presho, South Dakota will provide new markets to the region's agribusinesses and access to the local railroad infrastructure. Lyman County received a loan from the South Dakota Department of Transportation to rebuild an access road to the loading facility, to be repaid using tax increment financing revenue.

Lynnwood Link Extension - Seattle Metro Area, Washington
The Lynnwood Link Extension will extend the Link light rail transit system 8.5 miles from Northgate Transit Center in Seattle north to Shoreline in King County and on to Mountlake Terrace and Lynnwood in Snohomish County. The project includes the construction of four new stations, the addition of 3,790 parking spaces, and the acquisition of 34 light-rail vehicles, as well as partial funding for the construction of the Operations & Maintenance Facility: East. The extension is part of the regional mass transit system expansion (Sound Transit 2) approved by voters in 2008 and supported in large part by a dedicated local option sales tax.

Maryland I-95 Travel Plazas Redevelopment - Cecil County and Harford County, Maryland
In 2012, the Maryland Transportation Authority entered into a P3 long-term lease concession agreement with a private concessionaire, to redesign and rebuild two Maryland Travel Plazas along I-95 at a cost of $56 million, and then operate and maintain them over a 35-year lease term. The overall value to the State, including avoided capital, operations, and maintenance costs, as well as revenue sharing, is estimated to be $577 to $662 million in year-of-expenditure dollars.
MBTA Positive Train Control - Boston Metropolitan Region, Massachusetts
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority is adding positive train control technology to its 400-mile commuter rail network in compliance with federal requirements. The project is financed with TIFIA and RRIF loans backed by state sales tax revenues.

Metro Region Freeway Lighting P3 (Michigan) - Detroit Tri-County Area
This innovative DBFOM availability payment P3 project bundles the replacement of approximately 15,000 freeway lights on five Interstate corridors in metropolitan Detroit with energy-efficient, LED lighting estimated to save Michigan taxpayers $1.5 million annually. The private partner will also operate and maintain the lighting systems, subject to performance standards, for 13-years.

Mid-Coast Corridor - San Diego, California
The Mid-Coast Corridor project extends San Diego's existing light rail Blue Line 10.9 miles from the Old Town Transit Center in downtown San Diego to the University City area to the north. The nine-station extension will serve major activity centers including Old Town, the University of California, San Diego, and the Westfield UTC shopping center. The $2 billion project is funded 50 percent by a federal Full Funding Grant Agreement and 50 percent locally through TransNet, San Diego County's local option sales tax, which, among other financing, is supporting a $537.5 million TIFIA loan.

Moynihan Train Hall - New York, New York
The Moynihan Train Hall will convert the James A. Farley Post Office building in New York, NY into a modern, state of the art transportation facility serving Amtrak and Long Island Rail Road passengers and relieving congestion at adjacent Penn Station. The design-build project is being implemented by a private developer who is leasing the space for 99 years. Funding includes a TIFIA Loan and contributions from New York's Empire State Development Corporation, Amtrak, the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, and the private developer.

NoMa - Gallaudet U Metrorail Station - Washington, DC
The NoMa - Gallaudet U station, formerly known as the New York Avenue station, opened in 2004 as the Washington Metrorail's first infill station. The station was funded through a unique partnership between the District of Columbia, developers and property owners, community leaders, and WMATA. The private sector and local property owners funded $35 million (34 percent) of the $104 million project cost through land donations ($10 million) and the creation of a special assessment district ($25 million).

Northgate Link Extension - Seattle, Washington
The Northgate Link Extension expands Seattle's Sound Transit Link light rail system 4.3 miles north from the existing Capitol Hill and University of Washington Stations that opened in March 2016. The extension runs primarily underground through twin-bored tunnels and features three new stations. The extension is part of the regional mass transit system expansion (Sound Transit 2) approved by voters in 2008 and supported in large part by a dedicated local option sales tax. The project is the first to reach financial close under a TIFIA Master Credit Agreement under which USDOT may make a contingent commitment of future TIFIA credit assistance for a program of related projects secured by a common security pledge.

Northwest Parkway - Denver Metro Region, Colorado
The Northwest Parkway is a 9-mile segment of the Denver Beltway System, connecting E-470 in northern Denver to US 36 in Broomfield. The project was developed by a three-municipality joint powers agency and opened in 2003. It was subsequently leased in 2007 to a private consortium for 99 years after four years of toll revenues that did not meet expectation.

Ohio State University Parking Facility - Columbus, Ohio
In 2012, The Ohio State University (Ohio State) leased its Columbus campus parking facilities, and management of its daily parking operations, to a private concessionaire for 50 years as part of an innovative funding strategy. Over the lease term, CampusParc is responsible for the operation of Ohio State's parking system which comprises approximately 36,600 spaces across the Columbus campus. Ohio State estimates the 50-year value generation to be $3.1 billion. The endowment distributions are being used for student scholarships, hiring new tenure-track faculty, and support for capital projects in the Arts District. Funding has also gone to supporting the Campus Area Bus Service and other initiatives that provide sustainable transportation options.
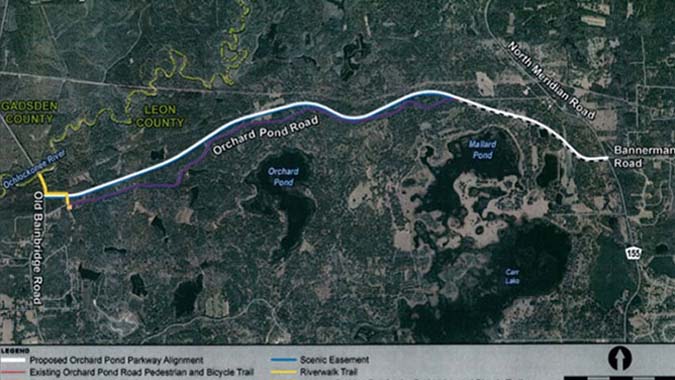
Orchard Pond Parkway - Tallahassee, Florida
The Orchard Pond Parkway is a 5.2-mile privately constructed toll road north of Tallahassee, Florida. The road was developed by a private landowner as a means to preserve the surrounding region from suburban development, and it incorporates a number of features to protect wildlife and the natural environment. The Florida Department of Transportation has supported the project financially with a State Infrastructure Bank loan that covers 80 percent of the $17 million project cost. Leon County owns the road and is leasing it back to the developer for 99 years.

Osceola County Roadway and Bridge Bundling Program - Osceola County, Florida
This bridge at the John Young Parkway/Osceola Parkway interchange in Osceola County, Florida is one of 11 projects completed under the roadway/bridge bundling program funded by development impact fees and delivered using the construction manager/general contractor alternative project delivery method. In total, the program completed $350 million in projects in the late 2000s.

Poplar Road Safety Improvements - Stafford County, Virginia
Stafford County, Virginia used revenue from its Central West Impact Fee Service Area Fund to complete improvements to Phase I of Poplar Road. This fund was created in 2003 and used to collect fees from developers to fund needed infrastructure improvements. Two additional phases use traditional revenue from the county's Transportation Fund.

Poinciana Parkway - Osceola and Polk Counties, Florida
Originally planned for development by a private real estate firm in the 2000s, the Poinciana Parkway was ultimately developed under an agreement between Osceola and Polk Counties and the developer, who donated existing work on design, permitting, and right-of-way. The $141 million, 9.7-mile arterial and toll road improvement connects the Poinciana community 25 miles south of Orlando with a major state route and I-4 to provide better commuting access and congestion relief. In addition to the private developer contribution, the project is financed with toll revenue bonds, a State Infrastructure Bank loan, and county contributions.

Poplar Road Safety Improvements - Stafford County, Virginia
Stafford County, Virginia used revenue from its Central West Impact Fee Service Area Fund to complete improvements to Phase I of Poplar Road. This fund was created in 2003 and used to collect fees from developers to fund needed infrastructure improvements. Two additional phases use traditional revenue from the county's Transportation Fund.

Port of Miami Tunnel - Florida
The Port of Miami Tunnel improves access to and from the Port of Miami, serving as a dedicated roadway connector linking the Port (located on an island in Biscayne) with the MacArthur Causeway and I-395 on the mainland. The project has been developed as a P3 with Miami Access Tunnel, LLC (MAT). The state has paid for approximately 50 percent of the capital costs (design and construction) and all operations and maintenance, while local governments provided the remaining 50 percent of the capital costs. FDOT made milestone payments to MAT at various stages of project development and is now making availability payments during a 30-year concession. Senior bank debt, a TIFIA loan, and private equity have been used to finance the project.

Portland Streetcar - Portland, Oregon
The Portland Streetcar network is a 14.7-mile modern streetcar network in Downtown Portland, Oregon. Property owners along the proposed alignment agreed to establish a special property tax levy through the formation of a Local Improvement District (LID), funding approximately 13.9 percent ($34.9 million) of the $251.4 million project. In addition, Tax Increment Financing also contributed to 8.2 percent ($21.5 million) of total project costs.

Potomac Yard Metrorail Station - City of Alexandria, Virginia
The City of Alexandria, Virginia negotiated exactions for developer contributions in return for land rezoning, dedicated net new tax revenues, and created two special assessment districts to fund the project costs of a proposed infill station on the Washington Metrorail system. The Potomac Yard station - estimated to begin construction in 2016 and open to service in 2018 - is the cornerstone of the redevelopment plan for the Potomac Yard, a 295-acre former rail yard near the Potomac River.

Presidio Parkway (Phase II) - San Francisco, California
The Presidio Parkway project is a replacement of Doyle Drive, the southern access to the Golden Gate Bridge. The existing structure, built in 1936, did not meet current highway standards and was seismically deficient. Through a competitive procurement process, Caltrans selected a private consortium to deliver Phase II as an availability-pay design, build, finance, operate, and maintain availability-pay concession.

Puerto Rico PR-22 and PR-5 Lease - Puerto Rico
PR-22 and PR-5, heavily traveled toll roads stretching about 55 miles along the northern coast of Puerto Rico from Bayamon westward through San Juan to Arecibo, was leased to consortium of Goldman Sachs and Abertis in 2011. The total $1.436 billion administrative concession will finance, rehabilitate, operate, and maintain the facilities over 40 years. Of that total, $1,080 million is an upfront payment of which about 90% was used to defease all outstanding tax-exempt toll-revenue debt ($902 million), and approximately $350 million will be expended on expected upgrades over the concession period, $56 million of which was spent in the first three years on "accelerated safety improvements."

Reno Transportation Rail Access Corridor (ReTRAC) - Reno, Nevada
Traffic congestion and safety concerns brought about the largest public works project ever undertaken in Northern Nevada, the Reno Transportation Rail Access Corridor, or ReTRAC. The project depressed a 2.3-mile stretch of freight rail that ran through downtown, eliminating 10 at-grade street crossings.

Route 28 Corridor Improvements - Northern Virginia
In 1987, property owners in Fairfax and Loudon Counties agreed to establish an additional property tax through the creation of a special assessment. Revenue has been dedicated to major highway improvements along the Route 28 corridor, including widenings and interchange reconstruction.

Route 33 Interchange Project - Easton, Pennsylvania Region
The Route 33 Interchange Project in Palmer Township, Pennsylvania (65 miles north of Philadelphia) involved the construction of a new interchange and associated access improvements to facilitate the mixed-use commercial development of over 600 acres of surrounding land. The interchange was constructed by PennDOT and other infrastructure improvements are being made by a private owner who is selling parcels of land to other third party developers. Tax increment financing provided partial funding for the improvements.

Route 36 FourLaning - Hannibal to Macon, Northeast Missouri
US Route 36 extends across northern Missouri from the City of Hannibal at the Illinois State Line to the City of St. Joseph at the Kansas State Line. The 52-mile segment from Hannibal west to Macon was the last to be expanded from two to four lanes to improve safety and reduce congestion. Completed in 2010, the project relied on a voter-approved, four-county sales tax district to fund roughly half the project's cost, as full state funding was not available. The sales tax revenue leveraged a loan from the state infrastructure bank, which was repaid in 2017, 3.5 years early.

Santa Monica City Net - Santa Monica, California
Santa Monica's City Net is a city-wide fiber optic broadband network connecting 43 city buildings along with school and college facilities in Santa Monica. The network was built incrementally according to a "dig once" policy, coordinating fiber optic installation with other capital projects, leading to significant savings and reduced traffic disruptions throughout Santa Monica.

Santa Monica City Net - Santa Monica, California
The extension of Salzman Road in Monroe, Ohio was a 0.52-mile connection between the road's existing terminus and the intersection of Todhunter Road and Yankee Road to the north. The $3.2 million project improved regional mobility for commuters and truck traffic, improved traffic safety, and promotes economic development. The project was overseen by the Butler County Transportation Improvement District.

Seagirt Marine Terminal - Baltimore, Maryland
In late 2009, the Maryland Port Administration entered into a 50-year long-term lease concession with Ports America Chesapeake to operate and maintain Seagirt Marine Terminal in Baltimore. The nearly $1.5 billion deal includes annual and per-container payments to the state, capital investment including addition of a fourth berth that accommodates post-Panamax ships, and a $140 million upfront payment that the state has invested in highways that serve the Port of Baltimore area.

Sound Transit Operations and Maintenance Facility East - Bellevue, Washington
The Operations and Maintenance Satellite Facility East (OMF East) will be developed in Bellevue, Washington to maintain, store, and deploy light rail vehicles on an extension of Sound Transit's light rail system serving East Link, Northgate, Lynnwood, and Federal Way. The project is the second to reach financial close under a TIFIA Master Credit Agreement and is financed with local sales tax revenue, bond proceeds, and grant proceeds.

South Bay Expressway (formerly SR 125 South Toll Road) - San Diego County, California
The South Bay Expressway toll road is a 9.2-mile privately-funded southern extension of SR 125, extending from SR 905 near the International Border to SR 54 near Sweetwater Reservoir in San Diego, California. The original operator, South Bay Expressway, L.P., held a 35-year franchise with the State of California under which it financed and built the highway, then transferred ownership to the State. The concessionaire emerged from bankruptcy in April 2011 as South Bay Expressway, LLC, and sold the toll road to the San Diego Association of Governments in December 2011.

South Hamilton Crossing - Hamilton, Ohio
The South Hamilton Crossing project constructed an overpass to replace a dangerous at-grade railroad crossing, improve east-west connectivity and traffic safety, and promote economic development. The project was sponsored by the Butler County Transportation Improvement District.

South Lake Union Streetcar - Seattle, Washington
The South Lake Union Streetcar project is a 2.6-mile modern streetcar connecting the South Lake Union area to Downtown Seattle, Washington. Forming the centerpiece of an innovative funding package, local businesses and property owners along the proposed alignment agreed to establish a special property tax levy through the formation of a Local Improvement District (LID), funding approximately 47 percent ($25 million) of the $53.5 million project.

SR 91 Corridor Improvement Project - Riverside County, California
The SR 91 Corridor Improvement Project is an eight-mile extension of the Orange County SR 91 Express Lanes east into Riverside County through conversion of existing HOV lanes. Two general purpose lanes will also be added, along with improvements made to interchanges and bridges. The project is supported by a TIFIA loan and is almost exclusively paid for with local funding through a combination of toll revenue and voter-approved county-level sales tax proceeds.
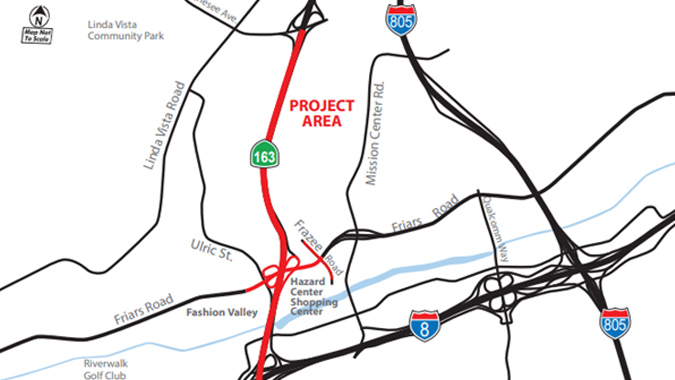
SR 163 and Friars Road Interchange Improvements - San Diego, California
The State Route 163 and Friars Road Interchange project modifies the interchange to improve traffic operations, provide improved access for bicyclists and pedestrians, and minimize weaving on south-bound SR 163 between Friars Road and I-8. Phase 1 of the three-phase project includes widening the SR 163-Friars Road overpass from three to four lanes in each direction and making improvements to the SR 163 on- and off-ramps. This $45 million phase is funded predominantly by development impact fees, local options sales tax collections, and private developer contributions.

Tallgrass Creek Project - City of Overland Park, Kansas
The City of West Lafayette, Indiana and Purdue University are jointly delivering the State Street Redevelopment Project to provide aesthetic and functional improvements to gateways into West Lafayette and Purdue University. The project improves the streetscape, provides pedestrian amenities to enhance community and campus resident cohesiveness, and expands transportation infrastructure to accommodate planned and future growth of West Lafayette and the University. The project is being delivered through an innovative design-build-finance-maintain availability payment P3 backed by tax increment finance district revenue.

Tangerine Road Corridor Project - Marana, Arizona
The Tangerine Road Corridor Project extends approximately 10 miles from its interchange with Interstate 10 in Marana, Arizona east to La Cañada Drive in Oro Valley. This project improves safety, access, and circulation in the region by widening the roadway to four lanes, improving stormwater management, and including accommodation for bicycles and pedestrians. Project funding included voter approved local options ales tax collections in Pima County and local funding including from a special assessment district in the Town of Marana.
Westside Purple Line Extension, Section 2 - Los Angeles, California
In 2006, the City of Overland Park, Kansas created a Transportation Development District to finance transportation improvements related to the development of Tallgrass Creek, a private retirement community. Nearly $12 million in improvements were financed through bonds backed by a special assessment.

The Cap at Union Station - Columbus, Ohio
The Cap at Union Station is a $7.8 million, 25,500-square-foot retail development located on three parallel bridges across I-670 reconnecting downtown Columbus, Ohio with the Short North arts and entertainment district.

Transbay Transit Center - San Francisco, California
The Transbay Transit Center Project will replace the current Transbay Terminal with a new multimodal transportation center and centralize the region's transportation network by accommodating nine transportation systems under one roof, as well as California High Speed Rail and an underground pedestrian connection to the Embarcadero BART/Muni station. The project consists of replacing the outdated Transbay Terminal with a modern transit hub, extending the Caltrain rail line from its current terminus and accommodating future high-speed rail, and redeveloping the area surrounding the Transbay Transit Center.
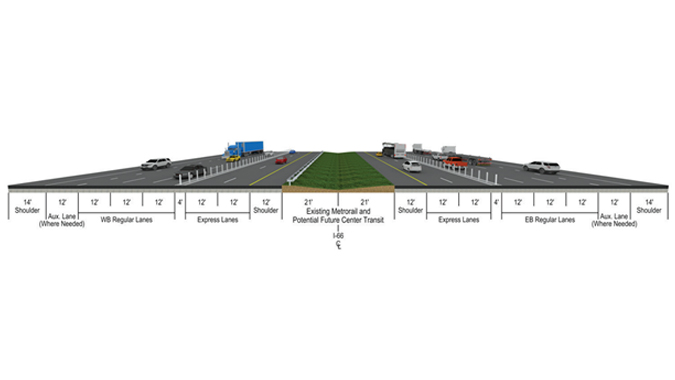
Transform 66 - Outside the Beltway - Fairfax and Prince William Counties, Virginia
Transform 66 - Outside the Beltway will reconstruct and expand 22.5 miles of I-66 in Virginia from the I-495 Capital Beltway to US 29 in Gainesville. The project will provide an additional general-purpose and a second HOV lane in each direction, together with auxiliary lanes, interchange reconfigurations, park-and-ride facilities, and new and improved bus service. The project is being delivered under a 50-year design-build-finance-operate-maintain public-private partnership concession and is financed with a TIFIA loan, private activity bonds, and substantial equity investments and project contributions from the private partner.

US 36 Express Lanes (Phase 1) - Denver Metro Area, Colorado
The US 36 Express Lanes Phase 1 is an initial 10-mile phase of improvements, including one HOT lane in each direction, along 15 miles of roadway between Denver and Boulder, Colorado. This $312 million first phase opened in July 2015 under a design-build contract. A second phase, which opened in January 2016, completes the improvements. The full corridor is operated and maintained by a private partner that developed Phase 2.

US 36 Express Lanes (Phase 2) - Denver Metro Area, Colorado
Phase 2 of a 15-mile reconstruction and expansion of US 36, a four-lane divided highway connecting Denver and Boulder, extends the 10-mile Phase 1 project five miles further northwest to Boulder. The corridor was reconstructed and augmented with a single HOT lane in each direction. The project also included the reconstruction or rehabilitation of three bridges, accommodations for bus rapid transit, provision for ITS, improvements to a commuter rail station, and a bikeway. Phase 2 has been delivered as a DBFOM P3. In addition to the Phase 2 construction, the concessionaire will operate and maintain the entire US 36 Express Lanes corridor as well as the existing I-25 Express Lanes, which connect at its southern terminus.

US 181 Harbor Bridge - Corpus Christi, Texas
The new US 181 Harbor Bridge will replace the existing Corpus Christi Harbor Bridge connecting downtown Corpus Christi to Rincon Point (North Beach) across the Corpus Christi Ship Channel. The replacement bridge will be on a new location alignment approximately 1,200 feet to the west and permit larger (post-Panamax) ships to pass beneath. A design-build contract with a 25-year maintenance (O&M) agreement is being used to deliver the $1 billion project using a combination of federal, state, and local funds raised from Transportation Reinvestment Zones (TRZ), a form of tax increment financing.
US Highway 441/27 Utility Relocation Project - Leesburg, Florida
The City of Leesburg, Florida US Highway 441/27 Community Redevelopment Agency used Tax Increment Revenue Bonds to finance the cost of undergrounding electric utility lines, relocating electrical distribution equipment and removing conduit poles. The work was done concurrently with a separate Florida Department of Transportation project in order to save money and time.

US Route 63 Corridor Expansion - Macon County, Missouri
The U.S. Route 63 Corridor Expansion added two additional highway lanes in each direction along U.S. 63 for 30 miles between the Cities of Kirksville and Macon in north-central Missouri. Local residents of Kirksville decided to form a transportation corporation to fund a portion of the project, after it was clear by the late 1990s that project implementation was 20 years away due to fiscal constraints. Backed by a 10-year local sales tax, the transportation corporation financed one-third of the project, and the Missouri Highways and Transportation Commission the remainder.

Veterans' Glass City Skyway Solar Array - Toledo, Ohio
The Veterans' Glass City Skyway Solar Array installed along I-280 highway right-of-way in Toledo, Ohio provides most of the power needed for the Toledo Skyway Bridge's lighting. The installation began as a research project at the University of Toledo and is the state's first solar installation along highway right-of-way.

Washington Metro Capital Improvement Program - Washington, D.C.
The WMATA $2.3 billion FY 1999 - FY 2004 capital improvement program (CIP) replaced vehicles and rehabilitated facilities and equipment on the rail and bus systems. Individual components of the CIP included procurement of new buses and rail cars; major maintenance and rehabilitation of electrical and mechanical systems, communications, and track and structures to improve system-wide performance; escalator and elevator rehabilitation and other station enhancements; parking lot improvements; and upgrades to several maintenance facilities. Program financing came from federal grant funds, local matching funds, and Grant Anticipation Notes. A $600 million line of credit guaranteed by TIFIA permitted WMATA to demonstrate adequate fiscal capacity under the terms of its funding agreement with local jurisdictions.
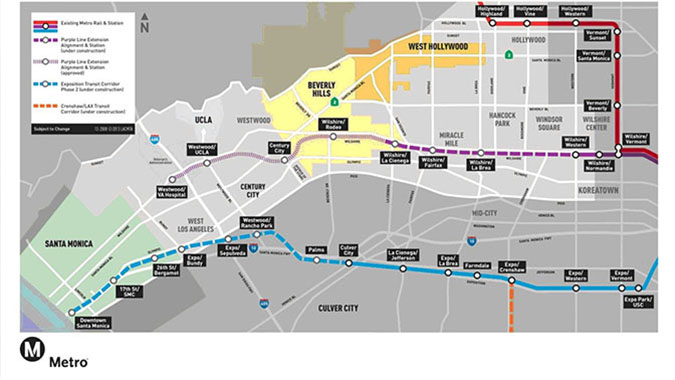
Westside Purple Line Extension, Section 1 - Los Angeles, California
The Westside Purple Line Extension comprises a three-phase, 8.9 mile extension of the LA Metro's existing Purple Line subway from its current terminus at Wilshire/Western Station to a new western terminus in West Los Angeles near the VA Hospital in Westwood. Section 1 will extend the Purple Line 3.9 miles from Wilshire/Western to Wilshire/La Cienega and includes three stations, procurement of 34 new heavy rail vehicles, and improvements to the existing Division 20 Rail Maintenance and Storage Yard. Section 1 has been procured through a design-build contract, and is financed with federal, state, and local sources, including a TIFIA loan and an FTA New Starts Full Funding Grant Agreement.

Westside Purple Line Extension, Section 2 - Los Angeles, California
The Westside Purple Line Extension involves a three-phase, 8.9-mile extension of the LA Metro's existing Purple Line subway from its current terminus at Wilshire/Western Station to a new western terminus in West Los Angeles near the VA Hospital in Westwood. Section 2 will extend the Purple Line 2.6 miles from the planned Section 1 terminus at Wilshire/La Cienega and continue to Century City, with stations at Wilshire/Rodeo and Century City Constellation. The project includes procurement of 20 new heavy rail vehicles. As with Section 1, Section 2 is being procured through a design-build contract, and is financed with federal, state, and local sources, including a TIFIA loan and an FTA New Starts Full Funding Grant Agreement.

Yankton County Napa Junction Service Road - Yankton County, South Dakota
The South Dakota Transportation Commission granted Yankton County a $6 million loan to construct a concrete industrial service road that connects South Dakota Highway 50 to the Napa Junction Rail Park, a new industrial/commercial development zone located around a state-owned and private rail line. To build the road, Yankton County applied for the state's first ever non-Infrastructure Bank highway loan, to be repaid through a tax increment financing (TIF) district centered around the growing rail park.
There are a variety of mechanisms that may be used to derive monetary value from transportation improvements to help defray the cost of their implementation.
Value capture strategies can be used to help pay for roadway and transit improvements by leveraging localized benefits. While more common with transit projects, value capture techniques may also be used with highway improvements, as is the case with the San Joaquin Toll Road in southern California and E-470 outside Denver, Colorado. Most value capture revenue is generated at the state or local level. The FHWA Center for Innovative Finance Support encourages state and local jurisdictions to look for new revenue sources to address funding shortfalls and is available to provide technical assistance in these areas.
In addition to value capture mechanisms, this section of the Center for Innovative Finance Support also provides information on other important sources of Federal state and local revenue to support transportation investment needs, including motor fuel taxes, vehicle-related fees, and local option taxes.